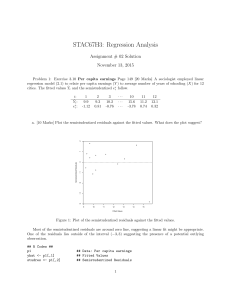
Doing HLM by SAS® PROC MIXED
... but for a school B the race effect is 6. But we are not yet talking about random effects. We are only talking about “different effects” at this point. If it is just different effects, even OLS can deal with it by using a series of dummy variables. HLM goes further than just estimating “different eff ...
... but for a school B the race effect is 6. But we are not yet talking about random effects. We are only talking about “different effects” at this point. If it is just different effects, even OLS can deal with it by using a series of dummy variables. HLM goes further than just estimating “different eff ...
3. Generalized linear models
... expected value of Y is E(Y) = and the variance of Y is Var(Y) = (1-). The goal in this section to find a GLM to model at specific values of explanatory variables (x’s) For example, suppose you want to estimate the probability of success, , of a field goal. The value of will probably be diff ...
... expected value of Y is E(Y) = and the variance of Y is Var(Y) = (1-). The goal in this section to find a GLM to model at specific values of explanatory variables (x’s) For example, suppose you want to estimate the probability of success, , of a field goal. The value of will probably be diff ...
Weighted Quantile Regression for Analyzing Health Care Cost Data
... knowledge of how the covariates influence high cost can be obtained by estimating a high quantile of the conditional distribution, for example the 0.9 conditional quantile. By considering different quantiles, we are able to obtain a more complete picture of the effects of the covariates on health ca ...
... knowledge of how the covariates influence high cost can be obtained by estimating a high quantile of the conditional distribution, for example the 0.9 conditional quantile. By considering different quantiles, we are able to obtain a more complete picture of the effects of the covariates on health ca ...
Part I Simple Linear Regression - the Department of Statistics Online
... During the analysis stage, the results will either support or discredit your hypothesis and, in some cases, be inconclusive. In this last case, you will need to assess whatever lessons were learned from the current research, implement those, and then proceed to run through another iteration of the r ...
... During the analysis stage, the results will either support or discredit your hypothesis and, in some cases, be inconclusive. In this last case, you will need to assess whatever lessons were learned from the current research, implement those, and then proceed to run through another iteration of the r ...
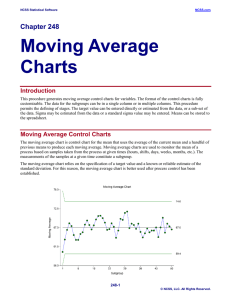
Moving Average Charts
... The moving average width is the number of subgroups averaged in each moving average. For example, if the moving average width is 3, the moving average for the 10th subgroup would be the average of the 8th 9th and 10th subgroups. At the beginning of the series, when the subgroup number has not yet re ...
... The moving average width is the number of subgroups averaged in each moving average. For example, if the moving average width is 3, the moving average for the 10th subgroup would be the average of the 8th 9th and 10th subgroups. At the beginning of the series, when the subgroup number has not yet re ...