may11_slides
... “much of the atomic volume was now assumed to contain only the very light electrons, which could not produce much deflection. Accordingly, many alpha particles would pass through the atom, deflected only slightly by the electrons and the long-range Coulomb interaction with the nucleus” ...
... “much of the atomic volume was now assumed to contain only the very light electrons, which could not produce much deflection. Accordingly, many alpha particles would pass through the atom, deflected only slightly by the electrons and the long-range Coulomb interaction with the nucleus” ...
Lecture 19: Motional emf
... Ex 18-3 A circular loop with a 10 cm-radius is placed in the presence of a uniform magnetic as shown in the figure. The field changes from 1.5 T to 0.5 T in 0.5 s. The loop has resistance 10W. What is the induced EMF? What current flows (specify the direction and magnitude)? ...
... Ex 18-3 A circular loop with a 10 cm-radius is placed in the presence of a uniform magnetic as shown in the figure. The field changes from 1.5 T to 0.5 T in 0.5 s. The loop has resistance 10W. What is the induced EMF? What current flows (specify the direction and magnitude)? ...
Ex10
... b. When E-E* the equation has a steady state solution=vd. Find the drift
velocity vd. Rewrite the equation in terms of ~
v z=vzvd and find the long time
limit of . From the condition that observation time<
... b. When E-E* the equation has a steady state solution
1. When a conductor carrying an electric current is placed in a
... the features of an electromagnet which control the strength of the magnetic field obtained. ...
... the features of an electromagnet which control the strength of the magnetic field obtained. ...
Fields Review - mackenziekim
... vertically downwards. An electron of mass me and charge e is fired horizontally with velocity v = 0.1c, where c = 3.00 x 108 m/s between the plates. Calculate the electron’s acceleration. If the plates have length 1 m, find the electron’s deflection from the horizontal when it emerges. (1.76 x 1014 ...
... vertically downwards. An electron of mass me and charge e is fired horizontally with velocity v = 0.1c, where c = 3.00 x 108 m/s between the plates. Calculate the electron’s acceleration. If the plates have length 1 m, find the electron’s deflection from the horizontal when it emerges. (1.76 x 1014 ...
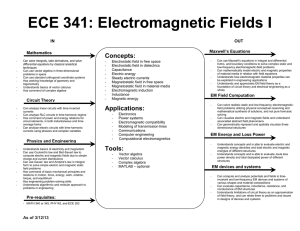
ECE 341: Electromagnetic Fields I Concepts: Maxwell’s Equations
... currents Can analyze RLC circuits in time-harmonic regime Has command of power and energy relations for circuit elements, in both instantaneous and timeaverage forms Can analyze electric circuits with time-harmonic currents using phasors and complex variables ...
... currents Can analyze RLC circuits in time-harmonic regime Has command of power and energy relations for circuit elements, in both instantaneous and timeaverage forms Can analyze electric circuits with time-harmonic currents using phasors and complex variables ...
Magnetism I Name: A proton moves with a speed of 1.00 x 105 m/s
... moves eastward? (c) Calculate the gravitational force on the proton and compare it with the magnetic force. Compare it also with the electric force if there were an electric field with a magnitude equal to E = 1.50 x 102 N/C at the location, a common value at Earth’s surface. Note that the mass of t ...
... moves eastward? (c) Calculate the gravitational force on the proton and compare it with the magnetic force. Compare it also with the electric force if there were an electric field with a magnitude equal to E = 1.50 x 102 N/C at the location, a common value at Earth’s surface. Note that the mass of t ...
Electric Potential - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... A circular loop of wire of radius r is in a uniform magnetic field, with the plane of the loop perpendicular to the direction of the field. The magnetic field varies with time according to B(t) = a + bt, where a and b are constants. a) Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop at t = 0. b) Calcul ...
... A circular loop of wire of radius r is in a uniform magnetic field, with the plane of the loop perpendicular to the direction of the field. The magnetic field varies with time according to B(t) = a + bt, where a and b are constants. a) Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop at t = 0. b) Calcul ...
Faraday`s Law - barransclass
... What’s the Point? • This is how electric current is harnessed to do mechanical work. • It’s another way to think about the Lorentz force. ☺ ...
... What’s the Point? • This is how electric current is harnessed to do mechanical work. • It’s another way to think about the Lorentz force. ☺ ...
Electromagnetism - David Brotherton CCCMC
... given surface (such as a conducting coil). The SI unit of magnetic flux is the weber (in derived units: volt-seconds). The CGS unit is the Maxwell. EMF – Electromagnetic Field - In the past, electrically charged objects were thought to produce two different, unrelated types of field associated with ...
... given surface (such as a conducting coil). The SI unit of magnetic flux is the weber (in derived units: volt-seconds). The CGS unit is the Maxwell. EMF – Electromagnetic Field - In the past, electrically charged objects were thought to produce two different, unrelated types of field associated with ...