Content Statement
... gravitational force and is often confused with mass. Weight is proportional to mass, but depends upon the gravitational field at a particular location. An object will have the same mass when it is on the moon as it does on Earth. However, the weight (force of gravity) will be different at these two ...
... gravitational force and is often confused with mass. Weight is proportional to mass, but depends upon the gravitational field at a particular location. An object will have the same mass when it is on the moon as it does on Earth. However, the weight (force of gravity) will be different at these two ...
Coulomb`s law
... electromagnetic wave propagation. The differential equations and boundary conditions that we use to formulate and solve EM problems are all derived from Maxwell’s equations in integral form. ...
... electromagnetic wave propagation. The differential equations and boundary conditions that we use to formulate and solve EM problems are all derived from Maxwell’s equations in integral form. ...
Physics 107 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #18
... times. What is (a) the speed of the -particle, (b) the magnitude of the magnetic force on it, and (c) the radius of its circular path? *20 Review Conceptual Example 2 as background for this problem. A charged particle moves through a velocity selector at a constant speed in a straight line. The elec ...
... times. What is (a) the speed of the -particle, (b) the magnitude of the magnetic force on it, and (c) the radius of its circular path? *20 Review Conceptual Example 2 as background for this problem. A charged particle moves through a velocity selector at a constant speed in a straight line. The elec ...
Electrostatics - curtehrenstrom.com
... 4) If the threads in the previous problem are 15.0 cm long, a) how far apart are the pith balls and b) what is the magnitude of the charge acting on the pith balls? 5) An object with a charge of 12.3 µC is acted upon by a force of 6.4 N when placed in an electric field. What is the field’s intensit ...
... 4) If the threads in the previous problem are 15.0 cm long, a) how far apart are the pith balls and b) what is the magnitude of the charge acting on the pith balls? 5) An object with a charge of 12.3 µC is acted upon by a force of 6.4 N when placed in an electric field. What is the field’s intensit ...
About that problem that we did in class
... The other approach is via the Electric Field concept where we remove the charge B entirely from the picture and calculate the effect that the other charges have on the space where B was located. After this, we return the charge to the point to calculate the force on it. The beauty of this approach i ...
... The other approach is via the Electric Field concept where we remove the charge B entirely from the picture and calculate the effect that the other charges have on the space where B was located. After this, we return the charge to the point to calculate the force on it. The beauty of this approach i ...
PHYS 241 Exam Review
... – You can always use it to calculate the current within a region and when there is a HIGH of degree symmetry you can figure out the magnetic field ...
... – You can always use it to calculate the current within a region and when there is a HIGH of degree symmetry you can figure out the magnetic field ...
Magnetic Field On
... Case 1: In what direction is the force on a positive charge with a velocity to the left in a uniform magnetic field directed down and to the left? Case 2: In what direction is the force on a negative charge with a velocity down in a uniform magnetic field directed out of the screen? Case 3: In what ...
... Case 1: In what direction is the force on a positive charge with a velocity to the left in a uniform magnetic field directed down and to the left? Case 2: In what direction is the force on a negative charge with a velocity down in a uniform magnetic field directed out of the screen? Case 3: In what ...
Magnetism III - Galileo and Einstein
... Finding the Drift Velocity • Suppose a one amp current is flowing down a wire of cross-section area A. Take a one meter length of the wire: it has volume A cubic meters. If the conductor has density , the mass of this 1 meter is A. If the conductor has atoms of mass m, each contributing one cond ...
... Finding the Drift Velocity • Suppose a one amp current is flowing down a wire of cross-section area A. Take a one meter length of the wire: it has volume A cubic meters. If the conductor has density , the mass of this 1 meter is A. If the conductor has atoms of mass m, each contributing one cond ...
MSPS2
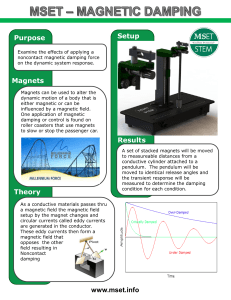
... Student investigation: Students will be given two bar magnets and conduct an investigation to prove that there is a force that can not be seen. This can be accomplished by placing the same poles of the magnets near each other causing the magnets to repel each other. ...
... Student investigation: Students will be given two bar magnets and conduct an investigation to prove that there is a force that can not be seen. This can be accomplished by placing the same poles of the magnets near each other causing the magnets to repel each other. ...
Electromagnetic induction Electric currents generate magnetic fields
... Power transmission Transformers ...
... Power transmission Transformers ...
forces - World of Teaching
... mass to the Earth’s centre. The weight of a body, of mass m, is defined to be the force, W, with which it is attracted to the Earth. On Earth, W = mg, where g is the acceleration due to gravity (g ≈ 9.81 m s−2 on Earth). ...
... mass to the Earth’s centre. The weight of a body, of mass m, is defined to be the force, W, with which it is attracted to the Earth. On Earth, W = mg, where g is the acceleration due to gravity (g ≈ 9.81 m s−2 on Earth). ...
Slide 1
... Manipulation of Maxwell’s equations leads to the following Equations on this slide are for waves plane wave equations for E and B: propagating along x-direction. 2E y x ...
... Manipulation of Maxwell’s equations leads to the following Equations on this slide are for waves plane wave equations for E and B: propagating along x-direction. 2E y x ...
Magnetic Fields
... Background reading: http://www.s-cool.co.uk/a-level/physics/forces-in-magnetic-fields/revise-it/themotor-effect-and-flemings-left-hand-rule ...
... Background reading: http://www.s-cool.co.uk/a-level/physics/forces-in-magnetic-fields/revise-it/themotor-effect-and-flemings-left-hand-rule ...
Physics 227: Lecture 15 Magnetic Fields from wires
... = µ0 �0 v 2 FE What is μ0ε0v2? From their numerical values, you can see that μ0ε0 = 1/(3x108)2. Later on we will learn that the speed of light is c2 = 1/μ0ε0, so μ0ε0 = v2/c2 < 1 always, and FM < FE for v < c. Thursday, October 27, 2011 ...
... = µ0 �0 v 2 FE What is μ0ε0v2? From their numerical values, you can see that μ0ε0 = 1/(3x108)2. Later on we will learn that the speed of light is c2 = 1/μ0ε0, so μ0ε0 = v2/c2 < 1 always, and FM < FE for v < c. Thursday, October 27, 2011 ...