Kepler`s Law of Areal Velocity in Cyclones
... 2ω, where ω is the angular velocity of the planet, because the solenoidally aligned sea of molecular vortices is a rigid solid which constitutes space for large bodies. See section V of ‘The Cause of Coriolis Force’ at, ...
... 2ω, where ω is the angular velocity of the planet, because the solenoidally aligned sea of molecular vortices is a rigid solid which constitutes space for large bodies. See section V of ‘The Cause of Coriolis Force’ at, ...
Center of trifold poster
... from particle motion in the magnetosphere is very available magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) difficult. code to move a number of charged particles • Electronic equipment, such as on satellites and while neglecting their own fields, energy orbiting telescopes, can be damaged by depositions, and relativisti ...
... from particle motion in the magnetosphere is very available magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) difficult. code to move a number of charged particles • Electronic equipment, such as on satellites and while neglecting their own fields, energy orbiting telescopes, can be damaged by depositions, and relativisti ...
Magnetic Induction
... 2. The magnetic field due to the induced current points in the opposite direction to the original field if the flux is increasing; in the same direction if it is decreasing; and is zero if the flux is not changing. 3. Use the right-hand rule to determine the direction of the current. 4. Remember tha ...
... 2. The magnetic field due to the induced current points in the opposite direction to the original field if the flux is increasing; in the same direction if it is decreasing; and is zero if the flux is not changing. 3. Use the right-hand rule to determine the direction of the current. 4. Remember tha ...
summer holiday homework (2016-2017) class -xii physics
... 1. Draw a plot showing the variation of i) Electric field and ii) electric potential with distance r due to a point charge Q. 2. Draw electric field lines for: i)Charge q>0 ii) q<0 iii)Two equal and opposite charges. iv)Two equal and similar charges. 3. State Gauss’ law in electrostatics. Find elect ...
... 1. Draw a plot showing the variation of i) Electric field and ii) electric potential with distance r due to a point charge Q. 2. Draw electric field lines for: i)Charge q>0 ii) q<0 iii)Two equal and opposite charges. iv)Two equal and similar charges. 3. State Gauss’ law in electrostatics. Find elect ...
Faraday`s Law
... turns of wire with a total resistance of 25 W and an enclosed area of 100 cm2. There is a perpendicular magnetic field of 0.50 T that is turned off in 200 ms. Find the current induced in the coil. ...
... turns of wire with a total resistance of 25 W and an enclosed area of 100 cm2. There is a perpendicular magnetic field of 0.50 T that is turned off in 200 ms. Find the current induced in the coil. ...
Physics Lecture #32 - WordPress for academic sites @evergreen
... A uniform magnetic field B is produced in a solenoid of radius a, as shown. A loop is concentric with the axis of the solenoid, and has radius b. The current in the solenoid varies with time, so the magnetic field in the solenoid also varies with time, such that B(t) = B0t, where is a B0 constant. a ...
... A uniform magnetic field B is produced in a solenoid of radius a, as shown. A loop is concentric with the axis of the solenoid, and has radius b. The current in the solenoid varies with time, so the magnetic field in the solenoid also varies with time, such that B(t) = B0t, where is a B0 constant. a ...
Magnetic field
... In motion, interaction occurs over a larger distance, R*, and the strength decreases. Coulombs law changes to ...
... In motion, interaction occurs over a larger distance, R*, and the strength decreases. Coulombs law changes to ...
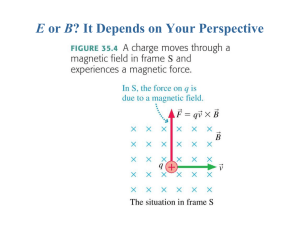
E or B? It Depends on Your Perspective
... where V is the velocity of frame S' relative to frame S and where the fields are measured at the same point in space by experimenters at rest in each reference frame. NOTE: These equations are only valid if V << c. ...
... where V is the velocity of frame S' relative to frame S and where the fields are measured at the same point in space by experimenters at rest in each reference frame. NOTE: These equations are only valid if V << c. ...
Solutions
... 3. A current balance is a device that has two parallel rigid wires carrying the same current in opposite directions. One of the wires is fixed while the other one is attached in such a way that it can pivot in response to a force from the second wire (see figure). First the pivot is adjusted to the ...
... 3. A current balance is a device that has two parallel rigid wires carrying the same current in opposite directions. One of the wires is fixed while the other one is attached in such a way that it can pivot in response to a force from the second wire (see figure). First the pivot is adjusted to the ...