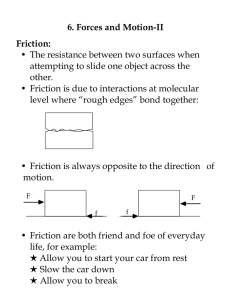
6. Forces and Motion-II Friction: • The resistance between two surfaces when
... 6. Forces and Motion-II Friction: • The resistance between two surfaces when attempting to slide one object across the other. • Friction is due to interactions at molecular level where “rough edges” bond together: ...
... 6. Forces and Motion-II Friction: • The resistance between two surfaces when attempting to slide one object across the other. • Friction is due to interactions at molecular level where “rough edges” bond together: ...
Question Booklet - Sunway Campus Library
... a) object's mass, m b) coefficient of kinetic friction, K c) normal force, FN d) applied force, FA e) gravitational field strength, g 6. A baseball is thrown vertically into the air. The instantaneous acceleration of the ball at the highest point in its travel is: a) 9.8 m/s2 up b) 9.8 m/s2 down c) ...
... a) object's mass, m b) coefficient of kinetic friction, K c) normal force, FN d) applied force, FA e) gravitational field strength, g 6. A baseball is thrown vertically into the air. The instantaneous acceleration of the ball at the highest point in its travel is: a) 9.8 m/s2 up b) 9.8 m/s2 down c) ...
t6_motors
... An electric motor is an electromechanical device that converts electrical energy to mechanical energy. The mechanical energy can be used to perform work such as rotating a pump impeller, fan, blower, driving a compressor, lifting materials etc. It is estimated that about 70% of the total electrical ...
... An electric motor is an electromechanical device that converts electrical energy to mechanical energy. The mechanical energy can be used to perform work such as rotating a pump impeller, fan, blower, driving a compressor, lifting materials etc. It is estimated that about 70% of the total electrical ...
Newton`s 2nd Law of Motion
... force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. This means that the acceleration (a) of an object is dependant on a force applied to the object and the mass of the object. Putting “Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion” in Conceptual terms: Newton’s 2nd law basically says the net force (unbalanced ...
... force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. This means that the acceleration (a) of an object is dependant on a force applied to the object and the mass of the object. Putting “Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion” in Conceptual terms: Newton’s 2nd law basically says the net force (unbalanced ...