lab 16 centripetal force - acceleration
... motion. In figure 1 v = vector velocity where the direction of the velocity is continually changing as the body moves around the circle, but the magnitude of the velocity remains constant. Since the velocity is changing direction there must be an acceleration which requires that a force act on the b ...
... motion. In figure 1 v = vector velocity where the direction of the velocity is continually changing as the body moves around the circle, but the magnitude of the velocity remains constant. Since the velocity is changing direction there must be an acceleration which requires that a force act on the b ...
Newtons, or dynes.
... an object is in equilibrium, the net force on it is zero, and If the net force on an object is zero, the object is in equilibrium. ...
... an object is in equilibrium, the net force on it is zero, and If the net force on an object is zero, the object is in equilibrium. ...
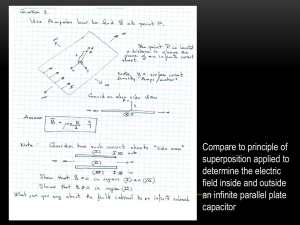
Lesson #3 – Gauss` Law
... Inquiry: What does Gauss’ law say (if anything) about the net charge on each of the objects we had on the previous inquiries in the module? ...
... Inquiry: What does Gauss’ law say (if anything) about the net charge on each of the objects we had on the previous inquiries in the module? ...
Electrostatics
... the positively charged ions on the unexposed areas on the drum's surface attractive. The same particles are subsequently even more drawn to the electrostatically charged paper. The plastic in the toner lets you keep it from jumping ship once you've finally got it on the paper; all you have to do i ...
... the positively charged ions on the unexposed areas on the drum's surface attractive. The same particles are subsequently even more drawn to the electrostatically charged paper. The plastic in the toner lets you keep it from jumping ship once you've finally got it on the paper; all you have to do i ...
AP Physics Free Response Practice – Torque
... A rail gun is a device that propels a projectile using a magnetic force. A simplified diagram of this device is shown above. The projectile in the picture is a bar of mass M and length D, which has a constant current I flowing through it in the +y direction, as shown. The space between the thin fric ...
... A rail gun is a device that propels a projectile using a magnetic force. A simplified diagram of this device is shown above. The projectile in the picture is a bar of mass M and length D, which has a constant current I flowing through it in the +y direction, as shown. The space between the thin fric ...
pptx
... infinity; units = V • Electric potential uniquely defined for every point in space -- independent of path! • Electric potential is a scalar -- add contributions from individual point charges • We calculated the electric potential produced: – by a single charge: V=kq/r, – by several charges using sup ...
... infinity; units = V • Electric potential uniquely defined for every point in space -- independent of path! • Electric potential is a scalar -- add contributions from individual point charges • We calculated the electric potential produced: – by a single charge: V=kq/r, – by several charges using sup ...
Chapter 15 – Electric Forces and Electric Fields
... All materials can have a charge, which we refer to as either “positive” or “negative”. The origin of this charge is the makeup of an atom, which consists of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons. The nucleus consists of protons, which have positive charge, and neutr ...
... All materials can have a charge, which we refer to as either “positive” or “negative”. The origin of this charge is the makeup of an atom, which consists of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons. The nucleus consists of protons, which have positive charge, and neutr ...
Hall Coefficient of Germanium - Wooster Physics
... concentration, and gives insight into the mechanism of conductivity in semi-conductors. The Hall Coefficient and the density of carriers in Ge are well known quantities, and have been verified in this paper, given experimental limitations, with values of the same order. Also, it is established that ...
... concentration, and gives insight into the mechanism of conductivity in semi-conductors. The Hall Coefficient and the density of carriers in Ge are well known quantities, and have been verified in this paper, given experimental limitations, with values of the same order. Also, it is established that ...
Chapter 7: Momentum
... An impulse produces a change in momentum. If the force is not constant but varies with time, we find impulse is the area under the curve of a F vs t graph. If the impulse is zero, there is no change of momentum -- it is conserved. Example: A rubber ball mass 0.100kg moving east at 10.0 m/s hits a wa ...
... An impulse produces a change in momentum. If the force is not constant but varies with time, we find impulse is the area under the curve of a F vs t graph. If the impulse is zero, there is no change of momentum -- it is conserved. Example: A rubber ball mass 0.100kg moving east at 10.0 m/s hits a wa ...