Physics 152 Walker, Chapter 20
... The three charges are held in place in the figure below, where L = 1.25 m. (a) Find the electric potential at point P [ans:76.9 kV] (b) Suppose that a fourth charge, with a charge of 6.11 mC and a mass of 4.71 g, is released from rest at point P. What is the speed of the fourth charge when it has mo ...
... The three charges are held in place in the figure below, where L = 1.25 m. (a) Find the electric potential at point P [ans:76.9 kV] (b) Suppose that a fourth charge, with a charge of 6.11 mC and a mass of 4.71 g, is released from rest at point P. What is the speed of the fourth charge when it has mo ...
3-Continental_Drift
... Using the distribution of till and striations that were created ~300 million years ago, Wegener saw that South America, southern Africa, India, Australia and Antarctica all experienced a glaciation. Today, these places are widely separated and tropical. The striations pointed to a common center of t ...
... Using the distribution of till and striations that were created ~300 million years ago, Wegener saw that South America, southern Africa, India, Australia and Antarctica all experienced a glaciation. Today, these places are widely separated and tropical. The striations pointed to a common center of t ...
Lesson 13 Moments – Turning forces
... different directions, so you will have to make one of them negative. In this case mv – mu = 5m - -3m = 8m ...
... different directions, so you will have to make one of them negative. In this case mv – mu = 5m - -3m = 8m ...
Name
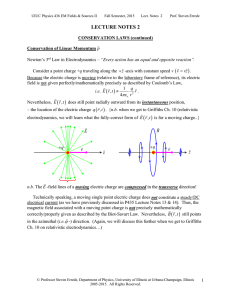
... The potential on a conductor is everywhere the same if the charges are static. An equipotential surface is a three-dimensional surface on which the electric potential V is the same at every point (like the surface of a conductor). If a test charge q is moved from point to point on such an equipo ...
... The potential on a conductor is everywhere the same if the charges are static. An equipotential surface is a three-dimensional surface on which the electric potential V is the same at every point (like the surface of a conductor). If a test charge q is moved from point to point on such an equipo ...
Chapter 15
... surface of an arbitrary shape, then any field line entering the surface leaves at another point • Thus the electric flux through a closed surface that surrounds no charge is zero ...
... surface of an arbitrary shape, then any field line entering the surface leaves at another point • Thus the electric flux through a closed surface that surrounds no charge is zero ...