Supplementary materials
... and r1 / H . It generally takes three to four iterations for a converged result. The validity of both the analytical modified uniform and radial fields in Eqs. (S1) and (S5) above were checked against numerical simulations. Figure S1 compares the analytical and numerical results for the radial field ...
... and r1 / H . It generally takes three to four iterations for a converged result. The validity of both the analytical modified uniform and radial fields in Eqs. (S1) and (S5) above were checked against numerical simulations. Figure S1 compares the analytical and numerical results for the radial field ...
Powerpoint
... charges shown below (ignore test charges A, B, and C for the moment.) Use arrows on field lines to show the direction of the field. b. Test charge particles A, B, and C are shot to the right. Predict and draw the path each particle will take. c. Where in the electric field will the particle’s paths ...
... charges shown below (ignore test charges A, B, and C for the moment.) Use arrows on field lines to show the direction of the field. b. Test charge particles A, B, and C are shot to the right. Predict and draw the path each particle will take. c. Where in the electric field will the particle’s paths ...
幻灯片 1
... Comparison of Electric Force with Electric Field • Electric Force (F) - the actual force felt by a charge at some location. • Electric Field (E) - found for a location only – tells what the electric force would be if a charge were located there: ...
... Comparison of Electric Force with Electric Field • Electric Force (F) - the actual force felt by a charge at some location. • Electric Field (E) - found for a location only – tells what the electric force would be if a charge were located there: ...
y - Copernicus.org
... background magnetic field lead a one-dimensional electron hole into several 2D electron holes which are isolated in both x and y directions. The electrons trapped in these 2D electron holes suffer the electric field drift due to the existence of the perpendicular electric field Ey, which generates t ...
... background magnetic field lead a one-dimensional electron hole into several 2D electron holes which are isolated in both x and y directions. The electrons trapped in these 2D electron holes suffer the electric field drift due to the existence of the perpendicular electric field Ey, which generates t ...
XI. On the Forces, Stresses, and Fluxes of Energy in the
... energy being the most prominent and important. We may, therefore, think of merely one medium, the most of which is uniform (the ether), whilst certain portions (matter as well) have different powers of supporting electric displacement and magnetic induc· tion from the rest, as well as a host of addi ...
... energy being the most prominent and important. We may, therefore, think of merely one medium, the most of which is uniform (the ether), whilst certain portions (matter as well) have different powers of supporting electric displacement and magnetic induc· tion from the rest, as well as a host of addi ...
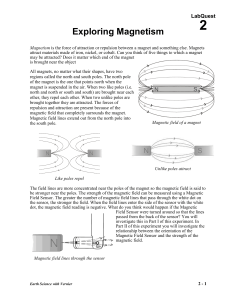
02 Expl Magnet LQ
... process is complete, the readings for the sensor should be close to zero. 5. Hold the magnet vertically about 20 cm above the Magnetic Field Sensor. One end of the magnet should be lined up with the white dot on the sensor as shown in Figure 1. 6. Start data collection. Slowly move the magnet toward ...
... process is complete, the readings for the sensor should be close to zero. 5. Hold the magnet vertically about 20 cm above the Magnetic Field Sensor. One end of the magnet should be lined up with the white dot on the sensor as shown in Figure 1. 6. Start data collection. Slowly move the magnet toward ...
PowerPoint
... If there is a nonconducting cavity inside the conductor, with a charge inside the cavity, Gauss’ Law tells us there is an equal and opposite induced charge on the interior surface of the conductor. Construct a Gaussian surface that includes the inner surface of the conductor. The electric field at t ...
... If there is a nonconducting cavity inside the conductor, with a charge inside the cavity, Gauss’ Law tells us there is an equal and opposite induced charge on the interior surface of the conductor. Construct a Gaussian surface that includes the inner surface of the conductor. The electric field at t ...