untitled - PhysRevLett.111.243901
... the ensemble averaged intensity distribution at the target arrival time is plotted in Fig. 4(c). The peak intensity after the optimization is about 2 orders of magnitude higher than that before the optimization. Moreover, the observed intensity in the region surrounding the target position also incr ...
... the ensemble averaged intensity distribution at the target arrival time is plotted in Fig. 4(c). The peak intensity after the optimization is about 2 orders of magnitude higher than that before the optimization. Moreover, the observed intensity in the region surrounding the target position also incr ...
Section 2 Chemical Formulas and Equations
... Atoms are never lost or gained in a chemical reaction. They are just rearranged. Every atom in the reactants becomes part of the products. When writing a chemical equation, make sure that the total number of atoms of each element in the reactants equals the total number of atoms of that element in t ...
... Atoms are never lost or gained in a chemical reaction. They are just rearranged. Every atom in the reactants becomes part of the products. When writing a chemical equation, make sure that the total number of atoms of each element in the reactants equals the total number of atoms of that element in t ...
Medical applications of Terahertz Imaging: a Review of Current
... An unavoidable issue when imaging with THz radiation is absorption by water. The entire THz band is strongly absorbed by water (or any polar liquid) [9] and consequently does not penetrate moist tissue to any significant depth. It has been reported that a THz pulse can be detected through 1.5 mm of ...
... An unavoidable issue when imaging with THz radiation is absorption by water. The entire THz band is strongly absorbed by water (or any polar liquid) [9] and consequently does not penetrate moist tissue to any significant depth. It has been reported that a THz pulse can be detected through 1.5 mm of ...
Cost-effective optical coherence tomography spectrometer based on
... demonstrated and depict a reasonable image quality for this preliminary low cost system that is well comparable to competing devices. Further improvement of the optical design and the TFBG fabrication process have potential to optimize the TFBG spectrometer towards smaller size and higher efficiency ...
... demonstrated and depict a reasonable image quality for this preliminary low cost system that is well comparable to competing devices. Further improvement of the optical design and the TFBG fabrication process have potential to optimize the TFBG spectrometer towards smaller size and higher efficiency ...
... AbstractID: 9348 Title: Dose sensitivity modification in polymer gel dosimeters improves the accuracy of optical CT scanning for gel dosimetry Optical CT scanning is a convenient, bench-top method of imaging 3D dose distributions in gel dosimeters such as BANG®. These scanners offer medical physicis ...
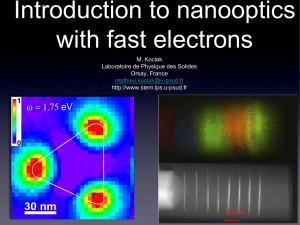
EELS
... J. Martin et al., High-Resolution Imaging and Spectroscopy of Multipolar Plasmonic Resonances in Aluminum Nanoantennas, ...
... J. Martin et al., High-Resolution Imaging and Spectroscopy of Multipolar Plasmonic Resonances in Aluminum Nanoantennas, ...
Fluorescence Spectroscopy
... • An absorption spectrum reflects the vibrational levels of the electronically excited state • An emission spectrum reflects the h vibrational ...
... • An absorption spectrum reflects the vibrational levels of the electronically excited state • An emission spectrum reflects the h vibrational ...
EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 7.0 by extrinsic factors (test conditions), such as hydrodynamics,
... given in Figure 2.9.31.-1. Other equipment may be used. The instrument comprises a laser light source, beam processing optics, a sample measurement region (or cell), a Fourier lens, and a multi-element detector for measuring the scattered light pattern. A data system is also required for deconvoluti ...
... given in Figure 2.9.31.-1. Other equipment may be used. The instrument comprises a laser light source, beam processing optics, a sample measurement region (or cell), a Fourier lens, and a multi-element detector for measuring the scattered light pattern. A data system is also required for deconvoluti ...
Urban - TEM aberration correction review
... electron waves. The technique most gen, can be identified. The atomic resolution is confirmed by image sim- spread, leading to parasitic or “crosswidely used is the focus-variation ulations. These indicate that, because of negligible point spread, neighboring talk” intensity at this site originating ...
... electron waves. The technique most gen, can be identified. The atomic resolution is confirmed by image sim- spread, leading to parasitic or “crosswidely used is the focus-variation ulations. These indicate that, because of negligible point spread, neighboring talk” intensity at this site originating ...
PDF - Grueber Lab
... 3D volumetric image. This dual-objective geometry, and the need for side-on illumination and physical translation are major limitations, requiring complex sample mounting and positioning that restricts the types of samples that can be imaged, and limits achievable volumetric imaging speeds. Recent a ...
... 3D volumetric image. This dual-objective geometry, and the need for side-on illumination and physical translation are major limitations, requiring complex sample mounting and positioning that restricts the types of samples that can be imaged, and limits achievable volumetric imaging speeds. Recent a ...