heat and temperature
... thermometer, making the value of the magnitude used, called thermometric, coincides with the corresponding temperature. In this way, in the familiar mercury thermometer the height of the column of mercury is made to correspond to the temperature, or in the case of digital thermometers an electric ci ...
... thermometer, making the value of the magnitude used, called thermometric, coincides with the corresponding temperature. In this way, in the familiar mercury thermometer the height of the column of mercury is made to correspond to the temperature, or in the case of digital thermometers an electric ci ...
Thermodynamics
... macroscopic quantities, such as the pressure P . Pressure in gases is due to the bombardment of the walls of the container by the flying atoms of the contained gas. It does not exist if there are only a few gas molecules. Macroscopic quantities such as pressure arise only in systems of a large numbe ...
... macroscopic quantities, such as the pressure P . Pressure in gases is due to the bombardment of the walls of the container by the flying atoms of the contained gas. It does not exist if there are only a few gas molecules. Macroscopic quantities such as pressure arise only in systems of a large numbe ...
Chapter Entropy Statistics
... The thermodynamic probability W is a function of no. of particles (n) (which is function of µ amount of substance, the total no. of available phase space cells (which in turn depends upon the volume) and the energy u of the system. S = f (u, v, µ) Therefore entropy s, is also a function of µ, v, u. ...
... The thermodynamic probability W is a function of no. of particles (n) (which is function of µ amount of substance, the total no. of available phase space cells (which in turn depends upon the volume) and the energy u of the system. S = f (u, v, µ) Therefore entropy s, is also a function of µ, v, u. ...
Chapter 1 - Default Home Page
... Semiconductors may also be used in resistance thermometry. For these materials, the resistance decreases approximately exponentially with increasing temperatures. Semiconductor thermometers are commonly used for precision measurements at very low temperatures. They are also used at higher temperatur ...
... Semiconductors may also be used in resistance thermometry. For these materials, the resistance decreases approximately exponentially with increasing temperatures. Semiconductor thermometers are commonly used for precision measurements at very low temperatures. They are also used at higher temperatur ...
Finite Temperature Field Theory
... elastic (acoustic) phenomena - the speed of sound va (in condensed matter, not in gas). ...
... elastic (acoustic) phenomena - the speed of sound va (in condensed matter, not in gas). ...
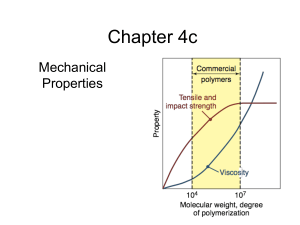
Chapter 4c - Loy Research Group
... semi-crystalline states. Changes in density must be taken into account when designing the mold. ...
... semi-crystalline states. Changes in density must be taken into account when designing the mold. ...
TRANSPORT PHENOMENA IN THE SILVER SULFIDE SINGLE
... temperature dependence of the electrical conductivity is the semiconductor course in the of temperature range 235÷446 K. At 443 K σ and RH undergo discontinuous change; this is a temperature of the polymorphic transition between α (low-temperature) and β (high-temperature) modifications. β-Ag2S exis ...
... temperature dependence of the electrical conductivity is the semiconductor course in the of temperature range 235÷446 K. At 443 K σ and RH undergo discontinuous change; this is a temperature of the polymorphic transition between α (low-temperature) and β (high-temperature) modifications. β-Ag2S exis ...
Temperature dependence of spectral functions for the one
... compare to the experiments of Ref. [5]. At the lowest temperatures considered in Ref. [5], the photoemission results compare favorably with T = 0 DDMRG calculations of Ref. [3]. In the photoemission spectra one can identify a spinon branch, a holon branch as well a holon shadow band. Those features ...
... compare to the experiments of Ref. [5]. At the lowest temperatures considered in Ref. [5], the photoemission results compare favorably with T = 0 DDMRG calculations of Ref. [3]. In the photoemission spectra one can identify a spinon branch, a holon branch as well a holon shadow band. Those features ...