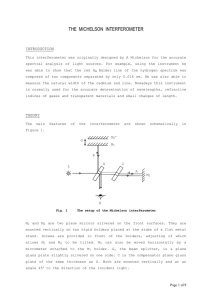
Polarization and Polarization Control
... Precise control of polarization behavior is necessary to obtain optimal performance from your optical components and systems. Characteristics such as reflectivity, insertion loss, and beam splitter ratios will be different for different polarizations. Such dependencies need to be carefully accounted ...
... Precise control of polarization behavior is necessary to obtain optimal performance from your optical components and systems. Characteristics such as reflectivity, insertion loss, and beam splitter ratios will be different for different polarizations. Such dependencies need to be carefully accounted ...
Holografie – lasery
... emits laser light in bursts. Continuous wave lasers are far more commonly used in standard holography. As discussed earlier, the recording of an interference pattern on the film forms a hologram. If the subject moves, even a microscopic amount, from one moment to the next, two different interference ...
... emits laser light in bursts. Continuous wave lasers are far more commonly used in standard holography. As discussed earlier, the recording of an interference pattern on the film forms a hologram. If the subject moves, even a microscopic amount, from one moment to the next, two different interference ...
Talk, ppt
... input light flux in the amplitude or the pupil is necessary. However, none of the methods of separation of the amplitude can not provide a wide FOV and a wide spectral range simultaneously. Therefore, we propose a scheme with the division of the pupil. Feature of this scheme is the need for the thre ...
... input light flux in the amplitude or the pupil is necessary. However, none of the methods of separation of the amplitude can not provide a wide FOV and a wide spectral range simultaneously. Therefore, we propose a scheme with the division of the pupil. Feature of this scheme is the need for the thre ...
Three-dimensional digitization of highly reflective and transparent
... at every pixel. The 3-D shape of specular and transparent objects could be recovered by three viewpoints if incoming light undergoes two reflections or refractions. They used an environment mapping procedure [16] for finding correspondence between the image and the display. Bonfort et al. [6] presen ...
... at every pixel. The 3-D shape of specular and transparent objects could be recovered by three viewpoints if incoming light undergoes two reflections or refractions. They used an environment mapping procedure [16] for finding correspondence between the image and the display. Bonfort et al. [6] presen ...
CHAPTER 1 PHYSICAL OPTICS: INTERFERENCE • Introduction
... interference effect between light rays reflected from the front and back surfaces of the thin film of soap making the bubble. The color depends on the thickness of film, ranging from black, where the film is thinnest, to magenta, where the film is thickest. ...
... interference effect between light rays reflected from the front and back surfaces of the thin film of soap making the bubble. The color depends on the thickness of film, ranging from black, where the film is thinnest, to magenta, where the film is thickest. ...
Mimicking the colourful wing scale structure of the
... through crossed polarisers has undergone a polarisation rotation via a double or triple bounce. The double bounce results in a single reflection peak and a triple bounce induces a double peak feature. The red curves model the reflection as a superposition of double and triple bounce. ing from a self ...
... through crossed polarisers has undergone a polarisation rotation via a double or triple bounce. The double bounce results in a single reflection peak and a triple bounce induces a double peak feature. The red curves model the reflection as a superposition of double and triple bounce. ing from a self ...
Measurement of the Wavelength of Light
... In addition to agreeing with the known wavelength better, the result of Method B also has a smaller uncertainty. The primary difference between these two methods is that the measurement of the zeroth order angle θ0 is used in each wavelength measurement in Method A as well as one of the other order ...
... In addition to agreeing with the known wavelength better, the result of Method B also has a smaller uncertainty. The primary difference between these two methods is that the measurement of the zeroth order angle θ0 is used in each wavelength measurement in Method A as well as one of the other order ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... indeed fixed (for a given mode) by the boundary conditions. But for wave packets in the free 3D space there is no such restriction: a function of ...
... indeed fixed (for a given mode) by the boundary conditions. But for wave packets in the free 3D space there is no such restriction: a function of ...
How can the reflections of light on the surface of
... With a transverse wave, we have something that is impossible for longitudinal wave: there are several possible directions for the electric field. When the direction of oscillation of the field changes, the polarization of light changes. The following image shows different possible directions for the ...
... With a transverse wave, we have something that is impossible for longitudinal wave: there are several possible directions for the electric field. When the direction of oscillation of the field changes, the polarization of light changes. The following image shows different possible directions for the ...
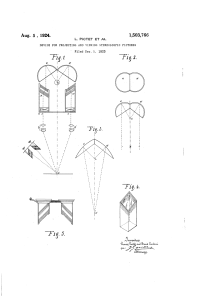
Device for projecting and viewing stereoscopic pictures
... ing to the invention use is made not only of the backward rays, but also of the lateral sess the disadvantage that they have a right rays which are usually lost. In this manner and a wrong side, one of theends having about twice as many rays are utilized and to be placed before the eyes: if the othe ...
... ing to the invention use is made not only of the backward rays, but also of the lateral sess the disadvantage that they have a right rays which are usually lost. In this manner and a wrong side, one of theends having about twice as many rays are utilized and to be placed before the eyes: if the othe ...
Light

Light is electromagnetic radiation within a certain portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The word usually refers to visible light, which is visible to the human eye and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), or 6993400000000000000♠400×10−9 m to 6993700000000000000♠700×10−9 m, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). This wavelength means a frequency range of roughly 430–750 terahertz (THz). Often, infrared and ultraviolet are also called light.The main source of light on Earth is the Sun. Sunlight provides the energy that green plants use to create sugars mostly in the form of starches, which release energy into the living things that digest them. This process of photosynthesis provides virtually all the energy used by living things. Historically, another important source of light for humans has been fire, from ancient campfires to modern kerosene lamps. With the development of electric lights and of power systems, electric lighting has all but replaced firelight. Some species of animals generate their own light, called bioluminescence. For example, fireflies use light to locate mates, and vampire squids use it to hide themselves from prey.Primary properties of visible light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum, and polarisation, while its speed in a vacuum, 299,792,458 meters per second, is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Visible light, as with all types of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), is experimentally found to always move at this speed in vacuum.In physics, the term light sometimes refers to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. Like all types of light, visible light is emitted and absorbed in tiny ""packets"" called photons, and exhibits properties of both waves and particles. This property is referred to as the wave–particle duality. The study of light, known as optics, is an important research area in modern physics.