Visualizing Earth Science
... – Rock is subjected to side to side or up and down forces, perpendicular to wave’s direction of travel – S (secondary) wave – Not transmitted through water – Travel slower than P waves ...
... – Rock is subjected to side to side or up and down forces, perpendicular to wave’s direction of travel – S (secondary) wave – Not transmitted through water – Travel slower than P waves ...
Seismic Waves
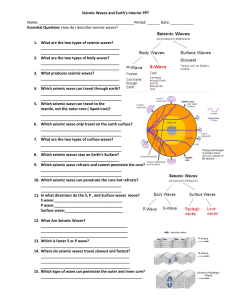
... Scientist study earthquakes to know more about the earth. To study earthquakes scientist use seismographs. Seismographs measures the the movement and vibration of earthquakes. It also tells what kind of seismic wave it is. Seismic waves are vibrations caused by rocks moving or breaking along faults ...
... Scientist study earthquakes to know more about the earth. To study earthquakes scientist use seismographs. Seismographs measures the the movement and vibration of earthquakes. It also tells what kind of seismic wave it is. Seismic waves are vibrations caused by rocks moving or breaking along faults ...
Earthquakes
... • This shaking is what causes most earthquake damage because it is so close to the focus. • As waves travel away from the focus they get weaker. ...
... • This shaking is what causes most earthquake damage because it is so close to the focus. • As waves travel away from the focus they get weaker. ...
Well-seismic bandwidth and time-lapse seismic characterization: physical considerations
... Reservoirs are commonly heterogeneous. Injection of CO2 related to enhanced oil recovery operations may cause strong lateral and depth-dependent changes of heterogeneity both within the reservoir and the surrounding formations. A seismic signal propagating through the reservoir and the surrounding f ...
... Reservoirs are commonly heterogeneous. Injection of CO2 related to enhanced oil recovery operations may cause strong lateral and depth-dependent changes of heterogeneity both within the reservoir and the surrounding formations. A seismic signal propagating through the reservoir and the surrounding f ...
Earthquakes
... They’re Caused by a Build-up of STRESS in Earth’s Crust As tectonic plates move, they cause stress in the crust, which in turn produces folds and faults. ...
... They’re Caused by a Build-up of STRESS in Earth’s Crust As tectonic plates move, they cause stress in the crust, which in turn produces folds and faults. ...
Earthquakes
... – These seismic waves spread out from the focus. As they do, their energy grows weaker. ...
... – These seismic waves spread out from the focus. As they do, their energy grows weaker. ...
Seismic communication

Seismic communication, sometimes called vibrational communication, describes the conveying of information through seismic vibrations of the substrate. The substrate may be the earth, a plant stem or leaf, the surface of a body of water, a spider’s web, a honeycomb, or any of the myriad types of soil substrates. Seismic cues are generally conveyed by Rayleigh waves generated through vibrations on the substrate, or acoustical waves that couple with the substrate. Vibrational communication is an ancient sensory modality and it is widespread in the animal kingdom where it has evolved several times independently. It has been reported in mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, insects, arachnids, crustaceans and nematode worms. Vibrations and other communication channels are not necessarily mutually exclusive, but can be used in multi-modal communication.