Overview of the Reticular Formation (RF)
... Diffuse modulatory system in part corresponds to the Ascending Reticular Activating System (ARAS) that is a physiological concept. The neurons of the diffuse modulatory system located around the border of the Reticular Formation and have long projections covering wide areas of the brain (e.g. entire ...
... Diffuse modulatory system in part corresponds to the Ascending Reticular Activating System (ARAS) that is a physiological concept. The neurons of the diffuse modulatory system located around the border of the Reticular Formation and have long projections covering wide areas of the brain (e.g. entire ...
Laboratory Exercise 10: Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord
... B., D. Histology and Functional Anatomy of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord and brain make up the central nervous system (CNS). The CNS analyzes incoming impulses from the peripheral nerves and integrates them with other neuronal activities to produce appropriate responses. The spinal cord is subdivi ...
... B., D. Histology and Functional Anatomy of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord and brain make up the central nervous system (CNS). The CNS analyzes incoming impulses from the peripheral nerves and integrates them with other neuronal activities to produce appropriate responses. The spinal cord is subdivi ...
15-2 Sensory Receptors
... The voluntary response, which is not immediate, can moderate, enhance, or supplement the relatively simple involuntary reflexive response. ...
... The voluntary response, which is not immediate, can moderate, enhance, or supplement the relatively simple involuntary reflexive response. ...
Sensory signals during active versus passive movement
... from several laboratories have, however, yielded major insights into our understanding of how sensory signals are processed during movement. In this review, I consider recent advances in this field, focusing on experiments in the vestibular system that have provided evidence for the differential pro ...
... from several laboratories have, however, yielded major insights into our understanding of how sensory signals are processed during movement. In this review, I consider recent advances in this field, focusing on experiments in the vestibular system that have provided evidence for the differential pro ...
spinal cord - Dr Magrann
... GANGLION is the term for a group of neuron cell bodies (both sensory and motor) found in the peripheral nervous system only. SENSORY NEURONS come in (via the spinal nerve) through the posterior root; their cell body is in the posterior root ganglion, and its axon goes into the posterior horn and syn ...
... GANGLION is the term for a group of neuron cell bodies (both sensory and motor) found in the peripheral nervous system only. SENSORY NEURONS come in (via the spinal nerve) through the posterior root; their cell body is in the posterior root ganglion, and its axon goes into the posterior horn and syn ...
CHAPTER 13: THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM MODULE
... Five major nerves of brachial plexus (continued): Musculocutaneous nerve – continuation of lateral cord; innervates anterior arm muscles, including biceps brachii, and skin covering lateral arm Median nerve – derived from fusion of lateral and medial cords; travels down middle of arm and forearm ...
... Five major nerves of brachial plexus (continued): Musculocutaneous nerve – continuation of lateral cord; innervates anterior arm muscles, including biceps brachii, and skin covering lateral arm Median nerve – derived from fusion of lateral and medial cords; travels down middle of arm and forearm ...
Chapter 13 PowerPoint
... • All neural structures outside the brain • Sensory receptors • Peripheral nerves and associated ganglia • Motor endings ...
... • All neural structures outside the brain • Sensory receptors • Peripheral nerves and associated ganglia • Motor endings ...
Part a
... • All neural structures outside the brain • Sensory receptors • Peripheral nerves and associated ganglia • Motor endings ...
... • All neural structures outside the brain • Sensory receptors • Peripheral nerves and associated ganglia • Motor endings ...
biological conditions for the emergence of musical arts in a
... continuously sounding musical tone). A theory of harmony based on a neural model for the central pitch processor was developed by Terhardt (1974). It is important to point out, however, that the function of a central pitch processor is not unique to humans: complex tone perception works in a similar ...
... continuously sounding musical tone). A theory of harmony based on a neural model for the central pitch processor was developed by Terhardt (1974). It is important to point out, however, that the function of a central pitch processor is not unique to humans: complex tone perception works in a similar ...
Neuroscience 14a – Introduction to Consciousness
... Persistent Vegetative State Patients who go into an irreversible coma can often enter persistent vegetative stage in which sleep-wake cycles are present even though the patient is unaware of their surroundings. Their brainstem is still able to function so reflexes and postural movements are still p ...
... Persistent Vegetative State Patients who go into an irreversible coma can often enter persistent vegetative stage in which sleep-wake cycles are present even though the patient is unaware of their surroundings. Their brainstem is still able to function so reflexes and postural movements are still p ...
Neurophysiological Mechanisms Underlying Auditory Image
... of neural activity. Thus, these methods are invaluable tools for localizing cognitive functions, and their application to issues of auditory imagery is described below. The temporal properties of neural responses in cognitive tasks are best captured by direct measures of the neural activity. The ele ...
... of neural activity. Thus, these methods are invaluable tools for localizing cognitive functions, and their application to issues of auditory imagery is described below. The temporal properties of neural responses in cognitive tasks are best captured by direct measures of the neural activity. The ele ...
Sensory Receptors
... the internal and external environment • Perception - the conscious interpretation of those stimuli ...
... the internal and external environment • Perception - the conscious interpretation of those stimuli ...
somatosensory area i
... Effect of removing somatosensory association area Unable to recognize complex objects/complex forms by feeling them on opposite side Loses sense of form of his/her own body / body ...
... Effect of removing somatosensory association area Unable to recognize complex objects/complex forms by feeling them on opposite side Loses sense of form of his/her own body / body ...
Nerves and Special Senses
... taste; motor fibers to the pharynx • X Vagus nerves – sensory and motor fibers for pharynx, larynx, and viscera • XI (Spinal) Accessory nerve – motor fibers to neck and upper back • XII Hypoglossal nerve – motor fibers to tongue, some sensory fibers from tongue. ...
... taste; motor fibers to the pharynx • X Vagus nerves – sensory and motor fibers for pharynx, larynx, and viscera • XI (Spinal) Accessory nerve – motor fibers to neck and upper back • XII Hypoglossal nerve – motor fibers to tongue, some sensory fibers from tongue. ...
Trichromatic theory of color vision
... Weber’s law – (pronounced “VAY-ber”) a basic law of psychophysics stating that a just noticeable difference is in constant proportion to the intensity of an initial stimulus. – For example, if you work at the fragrance department of a department store, you will notice the smells of the perfumes imme ...
... Weber’s law – (pronounced “VAY-ber”) a basic law of psychophysics stating that a just noticeable difference is in constant proportion to the intensity of an initial stimulus. – For example, if you work at the fragrance department of a department store, you will notice the smells of the perfumes imme ...
book ppt - Castle High School
... Intensity of sensation is coded as the frequency of action potentials. Some sensory cells transmit information to the brain about internal conditions, without conscious sensation. ...
... Intensity of sensation is coded as the frequency of action potentials. Some sensory cells transmit information to the brain about internal conditions, without conscious sensation. ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
... - 1 Coccygeal All are Mixed; both Sensory (Afferent) & Motor (Efferent) Attach to Spinal Cord by Ventral & Dorsal Root ...
... - 1 Coccygeal All are Mixed; both Sensory (Afferent) & Motor (Efferent) Attach to Spinal Cord by Ventral & Dorsal Root ...
Neurophysiology
... • Highly Adaptable • Sensitive to CHANGES in Frequency and Intensity – Coding virtual pitch – demodulating complex signals (e.g. speech) ...
... • Highly Adaptable • Sensitive to CHANGES in Frequency and Intensity – Coding virtual pitch – demodulating complex signals (e.g. speech) ...
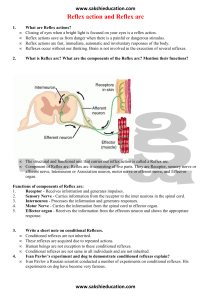
Reflex action and Reflex arc
... given food. After doing this for few days he noticed that the dog started salivating when it heard the bell even if the food was not given. Dog associated with sound of the bell with food and assumed that whenever the bell rang food was given In expectation of food, saliva started flowing from its m ...
... given food. After doing this for few days he noticed that the dog started salivating when it heard the bell even if the food was not given. Dog associated with sound of the bell with food and assumed that whenever the bell rang food was given In expectation of food, saliva started flowing from its m ...
030909.PHitchcock.IntroductoryLecture
... of the somaticsensory and motor systems, respectively. ...
... of the somaticsensory and motor systems, respectively. ...
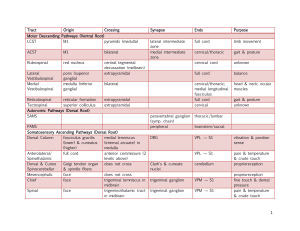
Tract Origin Crossing Synapse Ends Purpose Motor Descending
... pons: pontomesencephalic reticular formation (PRF) receives inputs from somatosensory (cord), limbic/cingulate cortex, frontoparietal association cortex, & thalamic reticular nucleus thalamic reticular nucleus: cortical input → modulate other thalamic structures → project to PRF locked-in syndrome: ...
... pons: pontomesencephalic reticular formation (PRF) receives inputs from somatosensory (cord), limbic/cingulate cortex, frontoparietal association cortex, & thalamic reticular nucleus thalamic reticular nucleus: cortical input → modulate other thalamic structures → project to PRF locked-in syndrome: ...
Chapter 11
... – Responsible for all conscious behavior by containing three kinds of functional areas, which include motor, sensory and association areas ...
... – Responsible for all conscious behavior by containing three kinds of functional areas, which include motor, sensory and association areas ...
Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception SW
... What does it mean to sense something? Sensory receptors are specialized neurons that respond to speci c types of stimuli. When sensory information is detected by a sensory receptor, ...
... What does it mean to sense something? Sensory receptors are specialized neurons that respond to speci c types of stimuli. When sensory information is detected by a sensory receptor, ...
Chapter1 (new window)
... Behavioral Responses (Step 5-7) • Experience and Action – Perception occurs as a conscious experience. – Recognition occurs when an object is placed in a category giving it meaning. – Action occurs when the perceiver initiates motor activity in response to recognition. ...
... Behavioral Responses (Step 5-7) • Experience and Action – Perception occurs as a conscious experience. – Recognition occurs when an object is placed in a category giving it meaning. – Action occurs when the perceiver initiates motor activity in response to recognition. ...