optical cavity
... eventually growing larger than the size of the cavity mirrors and being lost. By using methods such as ray transfer matrix analysis, it is possible to calculate a stability criterion: ...
... eventually growing larger than the size of the cavity mirrors and being lost. By using methods such as ray transfer matrix analysis, it is possible to calculate a stability criterion: ...
Note - The Eclecticon of Dr French
... the focusing effect results from the observation that the total angle of deflection passes through an extremum as the angle between incidence and raindrop surface normal is varied. The large multitude of raindrops within a raincloud allows us to assume that all possible angles of are explored wi ...
... the focusing effect results from the observation that the total angle of deflection passes through an extremum as the angle between incidence and raindrop surface normal is varied. The large multitude of raindrops within a raincloud allows us to assume that all possible angles of are explored wi ...
Quiz 9
... *1. (5pts) A person walks into a room that has, on opposite walls, two plane mirrors producing multiple images. Find the distance from the person to the third image seen in the left-hand mirror when the person is 1.50 m away from the mirror on the left wall and 2.50 m away from the mirror on the rig ...
... *1. (5pts) A person walks into a room that has, on opposite walls, two plane mirrors producing multiple images. Find the distance from the person to the third image seen in the left-hand mirror when the person is 1.50 m away from the mirror on the left wall and 2.50 m away from the mirror on the rig ...
Lecture 9
... is computed like ray-tracing and the indirect illumination is computed from querying the stored photons in the photon ...
... is computed like ray-tracing and the indirect illumination is computed from querying the stored photons in the photon ...
Devil physics The baddest class on campus IB Physics
... incidence, i (angle between the ray and the normal to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence) is equal to the angle of reflection, r (angle between the normal and the reflected ray). ...
... incidence, i (angle between the ray and the normal to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence) is equal to the angle of reflection, r (angle between the normal and the reflected ray). ...
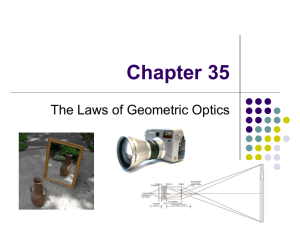
chapter35
... represent beams of light. Each ray is represented as a line. The rays are straight lines perpendicular to the wave fronts The path of light is reversible. ...
... represent beams of light. Each ray is represented as a line. The rays are straight lines perpendicular to the wave fronts The path of light is reversible. ...
micro-bending, macro-bending and less bend sensitive optical
... Macro-bends can be most easily classified as being optical fibres, or cables containing optical fibres, that are subjected to bend radii below the manufacturers recommended values to such an extent that the light cannot be guided along the core of optical fibre – thereby resulting in attenuation i.e ...
... Macro-bends can be most easily classified as being optical fibres, or cables containing optical fibres, that are subjected to bend radii below the manufacturers recommended values to such an extent that the light cannot be guided along the core of optical fibre – thereby resulting in attenuation i.e ...
lecture_three_2016
... serves as the source of spherical secondary waves also called wavelets, such that the primary wavefront at some later time is the envelope of these wavelets. Moreover, the wavelets advance with a speed and frequency equal to those of the primary wave at each point in space. This has since become kno ...
... serves as the source of spherical secondary waves also called wavelets, such that the primary wavefront at some later time is the envelope of these wavelets. Moreover, the wavelets advance with a speed and frequency equal to those of the primary wave at each point in space. This has since become kno ...
The present work gives recommendations for rational - Dimka
... limiting values ratio of field angles in the image and object domains at more than 0,4 max ) and nearly made it telocentric ( max 12º) by 2,8 times (up to max ...
... limiting values ratio of field angles in the image and object domains at more than 0,4 max ) and nearly made it telocentric ( max 12º) by 2,8 times (up to max ...
Chapter 6: Polarization and Crystal Optics
... Give for the following systems of polarizers and transmission directions the total transmitted intensity: (angles are measured in the same direction and relatively to the polarization direction of the incident light). a) one at 90 angle b) two at the angles 45 and 90 . c) three at the angles 30 ...
... Give for the following systems of polarizers and transmission directions the total transmitted intensity: (angles are measured in the same direction and relatively to the polarization direction of the incident light). a) one at 90 angle b) two at the angles 45 and 90 . c) three at the angles 30 ...
PowerPoint version
... if the reflective surface is not a smooth one, what is called diffuse reflection occurs. ...
... if the reflective surface is not a smooth one, what is called diffuse reflection occurs. ...
lecture5web
... Hot air is less dense, and is thus a “faster” medium than cold air. This leads to the ray bending away from the normal. Because we interpret rays as traveling in straight lines, we see a “reflection” in the road, and assume it is wet. ...
... Hot air is less dense, and is thus a “faster” medium than cold air. This leads to the ray bending away from the normal. Because we interpret rays as traveling in straight lines, we see a “reflection” in the road, and assume it is wet. ...
Specifying an Aspheric Surface
... Aspheres are widely used for a myriad of refractive and reflective applications due to their small number of surfaces and typically large apertures. New technology permits the utilization of increasingly complex aspheric surfaces for the cost-effective solution of optical problems and applications r ...
... Aspheres are widely used for a myriad of refractive and reflective applications due to their small number of surfaces and typically large apertures. New technology permits the utilization of increasingly complex aspheric surfaces for the cost-effective solution of optical problems and applications r ...
J. Spigulis. Side-emitting optical fibers brighten our world in new
... • Coupling light sources to both fiber ends may appear more complicated technically, but this design approach improves both the intensity and uniformity of the side glowing since the total side-emission at each point summarizes the contributions of both light sources [see graph (a) on p. 36, “Total”] ...
... • Coupling light sources to both fiber ends may appear more complicated technically, but this design approach improves both the intensity and uniformity of the side glowing since the total side-emission at each point summarizes the contributions of both light sources [see graph (a) on p. 36, “Total”] ...
Difficulties associated with working with UV and IR optics
... broadband, though narrow bandwidth filters can be designed for lower wavelengths [1]. One of the difficulties associated with coating UV optics is that coatings are applied at high temperatures, so stress is induced upon cooling, which pulls the flatness out of specification. This is not such a prob ...
... broadband, though narrow bandwidth filters can be designed for lower wavelengths [1]. One of the difficulties associated with coating UV optics is that coatings are applied at high temperatures, so stress is induced upon cooling, which pulls the flatness out of specification. This is not such a prob ...
Applications(2)
... deep ultraviolet, but geometric factors bring it close to the visible. • In doped semiconductors, the plasma frequency is usually in the infrared. • The plasmon energy for most metals corresponds to that of an ultraviolet photon. However, as mentioned above for some metals like silver, gold, the alk ...
... deep ultraviolet, but geometric factors bring it close to the visible. • In doped semiconductors, the plasma frequency is usually in the infrared. • The plasmon energy for most metals corresponds to that of an ultraviolet photon. However, as mentioned above for some metals like silver, gold, the alk ...
Practical No 6
... The equation (6) is Lambert’s cosine law called also „cosine emission law”. This law is valid only for socalled point light sources that is sources whose dimensions are small compared to the distance from a light source to an observer. Lambert’s law can be used for all light sources whose diameter i ...
... The equation (6) is Lambert’s cosine law called also „cosine emission law”. This law is valid only for socalled point light sources that is sources whose dimensions are small compared to the distance from a light source to an observer. Lambert’s law can be used for all light sources whose diameter i ...
Michelson Lab Guide UTSA
... expected in view of energy conservation. The beam splitter is a glass plate with a thin film on one surface that partially reflects and partially transmits light. For definiteness, we will assume that it is a few-nanometer-thick aluminum film. In Physics II, you studied thin films and learned that l ...
... expected in view of energy conservation. The beam splitter is a glass plate with a thin film on one surface that partially reflects and partially transmits light. For definiteness, we will assume that it is a few-nanometer-thick aluminum film. In Physics II, you studied thin films and learned that l ...
Introduction to Optical Engineering and Design ENSC 376
... optics, and less on the physics behind the behaviour. It starts with a basic explanation of the concepts of light, as electromagnetic radiation. Then it looks how light is generated, at both the atomic and black body level. Next optical interaction with materials is discussed beginning with reflecti ...
... optics, and less on the physics behind the behaviour. It starts with a basic explanation of the concepts of light, as electromagnetic radiation. Then it looks how light is generated, at both the atomic and black body level. Next optical interaction with materials is discussed beginning with reflecti ...
LBS-100 System
... LBS-100 Attenuator The LBS-100 system that is not as compact as the LBS-300 above but has larger aperture, and has versions for longer wavelengths. The system contains the mounting frame, 1 wedge beam splitter and several attenuators. The exit end of the LBS-100 is standard C mount thread so all our ...
... LBS-100 Attenuator The LBS-100 system that is not as compact as the LBS-300 above but has larger aperture, and has versions for longer wavelengths. The system contains the mounting frame, 1 wedge beam splitter and several attenuators. The exit end of the LBS-100 is standard C mount thread so all our ...
Topic 4.5 - Aurora City School
... pulse hits the fixed end, the rope attempts to move the fixed end upwards It exerts an upwards force on the fixed end By Newton’s third law, the fixed end will exert an equal but opposite force on the rope This means that a disturbance will be created in the rope which is “downwards” and will ...
... pulse hits the fixed end, the rope attempts to move the fixed end upwards It exerts an upwards force on the fixed end By Newton’s third law, the fixed end will exert an equal but opposite force on the rope This means that a disturbance will be created in the rope which is “downwards” and will ...