A Well-Founded Semantics for Logic Programs with Abstract
... While ASP assumes that solutions are given by answer sets, well-founded models (Van Gelder, Ross, and Schlipf 1991) have been found to be very useful as well. First, computing the well-founded model of a normal logic program is tractable. This compares to the NP-completeness of computing an answer s ...
... While ASP assumes that solutions are given by answer sets, well-founded models (Van Gelder, Ross, and Schlipf 1991) have been found to be very useful as well. First, computing the well-founded model of a normal logic program is tractable. This compares to the NP-completeness of computing an answer s ...
Natural deduction for predicate logic
... This suggests that to prove a formula of the form ∀xφ, we can prove φ with some arbitrary but fresh variable x0 substituted for x. That is, we want to prove the formula φ[x0 /x]. On the previous slide, we used n as a fresh variable, but in our formal proofs, we adopt the convention of using subscri ...
... This suggests that to prove a formula of the form ∀xφ, we can prove φ with some arbitrary but fresh variable x0 substituted for x. That is, we want to prove the formula φ[x0 /x]. On the previous slide, we used n as a fresh variable, but in our formal proofs, we adopt the convention of using subscri ...
On the Finite Model Property in Order-Sorted Logic
... model-finder that deduces sort information for unsorted problems and, under certain conditions, can bound the size of domains for certain sorts and improve the performance of the instantiation procedure. Order-sorting is not used, and there are restrictions on the use of equality. Momtahan [23] defi ...
... model-finder that deduces sort information for unsorted problems and, under certain conditions, can bound the size of domains for certain sorts and improve the performance of the instantiation procedure. Order-sorting is not used, and there are restrictions on the use of equality. Momtahan [23] defi ...
pdf file
... for a fresh identifier x̂ . We now attempt to prove (∀b : T.b.x̂) , since application of ∃-Introduction (3) will then prove C . Hence, for arbitrary b , we attempt to prove T.b.x̂ . Now, T occurs only in P 0 and P 3 , so it makes sense to investigate the use of these two in proving T.b.x̂ . An instan ...
... for a fresh identifier x̂ . We now attempt to prove (∀b : T.b.x̂) , since application of ∃-Introduction (3) will then prove C . Hence, for arbitrary b , we attempt to prove T.b.x̂ . Now, T occurs only in P 0 and P 3 , so it makes sense to investigate the use of these two in proving T.b.x̂ . An instan ...
Quantum Mechanics Made Simple: Lecture Notes
... length scale systems important for chemistry, materials, optics, electronics, and quantum information. The existence of orbitals and energy levels in atoms can only be explained by quantum mechanics. Quantum mechanics can explain the behaviors of insulators, conductors, semi-conductors, and giant ma ...
... length scale systems important for chemistry, materials, optics, electronics, and quantum information. The existence of orbitals and energy levels in atoms can only be explained by quantum mechanics. Quantum mechanics can explain the behaviors of insulators, conductors, semi-conductors, and giant ma ...
pdf file
... Theorem 3.5. i) Let Y (k) be as above, and let Y be the MBI-process defined by (3.1). If 3.E) holds, then for every µ ∈ M, r ≤ t1 < · · · < tn ∈ R and a ≥ 0, ...
... Theorem 3.5. i) Let Y (k) be as above, and let Y be the MBI-process defined by (3.1). If 3.E) holds, then for every µ ∈ M, r ≤ t1 < · · · < tn ∈ R and a ≥ 0, ...
Intuitionistic Logic
... disjunct is specified, this in contrast with classical logic, where one does not have to know which disjunct holds. Negation is also defined by means of proofs: p : ¬A says that each proof a of A can be converted by the construction p into a proof of an absurdity, say 0 = 1. A proof of ¬A thus tells ...
... disjunct is specified, this in contrast with classical logic, where one does not have to know which disjunct holds. Negation is also defined by means of proofs: p : ¬A says that each proof a of A can be converted by the construction p into a proof of an absurdity, say 0 = 1. A proof of ¬A thus tells ...
Formal systems of fuzzy logic and their fragments∗
... Many formal systems of fuzzy logic (or simply just fuzzy logics) were introduced and developed in the last decades. Also some well-established many-valued logics, like L Ã ukasiewicz ([42, 41]) or Gödel-Dummett logic ([20, 10]), have been adopted into a general framework of fuzzy logics (as extensi ...
... Many formal systems of fuzzy logic (or simply just fuzzy logics) were introduced and developed in the last decades. Also some well-established many-valued logics, like L Ã ukasiewicz ([42, 41]) or Gödel-Dummett logic ([20, 10]), have been adopted into a general framework of fuzzy logics (as extensi ...
Probability Captures the Logic of Scientific
... I have made these remarks about the choice of parameter values to indicate how it may be done but, except in examples, I will not assume any particular values of the parameters. What will be assumed is merely that λ > 0, 0 < γi < 1, and 0 < p(I) < 1. 6. Reasoning by analogy If individual b is known ...
... I have made these remarks about the choice of parameter values to indicate how it may be done but, except in examples, I will not assume any particular values of the parameters. What will be assumed is merely that λ > 0, 0 < γi < 1, and 0 < p(I) < 1. 6. Reasoning by analogy If individual b is known ...
A Concurrent Logical Framework: The Propositional Fragment Kevin Watkins , Iliano Cervesato
... the framework, explicit judgments specifying which computations should be considered equivalent, reasoning with or about such a specification can be exceedingly cumbersome. Concurrent LF (CLF), the topic of this paper, is a new logical framework that extends LLF with additional linear constructs (A1 ...
... the framework, explicit judgments specifying which computations should be considered equivalent, reasoning with or about such a specification can be exceedingly cumbersome. Concurrent LF (CLF), the topic of this paper, is a new logical framework that extends LLF with additional linear constructs (A1 ...
Logic as a Tool 3mm Chapter 2: Deductive Reasoning in
... Sometimes, the resolvent can (and should) be simplified, by removing duplicated literals on the fly: {A1 , . . . , C , C , . . . , Am } ⇒ {A1 , . . . , C , . . . , Am }. For instance: {p, ¬q, ¬r }{q, ¬r } {p, ¬q, ¬r }{q, ¬r } instead of {p, ¬r } {p, ¬r , ¬r } Goranko ...
... Sometimes, the resolvent can (and should) be simplified, by removing duplicated literals on the fly: {A1 , . . . , C , C , . . . , Am } ⇒ {A1 , . . . , C , . . . , Am }. For instance: {p, ¬q, ¬r }{q, ¬r } {p, ¬q, ¬r }{q, ¬r } instead of {p, ¬r } {p, ¬r , ¬r } Goranko ...
Quantum reflection and dwell times of
... 0.5 MeV from threshold hints toward the existence of an eta-mesic state close to threshold T. Mersmann et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 242301 (2007) The photoproduction of η - mesic 3He was investigated using the TAPS calorimeter at the Mainz Microtron accelerator facility MAMI. A binding energy of (-4 ...
... 0.5 MeV from threshold hints toward the existence of an eta-mesic state close to threshold T. Mersmann et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 242301 (2007) The photoproduction of η - mesic 3He was investigated using the TAPS calorimeter at the Mainz Microtron accelerator facility MAMI. A binding energy of (-4 ...
Exercise
... P(x) it is not enough to show that P(a) is true for one or some a’s. 2. To show that a statement of the form x P(x) is FALSE, it is enough to show that P(a) is false for one a ...
... P(x) it is not enough to show that P(a) is true for one or some a’s. 2. To show that a statement of the form x P(x) is FALSE, it is enough to show that P(a) is false for one a ...
Fano-Racah Tensorial Algebra
... where fb (t) and fg (t) are functions that describe the time dependent laser intensity, and Gk (t − t0 ) is the perturbation coefficient given by Fano and Macek, for example. The above expression expresses the dependence of A upon the geometrical parameters of the experimental apparatus. It was obta ...
... where fb (t) and fg (t) are functions that describe the time dependent laser intensity, and Gk (t − t0 ) is the perturbation coefficient given by Fano and Macek, for example. The above expression expresses the dependence of A upon the geometrical parameters of the experimental apparatus. It was obta ...
Effective gravitational interactions of dark matter axions
... The thermalization is confirmed only by numerical calculations of toy model. The photons also have thermal contact with axions, which drops photon temperature and leads to large effective d.o.f. of neutrino (Neff ~ 6.77). ...
... The thermalization is confirmed only by numerical calculations of toy model. The photons also have thermal contact with axions, which drops photon temperature and leads to large effective d.o.f. of neutrino (Neff ~ 6.77). ...
compactness slides
... and F. By the unique readability theorem C ∗ is freely generated from the set of sentence symbols by the functions in F. This guarantees the uniqueness of the extension of truth assignment v to v̄ by the recursion theorem below. ...
... and F. By the unique readability theorem C ∗ is freely generated from the set of sentence symbols by the functions in F. This guarantees the uniqueness of the extension of truth assignment v to v̄ by the recursion theorem below. ...
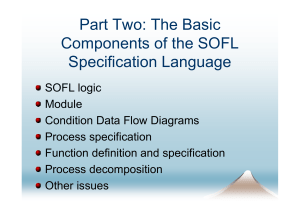
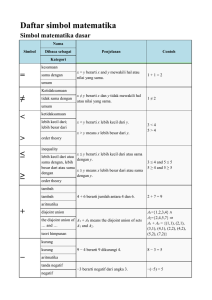
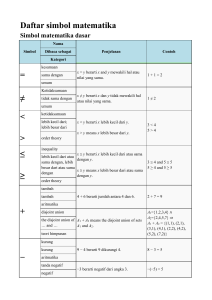
Daftar simbol matematika
... complex square root if z = r exp(iφ) is represented in polar the complex square coordinates with -π < φ ≤ π, then √z = √r √(-1) = i root of; square root ...
... complex square root if z = r exp(iφ) is represented in polar the complex square coordinates with -π < φ ≤ π, then √z = √r √(-1) = i root of; square root ...