• Use mathematical deduction to derive new knowledge. • Predicate
... • Predicate Logic is a powerful representation scheme used by many AI programs. • Propositional logic is much simpler (less ...
... • Predicate Logic is a powerful representation scheme used by many AI programs. • Propositional logic is much simpler (less ...
Tactical and Strategic Challenges to Logic (KAIST
... to be fruitfully applicable to inconsistent systems that might not be as big as Five Eyes, banking or health-care. Most information-systems that aren’t at all small aren’t big in the Five Eyes sense. All the same, they can be a lot bigger than we might think. The IR project is founded on assumptions ...
... to be fruitfully applicable to inconsistent systems that might not be as big as Five Eyes, banking or health-care. Most information-systems that aren’t at all small aren’t big in the Five Eyes sense. All the same, they can be a lot bigger than we might think. The IR project is founded on assumptions ...
Symbolic Logic II
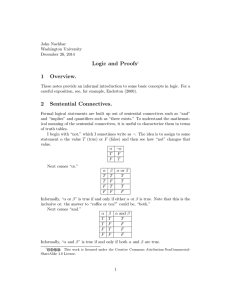
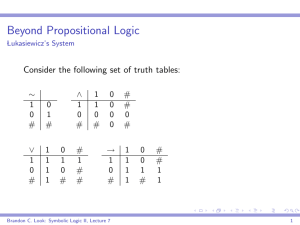
... In the case of Lukasiewicz-validity, we have designated {1} in our definition of validity and have so defined validity as “always true”. If we had wanted a definition of validity to mean never false, then we would have to designate {1, #}. ...
... In the case of Lukasiewicz-validity, we have designated {1} in our definition of validity and have so defined validity as “always true”. If we had wanted a definition of validity to mean never false, then we would have to designate {1, #}. ...
True
... • Logicians typically think in terms of models, which are formally structured worlds with respect to which truth can be evaluated • We say m is a model of a sentence α if α is true in m • M(α) is the set of all models of α • Then KB ╞ α iff M(KB) ⊆ M(α) ...
... • Logicians typically think in terms of models, which are formally structured worlds with respect to which truth can be evaluated • We say m is a model of a sentence α if α is true in m • M(α) is the set of all models of α • Then KB ╞ α iff M(KB) ⊆ M(α) ...