1Propositional Logic - Princeton University Press
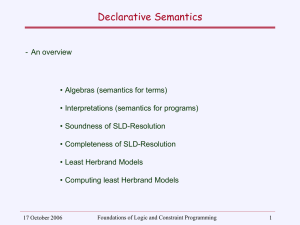
... Other meanings (i.e., semantics) for implication are considered in Part 3 of this book. Definition. A wff A is satisfiable iff there exists an interpretation I such that V I [ A] = T . We also say “I makes A true” and “I satisfies A.” Definition. A wff A is unsatisfiable iff the wff is not satisfiab ...
... Other meanings (i.e., semantics) for implication are considered in Part 3 of this book. Definition. A wff A is satisfiable iff there exists an interpretation I such that V I [ A] = T . We also say “I makes A true” and “I satisfies A.” Definition. A wff A is unsatisfiable iff the wff is not satisfiab ...
First-Order Loop Formulas for Normal Logic Programs
... variables, we can hopefully avoid this problem of having to compute similar loops and loop formulas every time a program is grounded on a domain. Thus extending loop formulas in logic programming to first-order case is not only theoretically interesting, but may also be of practical relevance. Speci ...
... variables, we can hopefully avoid this problem of having to compute similar loops and loop formulas every time a program is grounded on a domain. Thus extending loop formulas in logic programming to first-order case is not only theoretically interesting, but may also be of practical relevance. Speci ...
A Taste of Categorical Logic — Tutorial Notes
... Figure 2: Typing rules for logical connectives. Note that these are not introduction and elimination rules for connectives. These merely state that some things are propositions, i.e., of type Prop Notice that we did not include an equality predicate. This is just for brevity. In higher-order logic e ...
... Figure 2: Typing rules for logical connectives. Note that these are not introduction and elimination rules for connectives. These merely state that some things are propositions, i.e., of type Prop Notice that we did not include an equality predicate. This is just for brevity. In higher-order logic e ...
Predicate logic
... Let a, b ∈ Z s.t. a and b are odd. Then by definition of odd a = 2m + 1.m ∈ Z and b = 2n + 1.n ∈ Z So ab = (2m + 1)(2n + 1) = 4mn + 2m + 2n + 1 = 2(2mn + m + n) + 1 and since m, n ∈ Z it holds that (2mn + m + n) ∈ Z, so ab = 2k + 1 for some k ∈ Z. Thus ab is odd by definition of odd. QED ...
... Let a, b ∈ Z s.t. a and b are odd. Then by definition of odd a = 2m + 1.m ∈ Z and b = 2n + 1.n ∈ Z So ab = (2m + 1)(2n + 1) = 4mn + 2m + 2n + 1 = 2(2mn + m + n) + 1 and since m, n ∈ Z it holds that (2mn + m + n) ∈ Z, so ab = 2k + 1 for some k ∈ Z. Thus ab is odd by definition of odd. QED ...
A Tableau Calculus for Minimal Modal Model Generation
... attention for modal logics with non-monotonic operators and non-monotonic semantics, where the aim is the minimization of certain predicates (for example [6,7]). As the common modal logics can be translated into first-order logic [14], classical approaches for minimal model generation can be used to ...
... attention for modal logics with non-monotonic operators and non-monotonic semantics, where the aim is the minimization of certain predicates (for example [6,7]). As the common modal logics can be translated into first-order logic [14], classical approaches for minimal model generation can be used to ...
An Introduction to Mathematical Logic
... 1. a theorem 2. the claim that this theorem is a logical consequence of other sentences (in this case: the axioms of equivalence structures) 3. the proof of the theorem More generally: we deal with 1. a set Φ of sentences (“axioms”), a sentence ϕ (“theorem”) 2. the claim that ϕ follows logically fr ...
... 1. a theorem 2. the claim that this theorem is a logical consequence of other sentences (in this case: the axioms of equivalence structures) 3. the proof of the theorem More generally: we deal with 1. a set Φ of sentences (“axioms”), a sentence ϕ (“theorem”) 2. the claim that ϕ follows logically fr ...
1 Introduction to Categories and Categorical Logic
... of the basic ideas of category theory and categorical logic. The notes are based on a lecture course given at Oxford over the past few years. They contain numerous exercises, and hopefully will prove useful for self-study by those seeking a first introduction to the subject, with fairly minimal prer ...
... of the basic ideas of category theory and categorical logic. The notes are based on a lecture course given at Oxford over the past few years. They contain numerous exercises, and hopefully will prove useful for self-study by those seeking a first introduction to the subject, with fairly minimal prer ...
Classical Propositional Logic
... These are relatively new questions. Throughout the history of logic, soundness was an intuitive notion, and asked rule-by-rule; the assumption seems to have been that a logical system is sound if and only if all its rules are sound. ...
... These are relatively new questions. Throughout the history of logic, soundness was an intuitive notion, and asked rule-by-rule; the assumption seems to have been that a logical system is sound if and only if all its rules are sound. ...
THE PARADOXES OF STRICT IMPLICATION John L
... It cannot be denied that there is a strong temptation to identify implication with a relation between meanings. However, we must be more explicit about just what this relation is. Let us begin with the case of analytic equivalence. It is probably the predominant view that the statement that p (e.g., ...
... It cannot be denied that there is a strong temptation to identify implication with a relation between meanings. However, we must be more explicit about just what this relation is. Let us begin with the case of analytic equivalence. It is probably the predominant view that the statement that p (e.g., ...