Enhancing four-wave-mixing processes by nanowire arrays coupled to a gold film Ekaterina Poutrina,
... Four wave mixing (FWM) is a nonlinear optical process that has found numerous practical applications, including: optical processing [1–3]; nonlinear imaging [4, 5]; real-time holography and phase-conjugate optics [6–8]; phase-sensitive amplification [9, 10]; and entangled photon pair production [11, ...
... Four wave mixing (FWM) is a nonlinear optical process that has found numerous practical applications, including: optical processing [1–3]; nonlinear imaging [4, 5]; real-time holography and phase-conjugate optics [6–8]; phase-sensitive amplification [9, 10]; and entangled photon pair production [11, ...
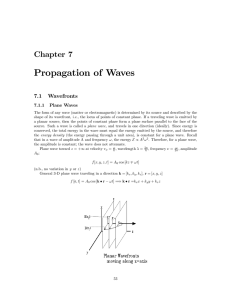
07 Propagation of Waves
... The spherical wave is the basic wave for light propagation using Huygens’ principle. In 1678, Christiaan Huygens theorized a model for light propagation that claimed that each point on a propagating wavefront (regardless of “shape”) could be assumed to be a source of a new spherical wave. The sum of ...
... The spherical wave is the basic wave for light propagation using Huygens’ principle. In 1678, Christiaan Huygens theorized a model for light propagation that claimed that each point on a propagating wavefront (regardless of “shape”) could be assumed to be a source of a new spherical wave. The sum of ...
幻灯片 1
... To break the diffraction limit described by Abbe we must go one step further. Diffraction will make a molecule look blurred out. Even so, we have a good idea where the molecule is. If you have many molecules in one small area it will be difficult to locate individual molecules. Chemical compounds ha ...
... To break the diffraction limit described by Abbe we must go one step further. Diffraction will make a molecule look blurred out. Even so, we have a good idea where the molecule is. If you have many molecules in one small area it will be difficult to locate individual molecules. Chemical compounds ha ...
Introduction to Fiber Optics
... The light in a fiber-optic cable travels through the core (hallway) by constantly bouncing from the cladding (mirror-lined walls), a principle called total internal reflection. Because the cladding does not absorb any light from the core, the light wave can travel great distances. However, some of t ...
... The light in a fiber-optic cable travels through the core (hallway) by constantly bouncing from the cladding (mirror-lined walls), a principle called total internal reflection. Because the cladding does not absorb any light from the core, the light wave can travel great distances. However, some of t ...
Electricity & Optics Physics 24100 Lecture 22 – Chapter 31 sec. 1-4,6
... • Quantum Mechanics naturally accounts for both of these effects, not just for light but for all forms of matter. ...
... • Quantum Mechanics naturally accounts for both of these effects, not just for light but for all forms of matter. ...
BPM Blatt 7
... Summary: Optical traps use radiation pressure, a term that refers generally to forces imparted to matter by the absorption, scattering, emission, or reradiation of light (i.e. by photons). The gradient force used by optical tweezers arises from fluctuating electric dipoles that are induced when ligh ...
... Summary: Optical traps use radiation pressure, a term that refers generally to forces imparted to matter by the absorption, scattering, emission, or reradiation of light (i.e. by photons). The gradient force used by optical tweezers arises from fluctuating electric dipoles that are induced when ligh ...
Moed A
... σ(+) optical pumping to |F = 3, mF = 3, ν = n − 2 >, at which point the cycle starts again. Note that the optical pumping only changes the electronic state of the atoms and does not affect the vibrational state. This process may be repeated until the atoms are in the lowest vibrational level. If the ...
... σ(+) optical pumping to |F = 3, mF = 3, ν = n − 2 >, at which point the cycle starts again. Note that the optical pumping only changes the electronic state of the atoms and does not affect the vibrational state. This process may be repeated until the atoms are in the lowest vibrational level. If the ...
EM Waves Summary Sheet File
... Know and explain that Total internal reflection occurs when a ray’s angle of incidence, within a dense material, is greater than the critical angle. (Higher tier only) Know and explain that a ray can be trapped within a long optical fibre if it always strikes the boundary at an angle greater th ...
... Know and explain that Total internal reflection occurs when a ray’s angle of incidence, within a dense material, is greater than the critical angle. (Higher tier only) Know and explain that a ray can be trapped within a long optical fibre if it always strikes the boundary at an angle greater th ...
Light waves Review
... The color that an object appears to be depends on the angle at which visible light is reflected off the object. b) use of additive rather than subtractive colors. c) wavelengths of visible light that reaches your eyes. d) speed with which visible light reaches it. a) ...
... The color that an object appears to be depends on the angle at which visible light is reflected off the object. b) use of additive rather than subtractive colors. c) wavelengths of visible light that reaches your eyes. d) speed with which visible light reaches it. a) ...