HIGH EFFICIENT LIGHT EMITTING DEVICES WITH ADDITIONAL
... The different possibilities of phosphor packaging around the chip are shown in Fig. 2. The best results from our experiments have been obtained in the case of uniform distribution of phosphors in reflector cup (b). In order to improve the color properties of the LED devices and the quantum yield of ...
... The different possibilities of phosphor packaging around the chip are shown in Fig. 2. The best results from our experiments have been obtained in the case of uniform distribution of phosphors in reflector cup (b). In order to improve the color properties of the LED devices and the quantum yield of ...
Sub-100 nm lithography using ultrashort wavelength of surface plasmons
... only excited on the hole array area. The exposure time in this experiment is only 10 s, corresponding to an exposure dose of 80 mJ/ cm2 at the mask. Surprisingly, this is comparable to a typical exposure dose used in conventional lithography with larger features. It implies a strong near-field inten ...
... only excited on the hole array area. The exposure time in this experiment is only 10 s, corresponding to an exposure dose of 80 mJ/ cm2 at the mask. Surprisingly, this is comparable to a typical exposure dose used in conventional lithography with larger features. It implies a strong near-field inten ...
Design and Fabrication of Tb -Doped Silicon Oxy
... emanating from the microdisk edge and focus it onto the entrance slit of a monochromator. The excitation power was about 10 mW, and the spectral resolution of the optical setup was about 0.5 nm. Fig. 4(a) shows the side-PL spectra from a microdisk, together with the calculated WGM resonance peak pos ...
... emanating from the microdisk edge and focus it onto the entrance slit of a monochromator. The excitation power was about 10 mW, and the spectral resolution of the optical setup was about 0.5 nm. Fig. 4(a) shows the side-PL spectra from a microdisk, together with the calculated WGM resonance peak pos ...
CP1: Investigation into the Feasibility of a Three Axis
... being colourless and transparent [12] and results in the need to use dyes to increase contrast. It is often the case that such features, despite being colourless and transparent, do have varying refractive indexes. This produces the reflections and/or changes in optical path length1 required for int ...
... being colourless and transparent [12] and results in the need to use dyes to increase contrast. It is often the case that such features, despite being colourless and transparent, do have varying refractive indexes. This produces the reflections and/or changes in optical path length1 required for int ...
How does a confocal microscope work
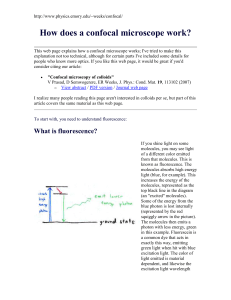
... the wrong directions. This particular style of fluorescence microscopy is known as epi-fluorescence, and uses the microscope objective to illuminate the sample (rather than illuminating the sample from the other side, which would be trans-fluorescence). ...
... the wrong directions. This particular style of fluorescence microscopy is known as epi-fluorescence, and uses the microscope objective to illuminate the sample (rather than illuminating the sample from the other side, which would be trans-fluorescence). ...
Energy gap–refractive index relations in semiconductors – An
... In a theoretical derivation of optical polarizability, Finkenrath [17] described a treatment in the transitions from the valence band to the conduction band. These transitions are represented by differential oscillator densities that occur at distributed resonant frequencies. The combined polarizabil ...
... In a theoretical derivation of optical polarizability, Finkenrath [17] described a treatment in the transitions from the valence band to the conduction band. These transitions are represented by differential oscillator densities that occur at distributed resonant frequencies. The combined polarizabil ...
n - Issaquah Connect
... • The temperature of the microscope stage is set so the RI of the oil is higher than that of the glass sample. • The temperature is then automatically lowered and the contrast between the glass shard and the oil is monitored. The match point (temperature of minimum contrast) is recorded. • This is t ...
... • The temperature of the microscope stage is set so the RI of the oil is higher than that of the glass sample. • The temperature is then automatically lowered and the contrast between the glass shard and the oil is monitored. The match point (temperature of minimum contrast) is recorded. • This is t ...
Chapter 8 Wave Optics
... This phenomenon is quite important. The resolution of many instrument like telescope and microscope depends on this. 8.2.3 The diffraction grating (衍射光栅) Suppose that, instead of a single slit, or two slits side by side in Yong’s experiments, we have a very large number of parallel slits, all of the ...
... This phenomenon is quite important. The resolution of many instrument like telescope and microscope depends on this. 8.2.3 The diffraction grating (衍射光栅) Suppose that, instead of a single slit, or two slits side by side in Yong’s experiments, we have a very large number of parallel slits, all of the ...
Guided Wave Analysis of Hollow Optical Fiber for Mode
... last century. There have been intensive research and development efforts to modify the optical fiber waveguide structures to flexibly control propagation properties such as the chromatic dispersion and its slope, polarization of guided modes, bending mode cutoff within optical communication bands lo ...
... last century. There have been intensive research and development efforts to modify the optical fiber waveguide structures to flexibly control propagation properties such as the chromatic dispersion and its slope, polarization of guided modes, bending mode cutoff within optical communication bands lo ...
Dispersion staining

The optical properties of all liquid and solid materials change as a function of the wavelength of light used to measure them. This change as a function of wavelength is called the dispersion of the optical properties. The graph created by plotting the optical property of interest by the wavelength at which it is measured is called a dispersion curve.The dispersion staining is an analytical technique used in light microscopy that takes advantage of the differences in the dispersion curve of the refractive index of an unknown material relative to a standard material with a known dispersion curve to identify or characterize that unknown material. These differences become manifest as a color when the two dispersion curves intersect for some visible wavelength. This is an optical staining technique and requires no stains or dyes to produce the color. Its primary use today is in the conformation of the presence of asbestos in construction materials but it has many other applications.