Tutorial on Optomechanical Beam Steering Mechanisms
... movements for each degree of freedom of the beam are kept separate. In this tutorial some examples of common optomechanical beam steering elements will be shown and their advantages and disadvantages compared. Additionally a new type of adjustable prism will be described and compared. Spatial light ...
... movements for each degree of freedom of the beam are kept separate. In this tutorial some examples of common optomechanical beam steering elements will be shown and their advantages and disadvantages compared. Additionally a new type of adjustable prism will be described and compared. Spatial light ...
Light scattering models of white blood cells and back
... The classification and detection of the biological cells have a very important application in many fields, such as life science, medical diagnosis, etc. Since the theory of light scattering was used in cell detection, applications of the various optical detection technologies to the study of the com ...
... The classification and detection of the biological cells have a very important application in many fields, such as life science, medical diagnosis, etc. Since the theory of light scattering was used in cell detection, applications of the various optical detection technologies to the study of the com ...
Photonic Devices I Purpose of the Lab
... In forward bias, on the n-type side free electrons are repelled from the contact and pushed towards the junction. On the p-type side holes are repelled from the positively charged contact towards the junction. At the junction electrons will cross from the n-type side to the p-type side and holes wil ...
... In forward bias, on the n-type side free electrons are repelled from the contact and pushed towards the junction. On the p-type side holes are repelled from the positively charged contact towards the junction. At the junction electrons will cross from the n-type side to the p-type side and holes wil ...
2 Pulsed Optics
... pulse has a linear time dependence as described by (2.9); in other words, the instantaneous frequency is time-independent. – For a given spectrum, one pulse envelope can be constructed that has the shortest possible duration. – The shortest constructed pulse can only be transform-limited if its spec ...
... pulse has a linear time dependence as described by (2.9); in other words, the instantaneous frequency is time-independent. – For a given spectrum, one pulse envelope can be constructed that has the shortest possible duration. – The shortest constructed pulse can only be transform-limited if its spec ...
Document
... appear to stand out from the mounting material, whether it is an immersion oil, Canada balsam or another mineral. ...
... appear to stand out from the mounting material, whether it is an immersion oil, Canada balsam or another mineral. ...
Resonant bio- and chemical sensors using low-refractive
... lot of progress during the last 10 years. This is due to the appealing properties of FOS such as immunity to electromagnetic interference, safety in explosive environments, and potential to provide continuous quantitative and qualitative real-time analysis. Chemically sensitive thin films deposited o ...
... lot of progress during the last 10 years. This is due to the appealing properties of FOS such as immunity to electromagnetic interference, safety in explosive environments, and potential to provide continuous quantitative and qualitative real-time analysis. Chemically sensitive thin films deposited o ...
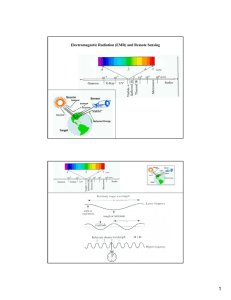
Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) and Remote Sensing
... by Rayleigh scattering. Rayleigh scattering can be called small particle scattering. In visible light, blue wavelength at 0.4 m is scattered 5 times as the red wavelength at 0.6 m. This explains why the clear sky appears blue. The scattering made blue light reach our eyes from all parts of the sky ...
... by Rayleigh scattering. Rayleigh scattering can be called small particle scattering. In visible light, blue wavelength at 0.4 m is scattered 5 times as the red wavelength at 0.6 m. This explains why the clear sky appears blue. The scattering made blue light reach our eyes from all parts of the sky ...
Dispersion staining

The optical properties of all liquid and solid materials change as a function of the wavelength of light used to measure them. This change as a function of wavelength is called the dispersion of the optical properties. The graph created by plotting the optical property of interest by the wavelength at which it is measured is called a dispersion curve.The dispersion staining is an analytical technique used in light microscopy that takes advantage of the differences in the dispersion curve of the refractive index of an unknown material relative to a standard material with a known dispersion curve to identify or characterize that unknown material. These differences become manifest as a color when the two dispersion curves intersect for some visible wavelength. This is an optical staining technique and requires no stains or dyes to produce the color. Its primary use today is in the conformation of the presence of asbestos in construction materials but it has many other applications.