Optics Ic
... Also align the green LED and the 1000 line/inch metal foil sample, and align the camera, placed at the end of the rail opposite the mirror. 3) For our first experiments, mount the LED near the end of the track by the mirror. Place the small mounted screen about 30 cm down the track from the LED. Pl ...
... Also align the green LED and the 1000 line/inch metal foil sample, and align the camera, placed at the end of the rail opposite the mirror. 3) For our first experiments, mount the LED near the end of the track by the mirror. Place the small mounted screen about 30 cm down the track from the LED. Pl ...
Plane Mirrors
... explains why the passenger side mirrors of cars, which are convex mirrors, display objects that look smaller than they are: the brain considers the diverging rays to have come from an image behind the mirror itself. ...
... explains why the passenger side mirrors of cars, which are convex mirrors, display objects that look smaller than they are: the brain considers the diverging rays to have come from an image behind the mirror itself. ...
ray optics and optical instruments
... spectrum (wavelength of about 400 nm to 750 nm) is called light. It is mainly through light and the sense of vision that we know and interpret the world around us. There are two things that we can intuitively mention about light from common experience. First, that it travels with enormous speed and ...
... spectrum (wavelength of about 400 nm to 750 nm) is called light. It is mainly through light and the sense of vision that we know and interpret the world around us. There are two things that we can intuitively mention about light from common experience. First, that it travels with enormous speed and ...
Lec02 - nptel
... propagation of what are called as phase-fronts of light as shown in figure 2.4. Phasefronts are nothing but constant phase surfaces in which the phase difference between any two points is zero. In reality they represent the spatial nature of propagation of a wave and hence are also called as wave-fr ...
... propagation of what are called as phase-fronts of light as shown in figure 2.4. Phasefronts are nothing but constant phase surfaces in which the phase difference between any two points is zero. In reality they represent the spatial nature of propagation of a wave and hence are also called as wave-fr ...
What is light? For the purposes of this class, light will refer to visible
... substance to another, the rays bend (change direction) depending on the wavelength (color) of light. In a rainbow white sunlight enters a raindrop and is broken into different colors heading in slightly different directions. The light is then reflected (and magnified) off the back of the raindrop an ...
... substance to another, the rays bend (change direction) depending on the wavelength (color) of light. In a rainbow white sunlight enters a raindrop and is broken into different colors heading in slightly different directions. The light is then reflected (and magnified) off the back of the raindrop an ...
Precision High Numerical Aperture Scanning System for
... Femtosecond laser micromachining has been developed for writing custom 3D refractive index modifications into ophthalmic hydrogels [1]. These results can be applied to the development of custom contact lenses, or customizing the refractive corrections in Intraocular lenses (IOLs). Recently, a design ...
... Femtosecond laser micromachining has been developed for writing custom 3D refractive index modifications into ophthalmic hydrogels [1]. These results can be applied to the development of custom contact lenses, or customizing the refractive corrections in Intraocular lenses (IOLs). Recently, a design ...
Слайд 1 - Eventry
... This method includes inverse adding-doubling (IAD) method developed by Prahl et al (Prahl S.A., et al. // Appl. Opt., 1993, Vol. 32(4), P. 559-568) and inverse Monte Carlo simulations. The IAD method is widely used in tissue optics for processing the experimental data of spectrophotometry with integ ...
... This method includes inverse adding-doubling (IAD) method developed by Prahl et al (Prahl S.A., et al. // Appl. Opt., 1993, Vol. 32(4), P. 559-568) and inverse Monte Carlo simulations. The IAD method is widely used in tissue optics for processing the experimental data of spectrophotometry with integ ...
Powerpoint template for scientific posters (Swarthmore College)
... Fade margin takes into consideration the characteristics of the FSO system (total transmitted power, total receiver aperture area, receiver sensitivity, coupling losses) and the enviroment where the link is to be deployed (geometric path loss, loss through windowpanes, beam misalignment loss). A sam ...
... Fade margin takes into consideration the characteristics of the FSO system (total transmitted power, total receiver aperture area, receiver sensitivity, coupling losses) and the enviroment where the link is to be deployed (geometric path loss, loss through windowpanes, beam misalignment loss). A sam ...
Materialanalytik Praktikum Ellipsometry B508
... Figure 2: Reflectance R vs. incidence angle ρ for an air-GaAs interface. The reflectance R differs for the two polarizations. The angle characterized by the minimum in reflectance for Rp is called the “Brewster Angle”. 2.3. Principle of Ellipsometry In Fig. 3 the basic principle of ellipsometry is i ...
... Figure 2: Reflectance R vs. incidence angle ρ for an air-GaAs interface. The reflectance R differs for the two polarizations. The angle characterized by the minimum in reflectance for Rp is called the “Brewster Angle”. 2.3. Principle of Ellipsometry In Fig. 3 the basic principle of ellipsometry is i ...
Optical Fibers in Communication
... Also crucial to understanding fibers is the principle of modes. A more in-depth analysis of the propagation of light along an optical fiber requires the light to be treated as an electromagnetic wave (rather that as a ray). ...
... Also crucial to understanding fibers is the principle of modes. A more in-depth analysis of the propagation of light along an optical fiber requires the light to be treated as an electromagnetic wave (rather that as a ray). ...
Document
... provides the basis for defining the optic sign of uniaxial minerals. Optically positive uniaxial minerals n omega < n epsilon (if extrordinary ray is the slow ray, then the mineral is optically positive.) Optically negative uniaxial minerals n omega > nepsilon (if extraordinary ray is the fast r ...
... provides the basis for defining the optic sign of uniaxial minerals. Optically positive uniaxial minerals n omega < n epsilon (if extrordinary ray is the slow ray, then the mineral is optically positive.) Optically negative uniaxial minerals n omega > nepsilon (if extraordinary ray is the fast r ...
lecture 5 infrared spectrometry
... FOURIER TRANSFORM INFRARED SPECTROMETER A photodiode array can measure an entire spectrum at once. The spectrum is spread into its component wavelength and each wavelength is directed onto one detector element. ...
... FOURIER TRANSFORM INFRARED SPECTROMETER A photodiode array can measure an entire spectrum at once. The spectrum is spread into its component wavelength and each wavelength is directed onto one detector element. ...
Modal and Material Dispersion
... in the refractive indices would change the phase difference between these two components & thereby the state of the polarization of the mode. However after certain length referred to as fiber beat length, the modal wave will produce its original state of polarization. This length is simply given by: ...
... in the refractive indices would change the phase difference between these two components & thereby the state of the polarization of the mode. However after certain length referred to as fiber beat length, the modal wave will produce its original state of polarization. This length is simply given by: ...
Presentation PPT
... In order to obtain a complete transfer of the energy from core 0 to the other cores the following condition should take place: ...
... In order to obtain a complete transfer of the energy from core 0 to the other cores the following condition should take place: ...
Slow Light - Duke Physics
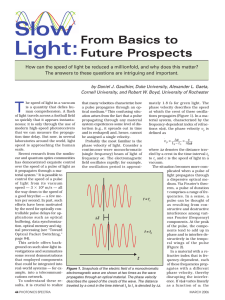
... atoms with a strong absorption resonance is an interesting candidate. The refractive index for such a sample is typically small (n21 ≈ 1023), but it varies rapidly in the region of the resonance so that dn/dω and, hence, ng can be large (Figure 3). As the carrier frequency of a pulse is tuned near t ...
... atoms with a strong absorption resonance is an interesting candidate. The refractive index for such a sample is typically small (n21 ≈ 1023), but it varies rapidly in the region of the resonance so that dn/dω and, hence, ng can be large (Figure 3). As the carrier frequency of a pulse is tuned near t ...