The Equation of Number the Total Internal of Reflection Angles
... aperture allows light to propagate down the fiber in rays both close to the axis and at various angles, allowing efficient coupling of light into the fiber .However, this high numerical aperture increases the amount of dispersion as rays at different angles have different path length and therefore t ...
... aperture allows light to propagate down the fiber in rays both close to the axis and at various angles, allowing efficient coupling of light into the fiber .However, this high numerical aperture increases the amount of dispersion as rays at different angles have different path length and therefore t ...
Basic Physical Optics
... in reality, if you were to examine such image points with a microscope, you would see structure in the “point,” a structure explained only when you invoke the true wave nature of light. In effect, then, we are saying that, with large objects such as prisms, mirrors, and lenses—large in the sense tha ...
... in reality, if you were to examine such image points with a microscope, you would see structure in the “point,” a structure explained only when you invoke the true wave nature of light. In effect, then, we are saying that, with large objects such as prisms, mirrors, and lenses—large in the sense tha ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... switching is facilitated by complex spatiotemporal dynamics. We find that the output pulse contains two distinct peaks only at transitional power levels within the sharp switching region, whereas the pulse has conventional shape below and above the switching threshold; see Figs. 3(b) and 3(c). Note ...
... switching is facilitated by complex spatiotemporal dynamics. We find that the output pulse contains two distinct peaks only at transitional power levels within the sharp switching region, whereas the pulse has conventional shape below and above the switching threshold; see Figs. 3(b) and 3(c). Note ...
Optical Fibers
... silica glass fiber is shown in Figure 7. It is clear that dips in a near 1.3 and 1.55um provide “windows” in the attenuation, which can be exploited to reduce the degradation of signals. The overall decrease in attenuation with increasing wavelength is due to the reduced scattering from small random ...
... silica glass fiber is shown in Figure 7. It is clear that dips in a near 1.3 and 1.55um provide “windows” in the attenuation, which can be exploited to reduce the degradation of signals. The overall decrease in attenuation with increasing wavelength is due to the reduced scattering from small random ...
12. confocal microscopy.
... illumination light is focused down to a small spot at the sample plane, while the detector records the light originating from the same spot, hence the name confocal. This method has been described in detail in many references [Wilson-Sheppard, ??]. In the following we describe the basic principles o ...
... illumination light is focused down to a small spot at the sample plane, while the detector records the light originating from the same spot, hence the name confocal. This method has been described in detail in many references [Wilson-Sheppard, ??]. In the following we describe the basic principles o ...
[pdf]
... Equations (9) and (10) are the basic equations of our paper. They are derived using the diffusion approximation to photon transport and without any other approximations. Eq. (9) is an intro-differential equation for the photon density wave and involves only the absorption and transport scattering c ...
... Equations (9) and (10) are the basic equations of our paper. They are derived using the diffusion approximation to photon transport and without any other approximations. Eq. (9) is an intro-differential equation for the photon density wave and involves only the absorption and transport scattering c ...
Module P6.4 Optical instruments
... In elementary discussions of optical systems it is usually assumed that the system is ‘ideal’. By this we mean: o that lenses and mirrors have perfectly formed spherical surfaces, o that all objects lie very close to the optical axis, o that all rays involved make small angles to this axis (i.e. are ...
... In elementary discussions of optical systems it is usually assumed that the system is ‘ideal’. By this we mean: o that lenses and mirrors have perfectly formed spherical surfaces, o that all objects lie very close to the optical axis, o that all rays involved make small angles to this axis (i.e. are ...
Evaluation and application of spatial light modulators for
... different grey values. In this way, the projection pattern can be adapted by local variation of the line frequency, the pattern type, and the intensity until the best possible evaluation is achieved. An important feature of the panel is also the high contrast (>0,9). In contrast to DMD that have a h ...
... different grey values. In this way, the projection pattern can be adapted by local variation of the line frequency, the pattern type, and the intensity until the best possible evaluation is achieved. An important feature of the panel is also the high contrast (>0,9). In contrast to DMD that have a h ...
Plasmonic orbital angular momentum manipulation through
... Surface plasmon polaritons (SPP) are electromagnetic surface modes trapped at metal/dielectric interface because of their strong interaction with free electrons of the metal [1]. The most attractive characteristics of SPP are high localization and remarkable field enhancement in nature, allowing th ...
... Surface plasmon polaritons (SPP) are electromagnetic surface modes trapped at metal/dielectric interface because of their strong interaction with free electrons of the metal [1]. The most attractive characteristics of SPP are high localization and remarkable field enhancement in nature, allowing th ...
Novel technique for thermal lens measurement in commonly used
... by the second-order Laguerre-Gauss mode LG10 using the basis given by the cavity eigenmodes [11]. When the waist position of the input beam has a small axial displacement δ z with respect to the fundamental mode of the resonator and its size differs from the waist size of the cavity eigenmode by a ...
... by the second-order Laguerre-Gauss mode LG10 using the basis given by the cavity eigenmodes [11]. When the waist position of the input beam has a small axial displacement δ z with respect to the fundamental mode of the resonator and its size differs from the waist size of the cavity eigenmode by a ...
Optics of Gaussian Beams
... apparent cylindrical symmetry both in construction and excitation geometry generate transverse mode with Cartesian rather than radial symmetry? The answer is that this usually results because there is indeed some feature of laser construction or method of excitation that removes an apparent equivale ...
... apparent cylindrical symmetry both in construction and excitation geometry generate transverse mode with Cartesian rather than radial symmetry? The answer is that this usually results because there is indeed some feature of laser construction or method of excitation that removes an apparent equivale ...
Accelerating Light Beams along Arbitrary Convex
... point which is exactly on the curve, Eq. (6) has only one solution, which is the ray tangent to the curve at that point. For a point above the curve, Eq. (6) has no solution at all, since there are no rays which are tangent to a convex curve and cross it at the same time. The configuration of critic ...
... point which is exactly on the curve, Eq. (6) has only one solution, which is the ray tangent to the curve at that point. For a point above the curve, Eq. (6) has no solution at all, since there are no rays which are tangent to a convex curve and cross it at the same time. The configuration of critic ...
Simultaneous calibration of optical tweezers spring constant and
... may be considerable variability in the axial position of the particle with respect to the tweezers center which affects the lateral calibration coefficients and which can only be minimized by sufficient averaging. This situation was remedied by Vermeulen et al. [8] who acquired the detector response ...
... may be considerable variability in the axial position of the particle with respect to the tweezers center which affects the lateral calibration coefficients and which can only be minimized by sufficient averaging. This situation was remedied by Vermeulen et al. [8] who acquired the detector response ...
Temporal coherence characteristics of a superluminescent
... important role in the optical coherence tomography system [2,3]. High output power and large optical bandwidth are key features for the SLD, and the extremely high optical gain in SLD active region may result in very high optical power sensitivity to external optical feedback [4]. Thus, once stimula ...
... important role in the optical coherence tomography system [2,3]. High output power and large optical bandwidth are key features for the SLD, and the extremely high optical gain in SLD active region may result in very high optical power sensitivity to external optical feedback [4]. Thus, once stimula ...
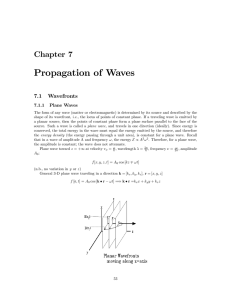
07 Propagation of Waves
... Christiaan Huygens theorized a model for light propagation that claimed that each point on a propagating wavefront (regardless of “shape”) could be assumed to be a source of a new spherical wave. The sum of these secondary spherical “wavelets” produced the subsequent wavefronts. Huygens’ principle h ...
... Christiaan Huygens theorized a model for light propagation that claimed that each point on a propagating wavefront (regardless of “shape”) could be assumed to be a source of a new spherical wave. The sum of these secondary spherical “wavelets” produced the subsequent wavefronts. Huygens’ principle h ...
Mimicking the colourful wing scale structure of the
... Figure 3 | An artificial optical mimic. a, b, SEM images of concavities which are covered by a conformal multilayer stack of 11 alternating layers of titania and alumina: a top view, 2 µm, b cross-section, 1 µm. c, At perpendicular light incidence the artificial replica appears green, while it, d, r ...
... Figure 3 | An artificial optical mimic. a, b, SEM images of concavities which are covered by a conformal multilayer stack of 11 alternating layers of titania and alumina: a top view, 2 µm, b cross-section, 1 µm. c, At perpendicular light incidence the artificial replica appears green, while it, d, r ...
measuring
... given by the luminosity function. The eye has different responses as a function of wavelength when it is adapted to light conditions (photopic vision) and dark conditions (scotopic vision). Photometry is based on the eye's photopic response, and so photometric measurements will not accurately indica ...
... given by the luminosity function. The eye has different responses as a function of wavelength when it is adapted to light conditions (photopic vision) and dark conditions (scotopic vision). Photometry is based on the eye's photopic response, and so photometric measurements will not accurately indica ...
Slide 1
... The OSA must have a very narrow passband and steep skirts A filter stopband should be ≥ 50 dB down to measure the smaller sidelobes. Question What determines the value of the stopband? OSAs do not have sufficient resolution to look at the detailed structure of a laser longitudinal mode ...
... The OSA must have a very narrow passband and steep skirts A filter stopband should be ≥ 50 dB down to measure the smaller sidelobes. Question What determines the value of the stopband? OSAs do not have sufficient resolution to look at the detailed structure of a laser longitudinal mode ...
Blind Optical Aberration Correction by Exploring
... requirement of using special devices limits their application range, especially for consumer applications. Given the limitations of hardware solutions, computationally removing optical aberration has attracted strong interests and has been exensively studied in the past decade [3–5, 12, 13]. However ...
... requirement of using special devices limits their application range, especially for consumer applications. Given the limitations of hardware solutions, computationally removing optical aberration has attracted strong interests and has been exensively studied in the past decade [3–5, 12, 13]. However ...





![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008852300_1-d148ed6e0d5b01d695ad45eecc203c0e-300x300.png)
![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008852277_1-2045a3551aa6b77e10f6e1bfc991b19e-300x300.png)