Optical losses
... The term launching loss refers to an optical fiber not being able to propagate all the incoming light rays from an optical source. These occur during the process of coupling light into the fiber (e.g., losses at the interface stages). Rays launched outside the angle of acceptance excite only dissipa ...
... The term launching loss refers to an optical fiber not being able to propagate all the incoming light rays from an optical source. These occur during the process of coupling light into the fiber (e.g., losses at the interface stages). Rays launched outside the angle of acceptance excite only dissipa ...
Mach Zehnder Interferometer and its Applications
... the core produce an interference pattern thus producing a very effective in-line MZI. This MZI has the same physical path length in both sensing and reference arms but has different optical path lengths because of modal dispersion as the beam passing through cladding experiences refractive index whi ...
... the core produce an interference pattern thus producing a very effective in-line MZI. This MZI has the same physical path length in both sensing and reference arms but has different optical path lengths because of modal dispersion as the beam passing through cladding experiences refractive index whi ...
EXPERIMENT 8. Monolayer Characterization: Contact angles
... significant amount of light reaches the back side Figure 4. Model used to calculate the thickness of the gold due to its large absorption of a thin organic layer using ellipsometry. coefficient.) Conversely, if we measure tan ψ and ∆, we can in principle calculate two of the parameters in the model, ...
... significant amount of light reaches the back side Figure 4. Model used to calculate the thickness of the gold due to its large absorption of a thin organic layer using ellipsometry. coefficient.) Conversely, if we measure tan ψ and ∆, we can in principle calculate two of the parameters in the model, ...
1.5 MB
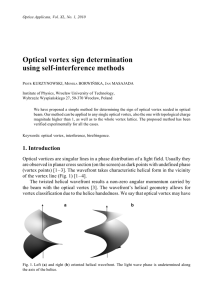
... line the positive and negative vortices can be observed while intersecting with the plane Σ. Here the single well defined singular line can be observed as carrying both the positive and negative topological charges. For the monochromatic waves propagating in a well defined direction the topological ...
... line the positive and negative vortices can be observed while intersecting with the plane Σ. Here the single well defined singular line can be observed as carrying both the positive and negative topological charges. For the monochromatic waves propagating in a well defined direction the topological ...
Noncollinear parametric amplification in the near
... operating at the wavelength of 800 nm [12]. However, to extend the tunability of ultrafast sources, it is common to rely on nonlinear optics for broadband frequency conversion. Methods based on third-order nonlinearities, that allow mixing processes in bulk materials [13] or in highly-nonlinear [14] ...
... operating at the wavelength of 800 nm [12]. However, to extend the tunability of ultrafast sources, it is common to rely on nonlinear optics for broadband frequency conversion. Methods based on third-order nonlinearities, that allow mixing processes in bulk materials [13] or in highly-nonlinear [14] ...
Effect of the refractive index change kinetics of
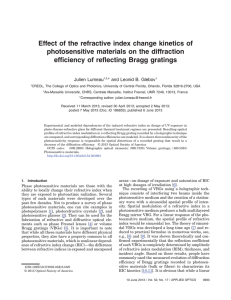
... One of the most promising photosensitive materials for the recording of high-efficiency robust diffractive optical elements is photo-thermo-refractive (PTR) glass [3]. Such material is a multicomponent silicate glass that exhibits RIC after successive UV exposure and thermal treatment at temperature ...
... One of the most promising photosensitive materials for the recording of high-efficiency robust diffractive optical elements is photo-thermo-refractive (PTR) glass [3]. Such material is a multicomponent silicate glass that exhibits RIC after successive UV exposure and thermal treatment at temperature ...
Aalborg Universitet Compact dipole nanoantenna coupler to plasmonic slot waveguide Andrei
... posted January 27, 2012 (Doc. ID 158936); published March 15, 2012 ...
... posted January 27, 2012 (Doc. ID 158936); published March 15, 2012 ...
Design Considerations and Performance Comparison of High-Order Modulation Formats using OFDM
... bitrates vary between 10 Gbit/s (4-QAM) and 30 Gbit/s (64-QAM). A. Peak-to-Average Power Ratio (PAPR) An OFDM signal consists of a number of independently modulated subcarriers, which can give a large PAPR when added up coherently [7]. As a result, the DAC, ADC, amplifiers and optical modulators lik ...
... bitrates vary between 10 Gbit/s (4-QAM) and 30 Gbit/s (64-QAM). A. Peak-to-Average Power Ratio (PAPR) An OFDM signal consists of a number of independently modulated subcarriers, which can give a large PAPR when added up coherently [7]. As a result, the DAC, ADC, amplifiers and optical modulators lik ...
Digital holography of total internal reflection
... In digital holography [1], the holographic interference pattern is optically generated by the superposition of object and reference waves. But, instead of a photographic plate, the hologram is digitally sampled by a CCD camera and transferred to a computer as an array of numbers. The propagation of ...
... In digital holography [1], the holographic interference pattern is optically generated by the superposition of object and reference waves. But, instead of a photographic plate, the hologram is digitally sampled by a CCD camera and transferred to a computer as an array of numbers. The propagation of ...
Shifting the spherical focus of a 4Pi focusing system
... radially polarized field: an annular intensity distribution with intensity minimum in the center, i.e., both are still fields with radial polarization. In fact, it can be verified that the modulation function has a constant modulus, suggesting that modulation does not change the intensity distributi ...
... radially polarized field: an annular intensity distribution with intensity minimum in the center, i.e., both are still fields with radial polarization. In fact, it can be verified that the modulation function has a constant modulus, suggesting that modulation does not change the intensity distributi ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... [20,21]. Figure 3(c) shows an example of a measured concave mirror surface which is integrated with gradient data in Fig. 3(a) and (b). 3. Method of dynamic 3D sensing for specular reflective surface For measuring dynamic specular scenes, one of the major problems is how to calculate the pattern poi ...
... [20,21]. Figure 3(c) shows an example of a measured concave mirror surface which is integrated with gradient data in Fig. 3(a) and (b). 3. Method of dynamic 3D sensing for specular reflective surface For measuring dynamic specular scenes, one of the major problems is how to calculate the pattern poi ...
A simple method for Bragg diffraction in volume holographic gratings Heifetz,
... A rigorous analysis of volume holographic gratings involves the coupled-wave theory,17–20 which is derived from Maxwell’s equations. Instructors often do not discuss volume holography in undergraduate optics courses because of the difficulty of communicating coupled-wave theory. In this paper, we sh ...
... A rigorous analysis of volume holographic gratings involves the coupled-wave theory,17–20 which is derived from Maxwell’s equations. Instructors often do not discuss volume holography in undergraduate optics courses because of the difficulty of communicating coupled-wave theory. In this paper, we sh ...
Wave Optics
... For each point in the upper half of the opening, in the direction , there is a point in the lower half that interferes destructively with it. A dark fringe occurs in this direction. Condition for dark fringes: ...
... For each point in the upper half of the opening, in the direction , there is a point in the lower half that interferes destructively with it. A dark fringe occurs in this direction. Condition for dark fringes: ...
Wave Optics
... For each point in the upper half of the opening, in the direction , there is a point in the lower half that interferes destructively with it. A dark fringe occurs in this direction. Condition for dark fringes: ...
... For each point in the upper half of the opening, in the direction , there is a point in the lower half that interferes destructively with it. A dark fringe occurs in this direction. Condition for dark fringes: ...
Proceedings Template
... aberrations, as well as providing opportunities for light to be lost due to absorption, scattering and misalignment. Also, properties of the scanning process can cause the color segments to change size as they travel over the modulator resulting in an overscan condition where areas outside the modul ...
... aberrations, as well as providing opportunities for light to be lost due to absorption, scattering and misalignment. Also, properties of the scanning process can cause the color segments to change size as they travel over the modulator resulting in an overscan condition where areas outside the modul ...
Isolated object invisibility cloak in the visible light
... S3 coincide with k0 and S0, respectively. Due to the symmetric pattern and the reciprocal principle, the ray will propagate through the remaining part of the cloak and appear at the background medium without any deviation. The hidden object is therefore invisible to this ray. Now let’s see what we ...
... S3 coincide with k0 and S0, respectively. Due to the symmetric pattern and the reciprocal principle, the ray will propagate through the remaining part of the cloak and appear at the background medium without any deviation. The hidden object is therefore invisible to this ray. Now let’s see what we ...
Module P6.3 Optical elements: prisms, lenses and spherical mirrors
... You will probably be familiar with the action of a prism in splitting white light into the colours of the rainbow, or of a simple magnifying lens, or of the curved reflectors used in vanity mirrors, shaving mirrors and driving mirrors. This module describes these optical elements and introduces you ...
... You will probably be familiar with the action of a prism in splitting white light into the colours of the rainbow, or of a simple magnifying lens, or of the curved reflectors used in vanity mirrors, shaving mirrors and driving mirrors. This module describes these optical elements and introduces you ...