R - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... • learn the definition of a Gaussian surface • learn how to count the net number of field lines passing into a Gaussian surface • learn Gauss’s Law of Electricity • learn about volume, surface, and linear charge ...
... • learn the definition of a Gaussian surface • learn how to count the net number of field lines passing into a Gaussian surface • learn Gauss’s Law of Electricity • learn about volume, surface, and linear charge ...
Physics 212
... “Because the two charges are positive, they repel (or go in opposite direction). Because the charges are from one atom to another, the sizes of the force go on opposite end.” “Due to the newton's third law, the forces acting on these two objects should be equal.” “When multiplying, the order of the ...
... “Because the two charges are positive, they repel (or go in opposite direction). Because the charges are from one atom to another, the sizes of the force go on opposite end.” “Due to the newton's third law, the forces acting on these two objects should be equal.” “When multiplying, the order of the ...
Demagnetisation of Permanent Magnets in Electrical Machines
... AlNiCo-materials are low temperature coefficients and very high Curie temperature [2]. However, a really low intrinsic coercivity (JHc) of AlNiComaterials restricts the use of these materials in many applications. AlNiCo-materials show highly nonlinear behaviour in the second quadrant of BH-plane, w ...
... AlNiCo-materials are low temperature coefficients and very high Curie temperature [2]. However, a really low intrinsic coercivity (JHc) of AlNiComaterials restricts the use of these materials in many applications. AlNiCo-materials show highly nonlinear behaviour in the second quadrant of BH-plane, w ...
ESD Systems` ESD Technical Newsletter
... separated. This is a charge separation or an IMBALANCE between quantities of positive and negative particles. During contact electrification, it is usually only the negative electrons, which are moved. As negative particles are pulled away from the positive particles, equal and opposite areas of imb ...
... separated. This is a charge separation or an IMBALANCE between quantities of positive and negative particles. During contact electrification, it is usually only the negative electrons, which are moved. As negative particles are pulled away from the positive particles, equal and opposite areas of imb ...
Physics STPM - Chung Hua Middle School STPM Community
... - Is there a difference in the net flux through the cube between the two situations? ...
... - Is there a difference in the net flux through the cube between the two situations? ...
f. Physics notes 2 (DOC).
... Figure 14: The equipotential surfaces (dashed lines) and the electric field-lines (solid lines) of a positive point charge. In Sect. 4.3, we found that the electric field immediately above the surface of a conductor is directed perpendicular to that surface. Thus, it is clear that the surface of a c ...
... Figure 14: The equipotential surfaces (dashed lines) and the electric field-lines (solid lines) of a positive point charge. In Sect. 4.3, we found that the electric field immediately above the surface of a conductor is directed perpendicular to that surface. Thus, it is clear that the surface of a c ...
Chapter 24
... the surface if (a) the charge is doubled, (b) the volume of the cube is doubled, (c) the surface is changed to a sphere, (d) the charge is moved to another location inside the surface, and (e) the charge is moved outside the surface. 7. A person is placed in a large, hollow, metallic sphere that is ...
... the surface if (a) the charge is doubled, (b) the volume of the cube is doubled, (c) the surface is changed to a sphere, (d) the charge is moved to another location inside the surface, and (e) the charge is moved outside the surface. 7. A person is placed in a large, hollow, metallic sphere that is ...
Ch. 24 Capacitance
... • An air-filled parallel-plate capacitor has a plate area of 2.0 cm2 and a plate separation of 1.00 mm. – Find its capacitance. – If a potential difference of 100 V is applied across the plates, what is • The charge on each plate and • The electric field between the plates? ...
... • An air-filled parallel-plate capacitor has a plate area of 2.0 cm2 and a plate separation of 1.00 mm. – Find its capacitance. – If a potential difference of 100 V is applied across the plates, what is • The charge on each plate and • The electric field between the plates? ...
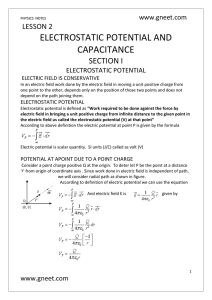
electrostatic potential and capacitance
... Thus in the case of metallic conductor, placed in an external electric field (1) A steady electric charge distribution is induced on the surface of the conductor (2) The net electric field inside the conductor is zero (3) The net electric charge inside the conductor is zero (4) On the outer surface ...
... Thus in the case of metallic conductor, placed in an external electric field (1) A steady electric charge distribution is induced on the surface of the conductor (2) The net electric field inside the conductor is zero (3) The net electric charge inside the conductor is zero (4) On the outer surface ...
CHAPTER 18 ELECTRIC FORCES AND ELECTRIC FIELDS
... the rod, and the sphere is left with a positive charge. If the rod were removed first, followed by the grounding wire, the sphere would not be left with a charge. Once the rod is removed, the repulsive force caused by the presence of the rubber rod is no longer present. Since the wire is still attac ...
... the rod, and the sphere is left with a positive charge. If the rod were removed first, followed by the grounding wire, the sphere would not be left with a charge. Once the rod is removed, the repulsive force caused by the presence of the rubber rod is no longer present. Since the wire is still attac ...
The Electric Field
... Here’s how electric field lines are related to the field: The electric field vector E is tangent to the field lines. The number of lines per unit area through a surface perpendicular to the lines is proportional to the electric field strength in that region The field lines begin on positive c ...
... Here’s how electric field lines are related to the field: The electric field vector E is tangent to the field lines. The number of lines per unit area through a surface perpendicular to the lines is proportional to the electric field strength in that region The field lines begin on positive c ...
The Two Kinds of Electric Charge
... which a neutral body is attracted to a charged body. This situation is resolved if we consider gravity to be negative electric charge, and that hence there are no neutral bodies. This might explain the electrostatic force that acts on so-called neutral objects. However, terrestrial objects cannot sh ...
... which a neutral body is attracted to a charged body. This situation is resolved if we consider gravity to be negative electric charge, and that hence there are no neutral bodies. This might explain the electrostatic force that acts on so-called neutral objects. However, terrestrial objects cannot sh ...
Document
... 13. What the charge on the wall? (A) positive (B) negative 14. What is F3? (A) 3 N (B) 4 N (C) 5 N 15. What is F1? (A) 3 N (B) 4 N (C) 5 N 16. What is F2? (A) 3 N (B) 4 N (C) 5 N Questions 22-25 The electric field strength is E at point p, which is r distance way from sphere A with charge +Q. +Q •p ...
... 13. What the charge on the wall? (A) positive (B) negative 14. What is F3? (A) 3 N (B) 4 N (C) 5 N 15. What is F1? (A) 3 N (B) 4 N (C) 5 N 16. What is F2? (A) 3 N (B) 4 N (C) 5 N Questions 22-25 The electric field strength is E at point p, which is r distance way from sphere A with charge +Q. +Q •p ...
Electrostatic generator

An electrostatic generator, or electrostatic machine, is an electromechanical generator that produces static electricity, or electricity at high voltage and low continuous current. The knowledge of static electricity dates back to the earliest civilizations, but for millennia it remained merely an interesting and mystifying phenomenon, without a theory to explain its behavior and often confused with magnetism. By the end of the 17th Century, researchers had developed practical means of generating electricity by friction, but the development of electrostatic machines did not begin in earnest until the 18th century, when they became fundamental instruments in the studies about the new science of electricity. Electrostatic generators operate by using manual (or other) power to transform mechanical work into electric energy. Electrostatic generators develop electrostatic charges of opposite signs rendered to two conductors, using only electric forces, and work by using moving plates, drums, or belts to carry electric charge to a high potential electrode. The charge is generated by one of two methods: either the triboelectric effect (friction) or electrostatic induction.