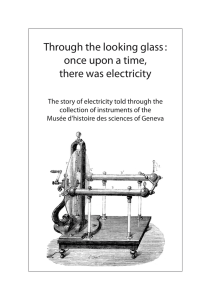
A Boundary-Element approach to Transient Simulation of Three-Dimensional Integrated Circuit Interconnect
... that at such time scales, the assumed constitutive relations between J and E are not likely to still apply, so (refeq:qdecay) should only be used as an indicator of longer time behavior. From (4), it follows that any initial charge in the interior of a conductor must rapidly decay, and this volume c ...
... that at such time scales, the assumed constitutive relations between J and E are not likely to still apply, so (refeq:qdecay) should only be used as an indicator of longer time behavior. From (4), it follows that any initial charge in the interior of a conductor must rapidly decay, and this volume c ...
ElEctricity
... with the rubbed sides facing each other. Because both balloons have the same charge they will swing away from, or repel, one another. Rubbing, or friction, does not create static electricity; it merely separates negative and positive charges and transfers them onto different bodies, or onto differen ...
... with the rubbed sides facing each other. Because both balloons have the same charge they will swing away from, or repel, one another. Rubbing, or friction, does not create static electricity; it merely separates negative and positive charges and transfers them onto different bodies, or onto differen ...
Clase 10 (´05)-Efecto corona
... Corona & Gap Discharges • Corona is an electrical discharge (i.e. partial breakdown of air insulation) occurring in the high electric field region, generally in the vicinity of conducting surfaces, but sometimes also near insulating surfaces, due to ionization processes in air. Resulta de procesos ...
... Corona & Gap Discharges • Corona is an electrical discharge (i.e. partial breakdown of air insulation) occurring in the high electric field region, generally in the vicinity of conducting surfaces, but sometimes also near insulating surfaces, due to ionization processes in air. Resulta de procesos ...
Charge conserving FEM-PIC schemes on general grids
... In this work we aim at bridging this gap and propose a unified formulation for curl-conforming finite elements (the so-called edge elements) coupled with particle schemes. This allows us to derive a general roadmap for the design of charge conserving FEM-PIC schemes of arbitrary order both in time a ...
... In this work we aim at bridging this gap and propose a unified formulation for curl-conforming finite elements (the so-called edge elements) coupled with particle schemes. This allows us to derive a general roadmap for the design of charge conserving FEM-PIC schemes of arbitrary order both in time a ...
Electric Forces and Fields
... individual hairs becomes charged the same way (either all positive or all negative, depending on what you rubbed on your hair), and the individual strands repel each other. Their repulsion makes them want to maximize the distance between them, which is achieved by standing on end, radiating outward. ...
... individual hairs becomes charged the same way (either all positive or all negative, depending on what you rubbed on your hair), and the individual strands repel each other. Their repulsion makes them want to maximize the distance between them, which is achieved by standing on end, radiating outward. ...
Magnetism and Electricity
... Atoms have negatively charged electrons that spin around a nucleus of positively charged protons and neutrons. Charges fill space with an electric field. Static electricity is associated with the gain or loss of electrons. Electromagnetic forces can attract or repel. Opposite charges attract each ot ...
... Atoms have negatively charged electrons that spin around a nucleus of positively charged protons and neutrons. Charges fill space with an electric field. Static electricity is associated with the gain or loss of electrons. Electromagnetic forces can attract or repel. Opposite charges attract each ot ...
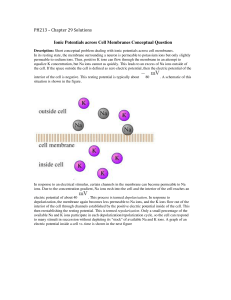
How Can Electricity Cause Magnetism?
... forth is a result of oscillating electricity. Electricity can either flow all in one direction (called DC or Direct Current electricity) or it can move back and forth (called AC or alternating current.) The doorbell hammer vibrates back and forth because of AC electricity. Vibrating electricity and ...
... forth is a result of oscillating electricity. Electricity can either flow all in one direction (called DC or Direct Current electricity) or it can move back and forth (called AC or alternating current.) The doorbell hammer vibrates back and forth because of AC electricity. Vibrating electricity and ...
Lesson 2 Flux and Gauss`s Law Charles Augustine de Coulomb
... Even though, as you saw in problem 2 of Practice Exercise 2-2, Gauss’s law generally does not yield simple solutions for the local field due to arrangement of point charges, it is a useful tool for analyzing the fields that arise from certain simple continuous charge distributions. Such distribution ...
... Even though, as you saw in problem 2 of Practice Exercise 2-2, Gauss’s law generally does not yield simple solutions for the local field due to arrangement of point charges, it is a useful tool for analyzing the fields that arise from certain simple continuous charge distributions. Such distribution ...
Static electricity
.jpg?width=300)
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it is able to move away by means of an electric current or electrical discharge. Static electricity is named in contrast with current electricity, which flows through wires or other conductors and transmits energy.A static electric charge is created whenever two surfaces contact and separate, and at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electric current (and is therefore an electrical insulator). The effects of static electricity are familiar to most people because people can feel, hear, and even see the spark as the excess charge is neutralized when brought close to a large electrical conductor (for example, a path to ground), or a region with an excess charge of the opposite polarity (positive or negative). The familiar phenomenon of a static shock–more specifically, an electrostatic discharge–is caused by the neutralization of charge.