PHY481 - Lecture 5: Electrostatics
... electric field line is a series of vectors where at each point the vector points in the direction of the force on a unit ~ The charge at that point and it has a length equal to the magnitude of the force. ie. we plot the vector function E. properties of electric field lines constructed in this way a ...
... electric field line is a series of vectors where at each point the vector points in the direction of the force on a unit ~ The charge at that point and it has a length equal to the magnitude of the force. ie. we plot the vector function E. properties of electric field lines constructed in this way a ...
Name Class Date Review for Electricity and Magnetism Test Units
... c. Increase the current in the wire. _______ 10. All magnetism is created by: a. Natural magnets. b. Movement of charges. c. Current–carrying wires. _______ 11. Which of the following will experience a force in a magnetic field? a. A magnet. b. A stationary charge. c. A moving charge. d. A and C. ...
... c. Increase the current in the wire. _______ 10. All magnetism is created by: a. Natural magnets. b. Movement of charges. c. Current–carrying wires. _______ 11. Which of the following will experience a force in a magnetic field? a. A magnet. b. A stationary charge. c. A moving charge. d. A and C. ...
Lesson 2 – Building Electromagnets
... through the coil, it will produce a strong magnetic field. The magnetic field will produce one "pole" at each end of the rod. This phenomenon is known as electromagnetism. 7. Use the magnetic compass to identify the "North" and "South" poles of the electromagnet. 8. [5 minutes] With the electromagne ...
... through the coil, it will produce a strong magnetic field. The magnetic field will produce one "pole" at each end of the rod. This phenomenon is known as electromagnetism. 7. Use the magnetic compass to identify the "North" and "South" poles of the electromagnet. 8. [5 minutes] With the electromagne ...
the electric force of a current: weber and the surface charge of
... square of the drift velocity of conduction electrons. In the past, many authors, including prominent physicists, held incorrect points of view regarding steady currents and some still do in recent years. The problem seems to stem from the fact that the frame of reference is rigidly chosen as an iner ...
... square of the drift velocity of conduction electrons. In the past, many authors, including prominent physicists, held incorrect points of view regarding steady currents and some still do in recent years. The problem seems to stem from the fact that the frame of reference is rigidly chosen as an iner ...
6-5.3 Magnetism and Electricity Support Doc
... producing a magnetic field. The magnet that results loses its magnetism if the electric current stops flowing. Generators A generator produces an electric current when a coil of wire wrapped around an iron core is rotated near a magnet. Generators at power plants produce electric energy for ou ...
... producing a magnetic field. The magnet that results loses its magnetism if the electric current stops flowing. Generators A generator produces an electric current when a coil of wire wrapped around an iron core is rotated near a magnet. Generators at power plants produce electric energy for ou ...
File
... friction and placed in contact with the wall, the wall is polarized. That is, an opposite charge is induced on the wall’s surface, to which the balloons then stick by the force of electrostatic attraction. The electrons on the balloon do not leave the balloon because its material (rubber) is a poor ...
... friction and placed in contact with the wall, the wall is polarized. That is, an opposite charge is induced on the wall’s surface, to which the balloons then stick by the force of electrostatic attraction. The electrons on the balloon do not leave the balloon because its material (rubber) is a poor ...
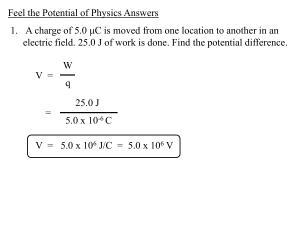
17-1 Electric Potential Energy
... When a system has a negative total energy (including the total kinetic energy, of which there is none in this situation), that is indicative of a bound system. In general, there is a greater degree of attraction in the system than repulsion. Key ideas for electric potential energy: Potential energy ...
... When a system has a negative total energy (including the total kinetic energy, of which there is none in this situation), that is indicative of a bound system. In general, there is a greater degree of attraction in the system than repulsion. Key ideas for electric potential energy: Potential energy ...
Chapter 21 - Interactive Learning Toolkit
... situation involving discrete charges in which the electric field could be defined? • Set up the sum. (Use whiteboard.) • What is an example of a complicated situation involving a continuous charge distribution in which the electric field could ...
... situation involving discrete charges in which the electric field could be defined? • Set up the sum. (Use whiteboard.) • What is an example of a complicated situation involving a continuous charge distribution in which the electric field could ...
Electric Fields
... magnitudes of electric forces between two small charged spheres • The force is inversely proportional to the square of the separation r between the charges and directed along the line joining them • The force is proportional to the product of the charges, q1 and q2, on the two particles • The electr ...
... magnitudes of electric forces between two small charged spheres • The force is inversely proportional to the square of the separation r between the charges and directed along the line joining them • The force is proportional to the product of the charges, q1 and q2, on the two particles • The electr ...
Glossary of Terms
... moving objects (Sliding, rolling, and fluid friction have different impacts on objects.) Fulcrum the point that a lever (or other rotating device) rotates around Function the use or need filled by an ...
... moving objects (Sliding, rolling, and fluid friction have different impacts on objects.) Fulcrum the point that a lever (or other rotating device) rotates around Function the use or need filled by an ...
Static electricity
.jpg?width=300)
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it is able to move away by means of an electric current or electrical discharge. Static electricity is named in contrast with current electricity, which flows through wires or other conductors and transmits energy.A static electric charge is created whenever two surfaces contact and separate, and at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electric current (and is therefore an electrical insulator). The effects of static electricity are familiar to most people because people can feel, hear, and even see the spark as the excess charge is neutralized when brought close to a large electrical conductor (for example, a path to ground), or a region with an excess charge of the opposite polarity (positive or negative). The familiar phenomenon of a static shock–more specifically, an electrostatic discharge–is caused by the neutralization of charge.