Packet #7- Chemical Reactions
... New substances are formed by chemical reactions. When elements react together to form compounds their atoms join to other atoms using chemical bonds. For example, iron and sulfur react together to form a compound called iron sulfide. Compounds usually have different properties from the elements they ...
... New substances are formed by chemical reactions. When elements react together to form compounds their atoms join to other atoms using chemical bonds. For example, iron and sulfur react together to form a compound called iron sulfide. Compounds usually have different properties from the elements they ...
The Chemical Context of Life by Dr. Ty C.M. Hoffman
... A second kind of chemical bond forms when electrons are shared by two atoms rather than being completely transferred from one atom to the other. When a pair of electrons (one from each of two a ...
... A second kind of chemical bond forms when electrons are shared by two atoms rather than being completely transferred from one atom to the other. When a pair of electrons (one from each of two a ...
An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be chemically
... atoms. Atoms of the same element have the same mass, but atoms of different elements have different masses. • Chemical combination of elements to make different substances occurs when atoms join together in small whole-number ratios. • Chemical reactions only rearrange the way that atoms are combine ...
... atoms. Atoms of the same element have the same mass, but atoms of different elements have different masses. • Chemical combination of elements to make different substances occurs when atoms join together in small whole-number ratios. • Chemical reactions only rearrange the way that atoms are combine ...
AP Chemistry
... o balance O, by adding H2O o balance H, by adding H+ o balance charge, by adding e multiple half-reactions to equalize electrons ...
... o balance O, by adding H2O o balance H, by adding H+ o balance charge, by adding e multiple half-reactions to equalize electrons ...
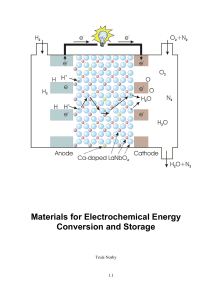
Materials for Electrochemical Energy Conversion and Storage
... Electrochemistry deals with the relation between chemical reactions and electrical phenomena – mainly potential and current of electrons. It is important for a large part of the metallurgical industry in which electrical energy is used to produce metals by electrolysis. Moreover, it is important for ...
... Electrochemistry deals with the relation between chemical reactions and electrical phenomena – mainly potential and current of electrons. It is important for a large part of the metallurgical industry in which electrical energy is used to produce metals by electrolysis. Moreover, it is important for ...
Redox
... Oxidation states only represent true charges on atoms in ionic compounds. In covalent compounds, they represent an effective charge. Assigning oxidation states allows us to keep track of electrons in chemical reactions This is essential in order to ensure that the conservation of charge is maintai ...
... Oxidation states only represent true charges on atoms in ionic compounds. In covalent compounds, they represent an effective charge. Assigning oxidation states allows us to keep track of electrons in chemical reactions This is essential in order to ensure that the conservation of charge is maintai ...
File - chemistryattweed
... The salt ions, Na+ and Cl-, are called spectator ions because they don't actually react. These ions are floating around separately in the base and acid solutions before mixing and are floating around in the neutralisation mixture after mixing. If the salt solution formed is evaporated, the salt ions ...
... The salt ions, Na+ and Cl-, are called spectator ions because they don't actually react. These ions are floating around separately in the base and acid solutions before mixing and are floating around in the neutralisation mixture after mixing. If the salt solution formed is evaporated, the salt ions ...
Enzymes - WordPress.com
... needed to start a chemical reaction is called the activation energy. A CATALYST is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction by reducing the amount of energy needed to start that reaction. This is called lowering the activation energy. Activation energy can be thought of as a hill that must be ...
... needed to start a chemical reaction is called the activation energy. A CATALYST is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction by reducing the amount of energy needed to start that reaction. This is called lowering the activation energy. Activation energy can be thought of as a hill that must be ...
Oxidation And Degradation Products Of Common Oxygen Scavengers
... For many years, sulfite and hydrazine were the principal materials used to protect boiler systems from oxygen attack. When hydrazine became listed as a suspected carcinogen, a search began for a replacement. During the search it became apparent that strong reducing agents (oxygen scavengers) should ...
... For many years, sulfite and hydrazine were the principal materials used to protect boiler systems from oxygen attack. When hydrazine became listed as a suspected carcinogen, a search began for a replacement. During the search it became apparent that strong reducing agents (oxygen scavengers) should ...
GCSE - WordPress.com
... 4. Explain the following in terms of bonding and structure ideas :. (i) Silicon dioxide and carbon dioxide both contain covalent bonds but the former melts at 1700oC whereas the latter is a gas at 0oC. (ii) Sodium oxide, carbon dioxide and silicon dioxide are all poor conductors of electricity ...
... 4. Explain the following in terms of bonding and structure ideas :. (i) Silicon dioxide and carbon dioxide both contain covalent bonds but the former melts at 1700oC whereas the latter is a gas at 0oC. (ii) Sodium oxide, carbon dioxide and silicon dioxide are all poor conductors of electricity ...
kinetic characterisation of catalysts for methanol synthesis
... In summary, the results show that the proposed rate Equation (4) describes the influence of process conditions very well, so it can be used to compare the activity of the four investigated catalysts at selected temperatures, pressures and gas composition in the range of their values studied in this ...
... In summary, the results show that the proposed rate Equation (4) describes the influence of process conditions very well, so it can be used to compare the activity of the four investigated catalysts at selected temperatures, pressures and gas composition in the range of their values studied in this ...
Homework Booklet [4,S]
... 4. Explain the following in terms of bonding and structure ideas :. (i) Silicon dioxide and carbon dioxide both contain covalent bonds but the former melts at 1700oC whereas the latter is a gas at 0oC. (ii) Sodium oxide, carbon dioxide and silicon dioxide are all poor conductors of electricity ...
... 4. Explain the following in terms of bonding and structure ideas :. (i) Silicon dioxide and carbon dioxide both contain covalent bonds but the former melts at 1700oC whereas the latter is a gas at 0oC. (ii) Sodium oxide, carbon dioxide and silicon dioxide are all poor conductors of electricity ...
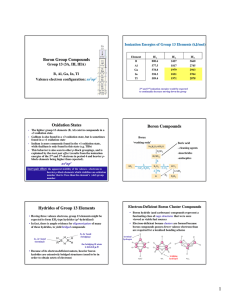
Boron Group Compounds Oxidation States Boron
... • Boron trihalides are monomeric under ordinary conditions • Studies on the thermodynamics of formation of boron ...
... • Boron trihalides are monomeric under ordinary conditions • Studies on the thermodynamics of formation of boron ...
An Introduction to Redox
... For monatomic ions, such as Mg2+, O2‐ the ON = the ion charge The sum of ON values for atoms in a molecule or formula unit = 0 ...
... For monatomic ions, such as Mg2+, O2‐ the ON = the ion charge The sum of ON values for atoms in a molecule or formula unit = 0 ...
6CH02 - MPPE
... 10 There would be a major peak in the mass spectrum for butan-1-ol, CH3CH2CH2CH2OH, but not for butan-2-ol, CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3, at m/e value A ...
... 10 There would be a major peak in the mass spectrum for butan-1-ol, CH3CH2CH2CH2OH, but not for butan-2-ol, CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3, at m/e value A ...
153KB PDF - Clydeview Academy
... (a) Suggest why the positive carbon electrodes need to be replaced regularly. ...
... (a) Suggest why the positive carbon electrodes need to be replaced regularly. ...
Complete the following equations
... The concentration of Mg2+ in seawater is about 0.055 M. (a) How many liters of seawater will produce 1.00 kg of magnesium. (b) How many kilograms of calcium oxide, CaO, must be added to the seawater sample of part (a) in order to precipitate all of Mg2+ as magnesium hydroxide. (c) Write a balanced e ...
... The concentration of Mg2+ in seawater is about 0.055 M. (a) How many liters of seawater will produce 1.00 kg of magnesium. (b) How many kilograms of calcium oxide, CaO, must be added to the seawater sample of part (a) in order to precipitate all of Mg2+ as magnesium hydroxide. (c) Write a balanced e ...
Theoretical problems (official version)
... Much of the photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts – organelles found in plant cells and containing chlorophyll – the light-absorbing substance. Hill isolated chloroplasts from the cells by grinding the leaves in the sucrose solutions. The cell-free chloroplasts did not produce oxygen under illu ...
... Much of the photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts – organelles found in plant cells and containing chlorophyll – the light-absorbing substance. Hill isolated chloroplasts from the cells by grinding the leaves in the sucrose solutions. The cell-free chloroplasts did not produce oxygen under illu ...
+ H 2 O(l)
... AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl (aq) AgCl (s) + NaNO3 (aq) HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) NH4Cl (aq) + NaOH (aq) NH3 (g) + H2O (l) + NaCl (aq) Blue color for the products represents the driving force which allows the chemical reaction to occur. ...
... AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl (aq) AgCl (s) + NaNO3 (aq) HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) NH4Cl (aq) + NaOH (aq) NH3 (g) + H2O (l) + NaCl (aq) Blue color for the products represents the driving force which allows the chemical reaction to occur. ...
Exercises to the Textbook “Physical Chemistry from
... A steel spring like for example the one in the picture on the right has a spring stiffness D of the order of 105 N m−1. a) How much energy W1 is needed to stretch the spring 10 cm from its unstretched length l0? b) How much energy W2 is needed to stretch the spring from 50 cm to 60 cm? c) A person w ...
... A steel spring like for example the one in the picture on the right has a spring stiffness D of the order of 105 N m−1. a) How much energy W1 is needed to stretch the spring 10 cm from its unstretched length l0? b) How much energy W2 is needed to stretch the spring from 50 cm to 60 cm? c) A person w ...
AQA_GCSE_Chemistry_Higher_Unit_2_Notes
... The important examples are diamond (C), graphite (C) and silicon dioxide (SiO2). The lastmentioned is the base for the structure of many rocks, such as flint or granite. Giant Metallic Structures The atoms in metals are in layers which can slide over each other, this makes it possible to bend them o ...
... The important examples are diamond (C), graphite (C) and silicon dioxide (SiO2). The lastmentioned is the base for the structure of many rocks, such as flint or granite. Giant Metallic Structures The atoms in metals are in layers which can slide over each other, this makes it possible to bend them o ...
Redox Balancing Worksheet
... The oxidation number of any pure element is zero. Thus the oxidation number of H in H2 is zero. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to its charge. Thus the oxidation number of Cl in the Clion is -1, that for Mg in the Mg+2 ion is +2, and that for oxygen in O2- ion is -2. The sum of the ...
... The oxidation number of any pure element is zero. Thus the oxidation number of H in H2 is zero. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to its charge. Thus the oxidation number of Cl in the Clion is -1, that for Mg in the Mg+2 ion is +2, and that for oxygen in O2- ion is -2. The sum of the ...
Artificial photosynthesis

Artificial photosynthesis is a chemical process that replicates the natural process of photosynthesis, a process that converts sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates and oxygen. The term is commonly used to refer to any scheme for capturing and storing the energy from sunlight in the chemical bonds of a fuel (a solar fuel). Photocatalytic water splitting converts water into Hydrogen Ions and oxygen, and is a main research area in artificial photosynthesis. Light-driven carbon dioxide reduction is another studied process, replicating natural carbon fixation.Research developed in this field encompasses design and assembly of devices (and their components) for the direct production of solar fuels, photoelectrochemistry and its application in fuel cells, and engineering of enzymes and photoautotrophic microorganisms for microbial biofuel and biohydrogen production from sunlight. Many, if not most, of the artificial approaches are bio-inspired, i.e., they rely on biomimetics.









![Homework Booklet [4,S]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010355871_1-63c750e3d1b58eaaebbb3f5d45651c44-300x300.png)