Human Anatomy and Physiology II Lab
... Anatomical Position of the Heart • What organs or tissues are around the heart? ...
... Anatomical Position of the Heart • What organs or tissues are around the heart? ...
Pathophysiologic consideration in patients with congenital
... Compression of lung parenchyma by enlarged heart and vessels . Pulmonary hypertension . ...
... Compression of lung parenchyma by enlarged heart and vessels . Pulmonary hypertension . ...
With right → left shunt
... Ventricular Septal Defect occurs in the interventricular septum, and is more frequent in males that females. ...
... Ventricular Septal Defect occurs in the interventricular septum, and is more frequent in males that females. ...
Cardiovascular System The Heart
... each other. Ventricles – the two lower chambers of the heart. All blood vessels leaving the heart begin in the ventricles. Interventricular septum – separates the two ventricles from each other Apex – lower tip of the heart http://www.bostonscientific.com/templatedata/imports/HTML/CRM/heart/hear t_c ...
... each other. Ventricles – the two lower chambers of the heart. All blood vessels leaving the heart begin in the ventricles. Interventricular septum – separates the two ventricles from each other Apex – lower tip of the heart http://www.bostonscientific.com/templatedata/imports/HTML/CRM/heart/hear t_c ...
Print - Circulation
... To the Editor: I feel that Dr. Greenwald's strong comments published in May 1974 issue of Circulation directed to Dr. McLaurin's paper of September 1973 are unjustified. Dr. Greenwald has done a disservice to the many excellent papers based on polaroid echocardiograms. While there is no doubt that s ...
... To the Editor: I feel that Dr. Greenwald's strong comments published in May 1974 issue of Circulation directed to Dr. McLaurin's paper of September 1973 are unjustified. Dr. Greenwald has done a disservice to the many excellent papers based on polaroid echocardiograms. While there is no doubt that s ...
Cardiovascular system
... •The heart has its own blood transport system •within which are the coronary arteries and cardiac veins • It relies on aerobic respiration for energy production • It needs a constant supply of oxygenated blood. • Its metabolic requirements are exceeded only by the brain ...
... •The heart has its own blood transport system •within which are the coronary arteries and cardiac veins • It relies on aerobic respiration for energy production • It needs a constant supply of oxygenated blood. • Its metabolic requirements are exceeded only by the brain ...
The Cardiovascular System
... Subject is seated and relaxed. Wrap the fabric cuff around the upper arm Locate the brachial artery Place the diaphragm of the stethoscope over the brachial artery so that you can hear Kortokoff ...
... Subject is seated and relaxed. Wrap the fabric cuff around the upper arm Locate the brachial artery Place the diaphragm of the stethoscope over the brachial artery so that you can hear Kortokoff ...
I. THE HEART
... a. Atria (atrium = singular) _Upper__ chambers of the heart that _receive__ blood. b. Ventricles - _Lower____ chambers of the heart that _pump____ blood. 2. Valves – Flaps of tissue that keep blood flowing _in one direction_______ to increase pumping efficiency of the heart; prevent _backwash_______ ...
... a. Atria (atrium = singular) _Upper__ chambers of the heart that _receive__ blood. b. Ventricles - _Lower____ chambers of the heart that _pump____ blood. 2. Valves – Flaps of tissue that keep blood flowing _in one direction_______ to increase pumping efficiency of the heart; prevent _backwash_______ ...
Sheep Heart Dissection Lab
... preservative as possible. Also run water into the larger blood vessels to force any blood clots out of the heart chambers. 2. Place the heart in a dissecting tray with its anterior surface up (See Figure 36.4 below). Proceed as follows: a. Locate the visceral pericardium, which appears as a thin, tr ...
... preservative as possible. Also run water into the larger blood vessels to force any blood clots out of the heart chambers. 2. Place the heart in a dissecting tray with its anterior surface up (See Figure 36.4 below). Proceed as follows: a. Locate the visceral pericardium, which appears as a thin, tr ...
Mammalian Heart Interior Anatomy Diagram
... Label the heart anatomy diagram below using the heart glossary on the back. Note: On the diagram, the right side of the heart appears on the left side of the picture (and vice versa) because you are looking at the heart from the front. ...
... Label the heart anatomy diagram below using the heart glossary on the back. Note: On the diagram, the right side of the heart appears on the left side of the picture (and vice versa) because you are looking at the heart from the front. ...
Pulmonary Atresia
... occurs when the pulmonary valve, located between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery, is not formed properly. The pulmonary valve has three leaflets that function like a one-way door, allowing blood to flow forward into the pulmonary artery, but not backward into the right ventricle. With pulmo ...
... occurs when the pulmonary valve, located between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery, is not formed properly. The pulmonary valve has three leaflets that function like a one-way door, allowing blood to flow forward into the pulmonary artery, but not backward into the right ventricle. With pulmo ...
142e926d30b7e6bb1fc54138a557531e
... diuretics), is usually low in the elderly C ✘ Secondary hypertension is most commonly detected in young subjects with resistant hypertension D ✔The risk of heart failure can be reduced by 30–40% E ✘ The risk of stroke is reduced by ~33% and MI by 25% 1.10 A ✘ Persistent, symptomatic second or third ...
... diuretics), is usually low in the elderly C ✘ Secondary hypertension is most commonly detected in young subjects with resistant hypertension D ✔The risk of heart failure can be reduced by 30–40% E ✘ The risk of stroke is reduced by ~33% and MI by 25% 1.10 A ✘ Persistent, symptomatic second or third ...
PigHeartDissection
... Pick these up (even if you are not cutting): Plastic apron Goggles Latex Gloves These should be at your table: Dissecting Tray Dissecting Kit Paper Towel Dissection Guide ...
... Pick these up (even if you are not cutting): Plastic apron Goggles Latex Gloves These should be at your table: Dissecting Tray Dissecting Kit Paper Towel Dissection Guide ...
Congenitally corrected transposition of the great
... Congenitally corrected transposition of the great vessels (CCTGV) characterized by atrioventricular (AV) and ventriculoarterial discordance is a rare congenital anomaly which accounts for about 1% of all congenital heart disease cases (1). Only 1% of these patients are without other congenital anoma ...
... Congenitally corrected transposition of the great vessels (CCTGV) characterized by atrioventricular (AV) and ventriculoarterial discordance is a rare congenital anomaly which accounts for about 1% of all congenital heart disease cases (1). Only 1% of these patients are without other congenital anoma ...
Animal Anatomy and Physiology Review
... E. The primary function of the large intestines is the absorption of usable material. F. The function of the liver is to produce bile. G. The correct or of the human digestive organs is mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestines, large intestines, anus. H. Unlike food and water, the two important g ...
... E. The primary function of the large intestines is the absorption of usable material. F. The function of the liver is to produce bile. G. The correct or of the human digestive organs is mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestines, large intestines, anus. H. Unlike food and water, the two important g ...
Cong HD Patho Samia 1 of 2
... Compression of lung parenchyma by enlarged heart and vessels . Pulmonary hypertension . ...
... Compression of lung parenchyma by enlarged heart and vessels . Pulmonary hypertension . ...
Cardiac Cycle - Mahtomedi Middle School
... If you squeeze the heart, this ventricle will feel squishier The _____________ is the muscle that runs up and down in the center of the heart. ...
... If you squeeze the heart, this ventricle will feel squishier The _____________ is the muscle that runs up and down in the center of the heart. ...
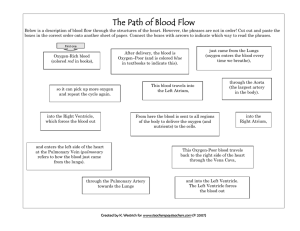
The Path of Blood Flow
... Below is a description of blood flow through the structures of the heart. However, the phrases are not in order! Cut out and paste the boxes in the correct order onto another sheet of paper. Connect the boxes with arrows to indicate which way to read the phrases. ...
... Below is a description of blood flow through the structures of the heart. However, the phrases are not in order! Cut out and paste the boxes in the correct order onto another sheet of paper. Connect the boxes with arrows to indicate which way to read the phrases. ...
After atrial excitation, impulse travels through the AV node
... volume, and ventricular systole includes both isovolumetric contraction and ventricular ejection. The ventricle does not empty completely during ejection, which is normally half diastole blood volume is pumped out. ...
... volume, and ventricular systole includes both isovolumetric contraction and ventricular ejection. The ventricle does not empty completely during ejection, which is normally half diastole blood volume is pumped out. ...
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
... the PDA to the systemic circulation. 4. The balance of pulmonary blood flow is dependent on the respective pulmonary and systemic resistance and the size of the PDA. 5. Coronary blood flow is provided by retrograde filling of the aorta through the PDA. B. Hypoplastic left heart syndrome with restric ...
... the PDA to the systemic circulation. 4. The balance of pulmonary blood flow is dependent on the respective pulmonary and systemic resistance and the size of the PDA. 5. Coronary blood flow is provided by retrograde filling of the aorta through the PDA. B. Hypoplastic left heart syndrome with restric ...
Chapter 11: The Cardiovascular System
... suddenly partake in physical exercise, then the increased demands of such vigorous exercise on your body are met primarily by? a- increased stroke volume b- increased heart rate c- increased blood volume d- all of a, b and c above are correct e- only b and c above are correct ...
... suddenly partake in physical exercise, then the increased demands of such vigorous exercise on your body are met primarily by? a- increased stroke volume b- increased heart rate c- increased blood volume d- all of a, b and c above are correct e- only b and c above are correct ...
heart and circulation sdg
... • Particularly with restrictive ASD and/or closure of the ductus arrteriosus Minimal or no murmur Physical Examination ...
... • Particularly with restrictive ASD and/or closure of the ductus arrteriosus Minimal or no murmur Physical Examination ...
Note - American Heart Association
... Underdevelopment of a ventricle can compromise blood flow to the body in some cases and the lungs in other cases. Without early intervention many patients die in infancy. In a small number of patients, the type of single ventricle results in a balanced circulation between the body and lungs, and sur ...
... Underdevelopment of a ventricle can compromise blood flow to the body in some cases and the lungs in other cases. Without early intervention many patients die in infancy. In a small number of patients, the type of single ventricle results in a balanced circulation between the body and lungs, and sur ...
Lecture_05_The mostly spread congenital heart diseases in
... • This extra blood may cause a volume overload of both the right atrium and the right ventricle. • Ultimately the RV must push out more blood than the LV due to the L-to-R shunt. This condition can result in eventually RV-failure (dilatation and decreased systolic function) and Pulm Htn. ...
... • This extra blood may cause a volume overload of both the right atrium and the right ventricle. • Ultimately the RV must push out more blood than the LV due to the L-to-R shunt. This condition can result in eventually RV-failure (dilatation and decreased systolic function) and Pulm Htn. ...
Slide 1
... wall stress which is determined by laplace law =(pressure*radius)/(2*wall thickness) • Most coronary flow occurs during diastole therefore diastolic pressure is the major pressure driving the coronary circulation ...
... wall stress which is determined by laplace law =(pressure*radius)/(2*wall thickness) • Most coronary flow occurs during diastole therefore diastolic pressure is the major pressure driving the coronary circulation ...
Atrial septal defect

Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria (upper chambers) of the heart. Normally, the atria are separated by a dividing wall, the interatrial septum. If this septum is defective or absent, then oxygen-rich blood can flow directly from the left side of the heart to mix with the oxygen-poor blood in the right side of the heart, or vice versa. This can lead to lower-than-normal oxygen levels in the arterial blood that supplies the brain, organs, and tissues. However, an ASD may not produce noticeable signs or symptoms, especially if the defect is small.A ""shunt"" is the presence of a net flow of blood through the defect, either from left to right or right to left. The amount of shunting present, if any, determines the hemodynamic significance of the ASD. A ""right-to-left-shunt"" typically poses the more dangerous scenario.During development of the fetus, the interatrial septum develops to separate the left and right atria. However, a hole in the septum called the foramen ovale, allows blood from the right atrium to enter the left atrium during fetal development. This opening allows blood to bypass the nonfunctional fetal lungs while the fetus obtains its oxygen from the placenta. A layer of tissue called the septum primum acts as a valve over the foramen ovale during fetal development. After birth, the pressure in the right side of the heart drops as the lungs open and begin working, causing the foramen ovale to close entirely. In approximately 25% of adults, the foramen ovale does not entirely seal. In these cases, any elevation of the pressure in the pulmonary circulatory system (due to pulmonary hypertension, temporarily while coughing, etc.) can cause the foramen ovale to remain open. This is known as a patent foramen ovale (PFO), which is a type of atrial septal defect.