Refractive Index Measurement within a Photonic Crystal Fibre Based on Short Wavelength Diffraction
... Solid-core photonic crystal fibres are often described by an analogous effective step index fibre. The effective core and cladding can be highly sensitive to the extent of the modal field into the cladding. As a consequence of the high core-cladding index contrast the contribution to modal propagati ...
... Solid-core photonic crystal fibres are often described by an analogous effective step index fibre. The effective core and cladding can be highly sensitive to the extent of the modal field into the cladding. As a consequence of the high core-cladding index contrast the contribution to modal propagati ...
Band gap characterization and slow light effects in
... The various symbols are defined in Fig. 1. In addition, we have assumed air (n C = 1) as top cladding. At λ = 1.55 μ m, the slot waveguide has a monomodal behavior with one quasi-TE and one quasi-TM modes. The quasi-TE mode shows an enhancement of the field in the slot region (slot mode), and has an ...
... The various symbols are defined in Fig. 1. In addition, we have assumed air (n C = 1) as top cladding. At λ = 1.55 μ m, the slot waveguide has a monomodal behavior with one quasi-TE and one quasi-TM modes. The quasi-TE mode shows an enhancement of the field in the slot region (slot mode), and has an ...
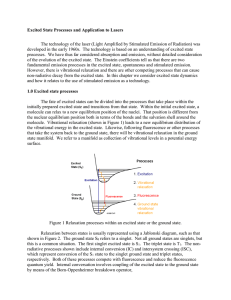
Excited State Processes and Application to Lasers The technology
... neodymium lasers, Nd:YAG and Nd:YLF, transition metal lasers, ruby and alexandrite, and the workhorse of modern laser technology, Ti:sapphire (titanium sapphire). 4.1 Argon ion and Krypton ion lasers The principle of operation of the noble gas ions laser involves creation of high energy ions in an e ...
... neodymium lasers, Nd:YAG and Nd:YLF, transition metal lasers, ruby and alexandrite, and the workhorse of modern laser technology, Ti:sapphire (titanium sapphire). 4.1 Argon ion and Krypton ion lasers The principle of operation of the noble gas ions laser involves creation of high energy ions in an e ...
Student Study Guide
... and consist of a positively charged nucleus of protons and neutrons orbited by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. Heat, light, and electricity are among the things that can excite atoms. Once excited, the atom’s electrons absorb energy and briefly move from their normal orbit level to one slig ...
... and consist of a positively charged nucleus of protons and neutrons orbited by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. Heat, light, and electricity are among the things that can excite atoms. Once excited, the atom’s electrons absorb energy and briefly move from their normal orbit level to one slig ...
Aalborg Universitet Near-field electrospinning of dielectric-loaded surface plasmon polariton waveguides
... plasmons. Various waveguiding structures for surface plasmons, fabricated with different techniques, such as metal stripes [3–5] and v-grooves [6,7] have already been investigated. The strong lateral confinement can be also achieved by depositing polymer stripes on a metal surface and using them as ...
... plasmons. Various waveguiding structures for surface plasmons, fabricated with different techniques, such as metal stripes [3–5] and v-grooves [6,7] have already been investigated. The strong lateral confinement can be also achieved by depositing polymer stripes on a metal surface and using them as ...
Fabry-Perot Interferometer
... where c denotes the vacuum velocity of light and the equality δν = c/(2d) holds for plane mirrors. ∆ν is usually defined as the full width (FWHM) of the resonance. The finesse F also indicates the effective number of interfering beams within the cavity. Since all light rays slightly diverge from the ...
... where c denotes the vacuum velocity of light and the equality δν = c/(2d) holds for plane mirrors. ∆ν is usually defined as the full width (FWHM) of the resonance. The finesse F also indicates the effective number of interfering beams within the cavity. Since all light rays slightly diverge from the ...
V.90-3-James H. Cole, Clay Kirkendall, Anthony Dandridge, Gary
... complex due to the required number of compensating interferometers. The importance of this multiplexing technique is that it forms the basis for the last multiplexing approach shown, time/coherence multiplexing17. In this case, each sensor interferometer has the same path length delay but a relative ...
... complex due to the required number of compensating interferometers. The importance of this multiplexing technique is that it forms the basis for the last multiplexing approach shown, time/coherence multiplexing17. In this case, each sensor interferometer has the same path length delay but a relative ...
Diffraction
... Figure 1.1. There, it is seen that the wave trains, which have been diffracted at the same angle with respect to the optical axis, a path difference of ∆ is exhibited. So some wave trains need to travel a greater distance than others. From the above discussion, the importance of the phase should be ...
... Figure 1.1. There, it is seen that the wave trains, which have been diffracted at the same angle with respect to the optical axis, a path difference of ∆ is exhibited. So some wave trains need to travel a greater distance than others. From the above discussion, the importance of the phase should be ...
Diffraction limited resolution - X-ray and Observational Astronomy
... • Unfortunately, the resolution of ground-based telescopes does not improve without limit as the mirror size increases • This is due to the turbulent nature of the Earth’s atmosphere • Local changes in atmospheric T and density over small distances create regions where the light is refracted in rand ...
... • Unfortunately, the resolution of ground-based telescopes does not improve without limit as the mirror size increases • This is due to the turbulent nature of the Earth’s atmosphere • Local changes in atmospheric T and density over small distances create regions where the light is refracted in rand ...
supporting material
... measurements are used, but actually increases this parameter. Similar increases in SNR could only be observed in COP images after low-pass filtering, which suppressed noise by smoothing pixel transitions, but also rendered a less accurate image. In contrast, PEDS retains high resolution photon posit ...
... measurements are used, but actually increases this parameter. Similar increases in SNR could only be observed in COP images after low-pass filtering, which suppressed noise by smoothing pixel transitions, but also rendered a less accurate image. In contrast, PEDS retains high resolution photon posit ...
Wavelength Converters in Optical Communication Systems
... wavelength to another without entering the electrical domain. A simple technique for the realization of this function is the use of cross gain modulation (XGM) in semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOA’s). The principle is depicted in Fig. 3.4.1(a)[9] [11] showing an intensity modulated input signal ...
... wavelength to another without entering the electrical domain. A simple technique for the realization of this function is the use of cross gain modulation (XGM) in semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOA’s). The principle is depicted in Fig. 3.4.1(a)[9] [11] showing an intensity modulated input signal ...
Versatile two-dimensional potentials for ultra
... the dipole potential, and the trap depth varied about the the torus (although the variation was less than the chemical potential of the BEC.) For a careful study of superfluidity it is desirable for the toroidal trap to have a constant potential depth about the entire ring, with fluctuations much sm ...
... the dipole potential, and the trap depth varied about the the torus (although the variation was less than the chemical potential of the BEC.) For a careful study of superfluidity it is desirable for the toroidal trap to have a constant potential depth about the entire ring, with fluctuations much sm ...
Experiment VI Polarized Light
... - Safety Note: Block the laser beam using the near-laser beam blocker, except when you are performing parts of your experiment that require the laser beam. 3. In this experiment one needs the light source to be a randomly polarized beam. But, the laser output is nearly 100% polarized. We solved this ...
... - Safety Note: Block the laser beam using the near-laser beam blocker, except when you are performing parts of your experiment that require the laser beam. 3. In this experiment one needs the light source to be a randomly polarized beam. But, the laser output is nearly 100% polarized. We solved this ...
Standards for Reporting the Aberrations of the Eye
... eye, the coordinate origin is at the center of the eye's entrance pupil, the +x axis is horizontal pointing to the right, the +y axis is vertical pointing up, and the +z Cartesian axis points out of the eye and coincides with the foveal line-of-sight in object space, as defined by a chief ray emitte ...
... eye, the coordinate origin is at the center of the eye's entrance pupil, the +x axis is horizontal pointing to the right, the +y axis is vertical pointing up, and the +z Cartesian axis points out of the eye and coincides with the foveal line-of-sight in object space, as defined by a chief ray emitte ...
Green's function formulation for third-harmonic generation microscopy
... With the Green’s function model we are able to investigate THG from interfaces of different orientations. Figure 4 shows that THG signals can arise from an interface perpendicular or parallel to the optical axis. Interestingly, the THG signal is dependent on the polarization direction of the excitat ...
... With the Green’s function model we are able to investigate THG from interfaces of different orientations. Figure 4 shows that THG signals can arise from an interface perpendicular or parallel to the optical axis. Interestingly, the THG signal is dependent on the polarization direction of the excitat ...
Plasmon-Induced Transparency in Metamaterials *
... shapes while maintaining consistent optical properties that do not depend on the dimensions of the device. They can be designed for applications in either free space optics or an integrated optical circuit and, in particular, for slow light and enhanced nonlinear effects [19,20]. Additionally, it is ...
... shapes while maintaining consistent optical properties that do not depend on the dimensions of the device. They can be designed for applications in either free space optics or an integrated optical circuit and, in particular, for slow light and enhanced nonlinear effects [19,20]. Additionally, it is ...
A new approach to sum frequency generation of single
... spectral region are available in the red, green and blue. The output power from single-mode visible diode lasers is limited to about 100 mW and these lasers tend to operate in multiple longitudinal modes. Higher output power is possible using broad area diode lasers but at the expense of a decrease ...
... spectral region are available in the red, green and blue. The output power from single-mode visible diode lasers is limited to about 100 mW and these lasers tend to operate in multiple longitudinal modes. Higher output power is possible using broad area diode lasers but at the expense of a decrease ...
Light Magic – Optics and Vision - New England Board of Higher
... 1. To separate the light into its basic colors, you could use a prism (difficult!) or a diffraction grating 2. Recycling: use a CD with the label stripped off! (This is a type of diffraction grating.) 3. To block out other nearby light sources, use a short cardboard tube. 4. To separate the colors s ...
... 1. To separate the light into its basic colors, you could use a prism (difficult!) or a diffraction grating 2. Recycling: use a CD with the label stripped off! (This is a type of diffraction grating.) 3. To block out other nearby light sources, use a short cardboard tube. 4. To separate the colors s ...
full text pdf
... valuable basic information about optical properties of that structure, valuable for diverse applications. The near−field's complicated pattern contains both, the components able to propagate and components confined to the surface and damped outside. Our study refers to the near−field imaging techniq ...
... valuable basic information about optical properties of that structure, valuable for diverse applications. The near−field's complicated pattern contains both, the components able to propagate and components confined to the surface and damped outside. Our study refers to the near−field imaging techniq ...
Matter-wave interferometry: towards antimatter interferometers
... average only over the source dimension xs , assuming a uniform probability density p(xs ) = σs−1 χ[−σs /2,σs /2] (x), σs being the source dimension. It is worth noting that in our simulations the average intensities are computed retaining the full accuracy of the Fresnel integral, i.e., without the ...
... average only over the source dimension xs , assuming a uniform probability density p(xs ) = σs−1 χ[−σs /2,σs /2] (x), σs being the source dimension. It is worth noting that in our simulations the average intensities are computed retaining the full accuracy of the Fresnel integral, i.e., without the ...
Production of coherent radiation by atoms and molecules
... that Nb > > N,. J. P. Gordon played a crucial role in making operable the first such system in 1954, after 2,5 years of experimental work9,10, and H. J. Zeiger was a valuable colleague in the first year of work and early designs. We called this general type of system the maser, an acronym for microw ...
... that Nb > > N,. J. P. Gordon played a crucial role in making operable the first such system in 1954, after 2,5 years of experimental work9,10, and H. J. Zeiger was a valuable colleague in the first year of work and early designs. We called this general type of system the maser, an acronym for microw ...
Optical and medical physics
... Magnification Now an erect image is obtained with a concave mirror only when the image is virtual then image distance v= +3x Object distance u= -x Focal length ...
... Magnification Now an erect image is obtained with a concave mirror only when the image is virtual then image distance v= +3x Object distance u= -x Focal length ...
Two-dimensional array of diffractive microlenses
... computing systems, for applications such as array illumination13 and optical interconnections.' 4 Specifically, we are interested in diffractive lenses since they are ...
... computing systems, for applications such as array illumination13 and optical interconnections.' 4 Specifically, we are interested in diffractive lenses since they are ...
Compact Optical Fiber Amplifier
... amplifiers, but it has the weak point that the backward Amplified Spontaneous Emission (ASE) wastes pumping power near the input terminal of the EDF, and this behavior causes a degradation of the output power of the amplifier and noise figure characteristics. Therefore, the middle isolator is used t ...
... amplifiers, but it has the weak point that the backward Amplified Spontaneous Emission (ASE) wastes pumping power near the input terminal of the EDF, and this behavior causes a degradation of the output power of the amplifier and noise figure characteristics. Therefore, the middle isolator is used t ...
Optical coherence tomography

Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an established medical imaging technique that uses light to capture micrometer-resolution, three-dimensional images from within optical scattering media (e.g., biological tissue). Optical coherence tomography is based on low-coherence interferometry, typically employing near-infrared light. The use of relatively long wavelength light allows it to penetrate into the scattering medium. Confocal microscopy, another optical technique, typically penetrates less deeply into the sample but with higher resolution.Depending on the properties of the light source (superluminescent diodes, ultrashort pulsed lasers, and supercontinuum lasers have been employed), optical coherence tomography has achieved sub- micrometer resolution (with very wide-spectrum sources emitting over a ~100 nm wavelength range).Optical coherence tomography is one of a class of optical tomographic techniques. A relatively recent implementation of optical coherence tomography, frequency-domain optical coherence tomography, provides advantages in signal-to-noise ratio, permitting faster signal acquisition. Commercially available optical coherence tomography systems are employed in diverse applications, including art conservation and diagnostic medicine, notably in ophthalmology and optometry where it can be used to obtain detailed images from within the retina. Recently it has also begun to be used in interventional cardiology to help diagnose coronary artery disease. It has also shown promise in dermatology to improve the diagnostic process.