Second-harmonic generation
... the phase-matching condition can only be reached if the polarization direction of the primary light is ordinary, while the second-harmonic light has an extra-ordinary polarization. Phase matching for the conversion 980 nm → 490 nm is then reached for rays at an angle of 24.9◦ with the c-axis, where ...
... the phase-matching condition can only be reached if the polarization direction of the primary light is ordinary, while the second-harmonic light has an extra-ordinary polarization. Phase matching for the conversion 980 nm → 490 nm is then reached for rays at an angle of 24.9◦ with the c-axis, where ...
Hydrogen Balmer Series High Resolution Spectroscopy : the
... investigations in the far ultraviolet and infrared regions confirmed his predictions with remarkable accuracy. The simplicity of the hydrogen spectrum is due to the fact that it contains only one electron, and that the potential felt by the electron is described precisely by Coulomb’s law. In quantu ...
... investigations in the far ultraviolet and infrared regions confirmed his predictions with remarkable accuracy. The simplicity of the hydrogen spectrum is due to the fact that it contains only one electron, and that the potential felt by the electron is described precisely by Coulomb’s law. In quantu ...
Demonstration of high waveguide bending efficiency (>90%) in a m wavelengths µ
... slab does not strongly scatter light, the output signal is a well-defined guassian-shaped mode. However, if it is out of focus and light is coupled, instead, into the undesired air mode or the substrate leaky mode, the output signal is typically broad and scattered in shape. The imaging camera at th ...
... slab does not strongly scatter light, the output signal is a well-defined guassian-shaped mode. However, if it is out of focus and light is coupled, instead, into the undesired air mode or the substrate leaky mode, the output signal is typically broad and scattered in shape. The imaging camera at th ...
Polarimeter - ScholarWorks@UNO
... the element indicated by the ?rst digit of the subscript 25 pli?ed ?rst by the use of only two modulators because , and its row by the second digit of the subscript. this simpli?es the matrix representing the optical sys Because the quarter-wave retarders 32 and 38 are tem. One modulator provides in ...
... the element indicated by the ?rst digit of the subscript 25 pli?ed ?rst by the use of only two modulators because , and its row by the second digit of the subscript. this simpli?es the matrix representing the optical sys Because the quarter-wave retarders 32 and 38 are tem. One modulator provides in ...
Absorption of low-loss optical materials measured at 1064 nm by a
... We used the collinear mirage technique to evaluate the absorption coefficients of various grades of Suprasil fused-silica samples. Figure 3 shows typical measurements recorded on one of our best samples, which had an absorption coefficient of 0.6 ppm兾cm at 1064 nm. The two measurements differ in the ...
... We used the collinear mirage technique to evaluate the absorption coefficients of various grades of Suprasil fused-silica samples. Figure 3 shows typical measurements recorded on one of our best samples, which had an absorption coefficient of 0.6 ppm兾cm at 1064 nm. The two measurements differ in the ...
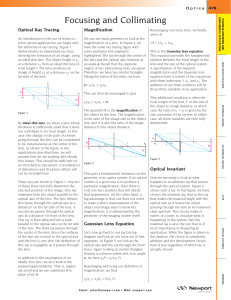
Reflection, Refraction and the Prism
... of the path of light through any optical system. However, as seen in the chapter on Light, the Huygens wavefront construction can be become complicated, especially in systems with a large number of optical components. A simpler approach to track the behavior of light is based on the propagation of l ...
... of the path of light through any optical system. However, as seen in the chapter on Light, the Huygens wavefront construction can be become complicated, especially in systems with a large number of optical components. A simpler approach to track the behavior of light is based on the propagation of l ...
CfE Advanced Higher Physics – Unit 2 – Waves
... sufficient to prevent any oscillation past the rest position - we say the system is critically damped. Systems which have a very large resistance, produce no oscillations and take a long time to come to rest are said to be over damped. In some systems over damping could mean that a system takes long ...
... sufficient to prevent any oscillation past the rest position - we say the system is critically damped. Systems which have a very large resistance, produce no oscillations and take a long time to come to rest are said to be over damped. In some systems over damping could mean that a system takes long ...
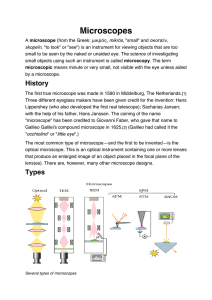
Microscopes - Biozentrum
... Updated microscopes may have many more features, including reflected light (incident) illumination, fluorescence microscopy, phase contrast microscopy and differential interference contrast microscopy, spectroscopy, automation, and digital imaging. On a typical compound optical microscope, there are ...
... Updated microscopes may have many more features, including reflected light (incident) illumination, fluorescence microscopy, phase contrast microscopy and differential interference contrast microscopy, spectroscopy, automation, and digital imaging. On a typical compound optical microscope, there are ...
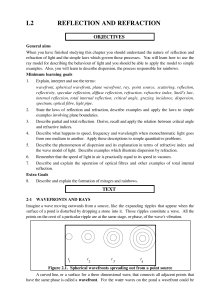
L2 REFLECTION AND REFRACTION
... at the same constant speed of 3.0 × 108 m.s-1, which we always denote by the symbol c. However when light travels through a material its speed is always less than c. The actual value of the speed can now depend on a number of factors such as the chemical composition and the density of the material. ...
... at the same constant speed of 3.0 × 108 m.s-1, which we always denote by the symbol c. However when light travels through a material its speed is always less than c. The actual value of the speed can now depend on a number of factors such as the chemical composition and the density of the material. ...
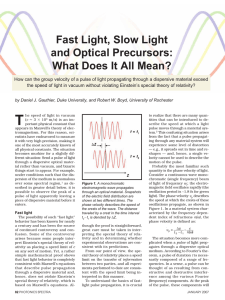
Fast Light, Slow Light and Optical Precursors: What
... Pulse propagation through vacuum is represented by the black line, and through a gas of potassium atoms pumped by a bichromatic laser beam is shown by the red line. Adapted from Reference 7. standing how fast light is consistent with the special theory of relativity is tied into the details of how s ...
... Pulse propagation through vacuum is represented by the black line, and through a gas of potassium atoms pumped by a bichromatic laser beam is shown by the red line. Adapted from Reference 7. standing how fast light is consistent with the special theory of relativity is tied into the details of how s ...
Diffractive optical element and optical pickup apparatus
... light beam of the ?rst Wavelength k1 nor the light beam of the third Wavelength k3 but diffracts the light beam of the second Wavelength k2, and a second diffractive surface that neither diffracts the light beam of the ?rst Wavelength k1 nor the light beam of the second Wavelength k2 but diffracts t ...
... light beam of the ?rst Wavelength k1 nor the light beam of the third Wavelength k3 but diffracts the light beam of the second Wavelength k2, and a second diffractive surface that neither diffracts the light beam of the ?rst Wavelength k1 nor the light beam of the second Wavelength k2 but diffracts t ...
Atom optics with microfabricated optical elements
... necessary ingredient for parallelized atom interferometers and atom clocks but also for quantum computing, thus making this system also very attractive for quantum information processing applications (see Section 7 below). The manipulation of atoms with microlens arrays is extremely ¯exible: it is e ...
... necessary ingredient for parallelized atom interferometers and atom clocks but also for quantum computing, thus making this system also very attractive for quantum information processing applications (see Section 7 below). The manipulation of atoms with microlens arrays is extremely ¯exible: it is e ...
Complex air-structured optical fibre drawn from a 3D
... finding new applications every day in a whole host of areas from science and engineering to medicine and the arts [1]. They are set to revolutionise manufacturing. Fused deposition modelling (FDM) is one of the most commonly used techniques, being the first and simplest demonstration of 3D printing ...
... finding new applications every day in a whole host of areas from science and engineering to medicine and the arts [1]. They are set to revolutionise manufacturing. Fused deposition modelling (FDM) is one of the most commonly used techniques, being the first and simplest demonstration of 3D printing ...
infos on Underwater optics theory
... This distance is linked to the camera’s tirage, the distance separating the optical centre from the film plane, by the equation: 1/p + 1/p’ = 1 / f p being the focusing, p' the tirage, f the focal length. ...
... This distance is linked to the camera’s tirage, the distance separating the optical centre from the film plane, by the equation: 1/p + 1/p’ = 1 / f p being the focusing, p' the tirage, f the focal length. ...
pdf
... been fabricated by direct laser writing in chalcogenide glasses in 2 h.[12] 3D photonic nanostructures operating at near-infrared and longer wavelengths larger than 100 µm × 100 µm × 100 µm with uniformity have been fabricated via laser lithography.[15] However, these 3D nanostructures typically hav ...
... been fabricated by direct laser writing in chalcogenide glasses in 2 h.[12] 3D photonic nanostructures operating at near-infrared and longer wavelengths larger than 100 µm × 100 µm × 100 µm with uniformity have been fabricated via laser lithography.[15] However, these 3D nanostructures typically hav ...
Document
... • Thus, both the signal power level and the pump power level vary along the length of the amplifier. At any point we can have only a finite number of erbium ions and therefore we can only achieve a finite gain (and a finite maximum power) per unit length of the amplifier. • In an amplifier designed ...
... • Thus, both the signal power level and the pump power level vary along the length of the amplifier. At any point we can have only a finite number of erbium ions and therefore we can only achieve a finite gain (and a finite maximum power) per unit length of the amplifier. • In an amplifier designed ...
Partially coherent beam shaping and imaging
... or by means of diffractive elements [24–32] with an appropriately designed phase transmission function [33], or with so-called harmonic diffractive elements [34–39], which provide a transition between purely diffractive elements and refractive elements. These different types of elements are equivale ...
... or by means of diffractive elements [24–32] with an appropriately designed phase transmission function [33], or with so-called harmonic diffractive elements [34–39], which provide a transition between purely diffractive elements and refractive elements. These different types of elements are equivale ...
Coherent Optical Systems
... The refractive index, n(ω), is frequency dependent. Since the group velocity is vg = c/n(ω), it depends on the refractive index, and therefore is also frequency-dependent. Lasers are not ideal monochromatic sources. Εach information-carrying pulse contains a number of spectral components that travel ...
... The refractive index, n(ω), is frequency dependent. Since the group velocity is vg = c/n(ω), it depends on the refractive index, and therefore is also frequency-dependent. Lasers are not ideal monochromatic sources. Εach information-carrying pulse contains a number of spectral components that travel ...
Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy
... elastic scattering spectroscopy, is a noninvasive spectroscopic technique used in quantitative optical characterization of tissue. The basic principle behind DRS is depicted in Figure 1.1. Here a broadband light source with wavelength range from UV to NIR is irradiating the sample, followed by recor ...
... elastic scattering spectroscopy, is a noninvasive spectroscopic technique used in quantitative optical characterization of tissue. The basic principle behind DRS is depicted in Figure 1.1. Here a broadband light source with wavelength range from UV to NIR is irradiating the sample, followed by recor ...
Light Source Notes
... mirror under investigation. Then, the reference trace is subtracted from the sample trace, providing data basically free of error due to pointing instability. A similar approach has been used in a Dual-beam laser deflection sensor described in Ref. [11]. Unfortunately, the compensation of the laser ...
... mirror under investigation. Then, the reference trace is subtracted from the sample trace, providing data basically free of error due to pointing instability. A similar approach has been used in a Dual-beam laser deflection sensor described in Ref. [11]. Unfortunately, the compensation of the laser ...
Advanced optics tutorials
... expanded by a negative lens with focal length –f1. From Applications 1.1 and 1.2 we know θ2 = y1/|–f1|, and the optical invariant tells us that the radius of the virtual image formed by this lens is y2 = θ1|–f1|. This image is at the focal point of the lens, s2 = –f1, because a wellcollimated laser ...
... expanded by a negative lens with focal length –f1. From Applications 1.1 and 1.2 we know θ2 = y1/|–f1|, and the optical invariant tells us that the radius of the virtual image formed by this lens is y2 = θ1|–f1|. This image is at the focal point of the lens, s2 = –f1, because a wellcollimated laser ...
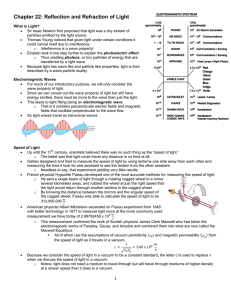
Chapter 22: Reflection and Refraction of Light
... Using the wave property of light along with Snell’s Law can explain why internal reflection may occur. As Snell observed, light will bend away from the normal (closer to the boundary surface). o That is because now, part of the wavefront has been able to speed up while the remaining portion in t ...
... Using the wave property of light along with Snell’s Law can explain why internal reflection may occur. As Snell observed, light will bend away from the normal (closer to the boundary surface). o That is because now, part of the wavefront has been able to speed up while the remaining portion in t ...
Optical tweezers using a diode laser
... have carefully distinguished amongst pressure (due to reflection and absorption), and the gradient forces (due to refraction), and radiometer forces due to thermal gradients. (Optical trapping occurs where the net gradient and radiation pressure balance each other.) The forces tend to be perpendicul ...
... have carefully distinguished amongst pressure (due to reflection and absorption), and the gradient forces (due to refraction), and radiometer forces due to thermal gradients. (Optical trapping occurs where the net gradient and radiation pressure balance each other.) The forces tend to be perpendicul ...
High-peak-power pulse generation from a
... devices [14]. We attribute the power degradation and the slight pulse broadening for amplifier currents above 4 A to thermal effects, as previously commented. The rollover of the pulse power as a function of the amplifier current is more pronounced than in the cw regime [compare Fig. 4(b) with Fig. ...
... devices [14]. We attribute the power degradation and the slight pulse broadening for amplifier currents above 4 A to thermal effects, as previously commented. The rollover of the pulse power as a function of the amplifier current is more pronounced than in the cw regime [compare Fig. 4(b) with Fig. ...
Optical bandwidth and fabrication tolerances of multimode
... are positioned at W/3 and 2W/3, in order not to excite the modes 2 , 5, 8 , - . .. For a geometrical width of W = 18 prn, the equivalent width is We, = 19.2 pm and 19.0 pm for TE and TM, respectively; this is due to the lateral penetration of the evanescent fields at the side of the MMI section. The ...
... are positioned at W/3 and 2W/3, in order not to excite the modes 2 , 5, 8 , - . .. For a geometrical width of W = 18 prn, the equivalent width is We, = 19.2 pm and 19.0 pm for TE and TM, respectively; this is due to the lateral penetration of the evanescent fields at the side of the MMI section. The ...
Optical coherence tomography

Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an established medical imaging technique that uses light to capture micrometer-resolution, three-dimensional images from within optical scattering media (e.g., biological tissue). Optical coherence tomography is based on low-coherence interferometry, typically employing near-infrared light. The use of relatively long wavelength light allows it to penetrate into the scattering medium. Confocal microscopy, another optical technique, typically penetrates less deeply into the sample but with higher resolution.Depending on the properties of the light source (superluminescent diodes, ultrashort pulsed lasers, and supercontinuum lasers have been employed), optical coherence tomography has achieved sub- micrometer resolution (with very wide-spectrum sources emitting over a ~100 nm wavelength range).Optical coherence tomography is one of a class of optical tomographic techniques. A relatively recent implementation of optical coherence tomography, frequency-domain optical coherence tomography, provides advantages in signal-to-noise ratio, permitting faster signal acquisition. Commercially available optical coherence tomography systems are employed in diverse applications, including art conservation and diagnostic medicine, notably in ophthalmology and optometry where it can be used to obtain detailed images from within the retina. Recently it has also begun to be used in interventional cardiology to help diagnose coronary artery disease. It has also shown promise in dermatology to improve the diagnostic process.