Reflect/Refract
... this approximation Mirror •It’s called geometric optics •Physical optics will come later •In geometric optics, light waves are represented by rays •You can think of light as if it is made of little particles •In fact, waves and particles act very similarly •First hint of quantum mechanics! ...
... this approximation Mirror •It’s called geometric optics •Physical optics will come later •In geometric optics, light waves are represented by rays •You can think of light as if it is made of little particles •In fact, waves and particles act very similarly •First hint of quantum mechanics! ...
6.1 Characteristics Because VCSELs emit from the top surface of the
... output, as this output varies with temperature. In today’s optical networks, binary digital modulation is typically used, namely on (i.e., light on) and off (no light) to transmit data. These semiconductor laser devicesgenerate output light intensity which is proportional to the current applied to t ...
... output, as this output varies with temperature. In today’s optical networks, binary digital modulation is typically used, namely on (i.e., light on) and off (no light) to transmit data. These semiconductor laser devicesgenerate output light intensity which is proportional to the current applied to t ...
Low-Coherence Fibre-Optic Interferometric Sensors
... tion about the measurand as it is shown in Fig. 1. It can be noted that if ∆φ = 0, then there is no spectral modulation (Fig. 1a). If the phase difference between the interfering beams varies from zero, then the function takes the form of the cosine curve (Fig. 1b). The spacing of adjacent transmiss ...
... tion about the measurand as it is shown in Fig. 1. It can be noted that if ∆φ = 0, then there is no spectral modulation (Fig. 1a). If the phase difference between the interfering beams varies from zero, then the function takes the form of the cosine curve (Fig. 1b). The spacing of adjacent transmiss ...
4.6.2 Reflection, Refraction, Diffraction
... band structure. For this we would have to superimpose multiple contours on the isofrequency plot • On the other hand, we could cut our interface at a different angle. Then the fixed ‖ -line can intersect a given contour at inequivalent points in different periodic unit cells. • Conversely, there are ...
... band structure. For this we would have to superimpose multiple contours on the isofrequency plot • On the other hand, we could cut our interface at a different angle. Then the fixed ‖ -line can intersect a given contour at inequivalent points in different periodic unit cells. • Conversely, there are ...
1: Inroduction
... shape. In the healthy eye, the long axes of the cells are pointed precisely toward a common location near the center of the pupil.24 When illuminated by a narrow beam of light impinging parallel to their long axes, they act as a tiny flash-torch in the reverse direction, reflecting predominately tow ...
... shape. In the healthy eye, the long axes of the cells are pointed precisely toward a common location near the center of the pupil.24 When illuminated by a narrow beam of light impinging parallel to their long axes, they act as a tiny flash-torch in the reverse direction, reflecting predominately tow ...
new challenges in thermo-fluiddynamic research by advanced
... work in a non-invasive and inertialess way they do not influence the process that has to be investigated and can be used for highly transient processes. The development of optical methods is supported by the availability of new equipment like high energy light sources, intensified electronical camer ...
... work in a non-invasive and inertialess way they do not influence the process that has to be investigated and can be used for highly transient processes. The development of optical methods is supported by the availability of new equipment like high energy light sources, intensified electronical camer ...
A simple and accurate method of alignment for toric intraocular lens
... – Free from the misalignment related to marking the reference point due to the differences in the head position at the time of topography and the time when the reference point is marked, including cyclorotation of the eye during surgery. – Reference and alignment axis can be marked under the surgica ...
... – Free from the misalignment related to marking the reference point due to the differences in the head position at the time of topography and the time when the reference point is marked, including cyclorotation of the eye during surgery. – Reference and alignment axis can be marked under the surgica ...
12. Infrared and Visible Waves
... How do infrared thermometers work? An infrared thermometer enables the remote sensing of temperature. It does this by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by an object and converting it into a temperature. The eardrum is an accurate point for measuring the body’s temperature, because it is deep ...
... How do infrared thermometers work? An infrared thermometer enables the remote sensing of temperature. It does this by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by an object and converting it into a temperature. The eardrum is an accurate point for measuring the body’s temperature, because it is deep ...
Direct Patterning of Three-Dimensional Periodic
... Although the far-field interference is more suitable for largescale patterning of periodic structures, our approach is ideal for its nano- and microscale patterning capabilities. The dimensions of the overall structures that can be produced are as small as a few micrometers in size, which we believe ...
... Although the far-field interference is more suitable for largescale patterning of periodic structures, our approach is ideal for its nano- and microscale patterning capabilities. The dimensions of the overall structures that can be produced are as small as a few micrometers in size, which we believe ...
Full-Spectrum, Angle-Resolved Reflectance and
... Optical coatings composed of thin films of dielectric materials have long been commonplace in both the optics and glass industries. For instance, stacks of alternating high- and lowrefractive-index layers are used to form Bragg mirrors in laser cavities, and magnesium fluoride layers are used as ant ...
... Optical coatings composed of thin films of dielectric materials have long been commonplace in both the optics and glass industries. For instance, stacks of alternating high- and lowrefractive-index layers are used to form Bragg mirrors in laser cavities, and magnesium fluoride layers are used as ant ...
properties of laser beams
... gravitational wave detection). • For more common applications, such as interferometric measurements of distances, coherent laser radar, and coherent optical communications, the required monochromaticity falls in the 10-100 kHz range. • A monochromaticity of ~1 MHz is typically needed for much of hig ...
... gravitational wave detection). • For more common applications, such as interferometric measurements of distances, coherent laser radar, and coherent optical communications, the required monochromaticity falls in the 10-100 kHz range. • A monochromaticity of ~1 MHz is typically needed for much of hig ...
paper - Crescimanno page - Youngstown State University
... light signal at that phase that would correspond to either a maximum or a minimum. Because there is a stable, but frequencydependent, phase offset at each detuning, we are not able to measure independently the absolute phase difference of the incoming lightfields across the TGG plate. The two traces ...
... light signal at that phase that would correspond to either a maximum or a minimum. Because there is a stable, but frequencydependent, phase offset at each detuning, we are not able to measure independently the absolute phase difference of the incoming lightfields across the TGG plate. The two traces ...
Proposal for an Optical Laser Producing Light at Half the... Frans Godschalk, Fabian Hassler, and Yuli V. Nazarov
... Lasers and superconductors are both systems with macroscopic quantum coherence. In lasers, photons form a coherent state induced by stimulated emission of a driven system into a cavity mode. The resulting visible coherent light is characterized by an optical phase [1]. In superconductors, the ground ...
... Lasers and superconductors are both systems with macroscopic quantum coherence. In lasers, photons form a coherent state induced by stimulated emission of a driven system into a cavity mode. The resulting visible coherent light is characterized by an optical phase [1]. In superconductors, the ground ...
Refractive Index Measurement Principle - K
... and the intensity of light is high. On the right side of the critical angle the intensity falls rapidly, as most light enters the sample and is not reflected back. ...
... and the intensity of light is high. On the right side of the critical angle the intensity falls rapidly, as most light enters the sample and is not reflected back. ...
6288-18 talk - LOFT, Large Optics Fabrication and Testing group
... Image shift has same effect as change of line of sight direction (defined as where the system is looking) ...
... Image shift has same effect as change of line of sight direction (defined as where the system is looking) ...
Slide 1
... Image shift has same effect as change of line of sight direction (defined as where the system is looking) ...
... Image shift has same effect as change of line of sight direction (defined as where the system is looking) ...
Investigation of External Electromagnetic Disturbance in
... of polarization (SOP) in WDM transmission systems occur not only due to the polarization mode dispersion (PMD) but also due to non-linear effects (NOE). Therefore, the refractivity depends not only on the frequency but also on the intensity of electric field that is propagating through a dielectric ...
... of polarization (SOP) in WDM transmission systems occur not only due to the polarization mode dispersion (PMD) but also due to non-linear effects (NOE). Therefore, the refractivity depends not only on the frequency but also on the intensity of electric field that is propagating through a dielectric ...
BMS 631 - Lecture 4
... Scatter - Rayleigh Scatter - directly proportional to property of the scattering molecule called molecular polarizability (ie dipole formation), inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength of the incident light (blue light has highest scatter - thus blue sky!) Scatter - Raman Scatte ...
... Scatter - Rayleigh Scatter - directly proportional to property of the scattering molecule called molecular polarizability (ie dipole formation), inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength of the incident light (blue light has highest scatter - thus blue sky!) Scatter - Raman Scatte ...
Diffuse optical imaging
... absorption spectra of oxy- and deoxyhaemoglobin (HbO and HHb, respectively) to assess blood oxygenation. This demonstrated that biomedical optics could provide clinically useful information by examination of the absorption of tissue, provided that the confounding effects of scatter were minimized, b ...
... absorption spectra of oxy- and deoxyhaemoglobin (HbO and HHb, respectively) to assess blood oxygenation. This demonstrated that biomedical optics could provide clinically useful information by examination of the absorption of tissue, provided that the confounding effects of scatter were minimized, b ...
A crash course in optics
... The eye and the brain has the tendency not to see what’s actually there but what it thinks is there – this makes judging color, brightness and ...
... The eye and the brain has the tendency not to see what’s actually there but what it thinks is there – this makes judging color, brightness and ...
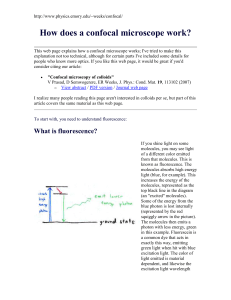
How does a confocal microscope work
... of one lens to another point. This is represented by the blue rays of light in the above picture. The red rays of light represent light from another point in the sample, which is not at the focal point of the lens, but which nonetheless get imaged by the lenses of the microscope. (Note that the red ...
... of one lens to another point. This is represented by the blue rays of light in the above picture. The red rays of light represent light from another point in the sample, which is not at the focal point of the lens, but which nonetheless get imaged by the lenses of the microscope. (Note that the red ...
Department of Physics, Technical University Ostrava 17. listopadu
... wavelength is in this case a wavelength at which the group optical path difference (OPD) between beams in the interferometer is zero. Most recently, we have extended the use of spectral interferometry for measuring mirror distances and displacements of a slightly dispersive Michelson interferometer ...
... wavelength is in this case a wavelength at which the group optical path difference (OPD) between beams in the interferometer is zero. Most recently, we have extended the use of spectral interferometry for measuring mirror distances and displacements of a slightly dispersive Michelson interferometer ...
Third Order Nonlinear Distortion Reduction in Broadband ASE Source - Based Full-Duplex ROF Transport Systems
... causing system with higher SNR value, finally leading to an improvement BER performance. Cross talk from down-link optical signal to up-link optical signal may influence the BER performance because 10 GHz carrier is used both at CS and BS in the experiment. However, since the OADM has a high add/dro ...
... causing system with higher SNR value, finally leading to an improvement BER performance. Cross talk from down-link optical signal to up-link optical signal may influence the BER performance because 10 GHz carrier is used both at CS and BS in the experiment. However, since the OADM has a high add/dro ...
A Hypothesis for the Speed of Propagation of Light in electric and
... The experimental verification of these theoretical predictions can not be regarded as already done. [Rik 03] calls all electro- and magneto- optical effects of the vacuum as „far from being experimentally demonstrated“. The situation is not changed up to now. At [Riz 07] we find a presentation at a ...
... The experimental verification of these theoretical predictions can not be regarded as already done. [Rik 03] calls all electro- and magneto- optical effects of the vacuum as „far from being experimentally demonstrated“. The situation is not changed up to now. At [Riz 07] we find a presentation at a ...
Optical coherence tomography

Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an established medical imaging technique that uses light to capture micrometer-resolution, three-dimensional images from within optical scattering media (e.g., biological tissue). Optical coherence tomography is based on low-coherence interferometry, typically employing near-infrared light. The use of relatively long wavelength light allows it to penetrate into the scattering medium. Confocal microscopy, another optical technique, typically penetrates less deeply into the sample but with higher resolution.Depending on the properties of the light source (superluminescent diodes, ultrashort pulsed lasers, and supercontinuum lasers have been employed), optical coherence tomography has achieved sub- micrometer resolution (with very wide-spectrum sources emitting over a ~100 nm wavelength range).Optical coherence tomography is one of a class of optical tomographic techniques. A relatively recent implementation of optical coherence tomography, frequency-domain optical coherence tomography, provides advantages in signal-to-noise ratio, permitting faster signal acquisition. Commercially available optical coherence tomography systems are employed in diverse applications, including art conservation and diagnostic medicine, notably in ophthalmology and optometry where it can be used to obtain detailed images from within the retina. Recently it has also begun to be used in interventional cardiology to help diagnose coronary artery disease. It has also shown promise in dermatology to improve the diagnostic process.