2. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
... in English some adjectives take -ness as a suffix when being used to create nouns (happy → happiness). The same principles apply in most human languages though the rules are different1. Compounding: new words are formed by grouping existing words. This occurs infrequently in English (examples includ ...
... in English some adjectives take -ness as a suffix when being used to create nouns (happy → happiness). The same principles apply in most human languages though the rules are different1. Compounding: new words are formed by grouping existing words. This occurs infrequently in English (examples includ ...
Context Free Grammars
... shown in Figure 1 for the sentence The birds in the field eat the corn. A tree consists of labeled nodes with arcs indicates a parent-child relationship. Trees have a unique root node (S in figure 1). Every node except the root has exactly one parent node, and 0 or more children. Nodes without child ...
... shown in Figure 1 for the sentence The birds in the field eat the corn. A tree consists of labeled nodes with arcs indicates a parent-child relationship. Trees have a unique root node (S in figure 1). Every node except the root has exactly one parent node, and 0 or more children. Nodes without child ...
Formalizing the Dynamic Semantics of Java
... Programming linguistics is the study of programming languages (PLs). This is by analogy with linguistics, the study of natural languages (NLs): • Both PLs and NLs have syntax (form) and semantics (meaning). ...
... Programming linguistics is the study of programming languages (PLs). This is by analogy with linguistics, the study of natural languages (NLs): • Both PLs and NLs have syntax (form) and semantics (meaning). ...
20179
... This course is taught over two terms. Its general aim is to continue analysing the use, structure and meaning of the English language, especially in connection with sentential phenomena that reflect co-textual factors and issues in linguistic interaction. The course also delves into cultural, histor ...
... This course is taught over two terms. Its general aim is to continue analysing the use, structure and meaning of the English language, especially in connection with sentential phenomena that reflect co-textual factors and issues in linguistic interaction. The course also delves into cultural, histor ...
ppt
... Can we determine if a sentence is grammatical? Can we determine how likely a sentence is to be grammatical? to be an English sentence? Can we generate candidate, grammatical sentences? ...
... Can we determine if a sentence is grammatical? Can we determine how likely a sentence is to be grammatical? to be an English sentence? Can we generate candidate, grammatical sentences? ...
syntax basics
... T: finite set of terminal symbols, NT and T are disjoint P: finite set of productions of the form A → α, A ∈ NT and α ∈ (T ∪ NT)* ...
... T: finite set of terminal symbols, NT and T are disjoint P: finite set of productions of the form A → α, A ∈ NT and α ∈ (T ∪ NT)* ...
____________________________________________________ Write a program using “for” statements that print the
... Write a program that takes a one-line sentence as input and then outputs the following response: If the sentence ends with a question mark „?‟ and the input contains an even number of characters, then output the word “Yes”. If the sentence ends with a question mark „?‟ and the input contains an odd ...
... Write a program that takes a one-line sentence as input and then outputs the following response: If the sentence ends with a question mark „?‟ and the input contains an even number of characters, then output the word “Yes”. If the sentence ends with a question mark „?‟ and the input contains an odd ...
Towards a rationalist theory of language acquisition
... 2010). Instead of strings in Σ∗ and contexts in (Σ∗ )2 , with a k-MCFG, categories can derive i-tuples in (Σ∗ )i for i ≤ k, with contexts in (Σ∗ )i+1 . And when these languages have the analogous finite kernel and finite context properties, similar distributional grammar inference methods can succee ...
... 2010). Instead of strings in Σ∗ and contexts in (Σ∗ )2 , with a k-MCFG, categories can derive i-tuples in (Σ∗ )i for i ≤ k, with contexts in (Σ∗ )i+1 . And when these languages have the analogous finite kernel and finite context properties, similar distributional grammar inference methods can succee ...
- ePrints@Bangalore University
... A. Parsing and Structural Representation In this method we use shift reduce parsing technique to construct a parse tree [9] where a shift-reduce parser tries to find sequences of words and phrases that correspond to the left hand side of a grammar production, and replace them with the right-hand sid ...
... A. Parsing and Structural Representation In this method we use shift reduce parsing technique to construct a parse tree [9] where a shift-reduce parser tries to find sequences of words and phrases that correspond to the left hand side of a grammar production, and replace them with the right-hand sid ...
LARG-20010510
... AGI • In practice languages are not logical structures. • Often said sentences are not precisely grammatical. The solution of expanding the grammar leads to explosion of grammar rules. • A large grammar will lead to many parses of the same sentences. Clearly, some parses are more accurate than other ...
... AGI • In practice languages are not logical structures. • Often said sentences are not precisely grammatical. The solution of expanding the grammar leads to explosion of grammar rules. • A large grammar will lead to many parses of the same sentences. Clearly, some parses are more accurate than other ...
Semio-linguistics and Stemmatic Syntax - fflch-usp
... things in time and space, we use naming as a natural part of the implied mental act. Naming exploits our capacity to bodily produce acoustic form and to monitor and control it by auditory auto-perception. So phonetics is in fact a natural part of our categorization and ordinary use of categories fo ...
... things in time and space, we use naming as a natural part of the implied mental act. Naming exploits our capacity to bodily produce acoustic form and to monitor and control it by auditory auto-perception. So phonetics is in fact a natural part of our categorization and ordinary use of categories fo ...
Interpreting Manipulation Actions: a Cognitive Approach
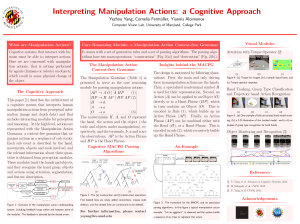
... Context-free Grammar The Manipulation Grammar (Table 1) is presented to serve as the core reasoning module for parsing manipulation actions. ...
... Context-free Grammar The Manipulation Grammar (Table 1) is presented to serve as the core reasoning module for parsing manipulation actions. ...
Intermediate New Testament Greek
... Chapters 17 and 18, "Discourse Analysis" and "Diagramming,"are helpful in conceptualizing the exegetical task. Chapter 17 examines seven interrelated features: genre, structure, cohesion, propositions, relations, prominence, and setting and provides some illustrative biblical references. Chapter 18 ...
... Chapters 17 and 18, "Discourse Analysis" and "Diagramming,"are helpful in conceptualizing the exegetical task. Chapter 17 examines seven interrelated features: genre, structure, cohesion, propositions, relations, prominence, and setting and provides some illustrative biblical references. Chapter 18 ...
Chapter 13
... have what we can call an “empty subject,” with it: it rained, it looks nice out today, it doesn’t matter. There is nothing that the it really refers to. It just fills up the subject position when we mean something very general. Sometimes “I” subjects disappear under what can be called “Diary ...
... have what we can call an “empty subject,” with it: it rained, it looks nice out today, it doesn’t matter. There is nothing that the it really refers to. It just fills up the subject position when we mean something very general. Sometimes “I” subjects disappear under what can be called “Diary ...
Sentence-Level Editing
... The “Paramedic Method” for prose revision was introduced by Richard Lanham in his textbook Revising Prose. The following process is a simplified version of Lanham’s method; it will help you revise with an eye to clarity and concision. (Note: it is not inevitable that those two stylistic virtues go t ...
... The “Paramedic Method” for prose revision was introduced by Richard Lanham in his textbook Revising Prose. The following process is a simplified version of Lanham’s method; it will help you revise with an eye to clarity and concision. (Note: it is not inevitable that those two stylistic virtues go t ...
Lexicalising a robust parser grammar using the WWW
... Many robust parsing systems that can process real-world texts were developed in the nineties (Abney 1996, Grefenstette 1996, Collins 1996, Aït-Mokhtar and Chanod 1997, Charniak 2000). These parsers assign linguistic structures to text sentences and are used with some success in various applications, ...
... Many robust parsing systems that can process real-world texts were developed in the nineties (Abney 1996, Grefenstette 1996, Collins 1996, Aït-Mokhtar and Chanod 1997, Charniak 2000). These parsers assign linguistic structures to text sentences and are used with some success in various applications, ...
Categorial Grammar – Introduction
... then application of the function (S\N P )/N P results in the two words being identified as having syntactic type S\N P . This type is analogous to the verb phrase category constituting the predicate of a sentence. If the substring ‘like cats’ is preceded by the substring ‘nice dogs’ previously analy ...
... then application of the function (S\N P )/N P results in the two words being identified as having syntactic type S\N P . This type is analogous to the verb phrase category constituting the predicate of a sentence. If the substring ‘like cats’ is preceded by the substring ‘nice dogs’ previously analy ...
Why study programming languages?
... Design specification • Programming environment - external support for the language Debugger, syntax-directed editor Supporting function, platforms Smalltalk Supporting all the software lifecycle phases ...
... Design specification • Programming environment - external support for the language Debugger, syntax-directed editor Supporting function, platforms Smalltalk Supporting all the software lifecycle phases ...
ai-prolog9
... representation that can be used in inference. (often referred to as sentence meaning) • Possible representations: • SQL. Map “Find me all the students who are taking AI3” to relevant SQL query. • Predicate Logic: Map “John loves anyone who is tall” onto relevant statement in predicate logic. • Other ...
... representation that can be used in inference. (often referred to as sentence meaning) • Possible representations: • SQL. Map “Find me all the students who are taking AI3” to relevant SQL query. • Predicate Logic: Map “John loves anyone who is tall” onto relevant statement in predicate logic. • Other ...
PL Intro
... – Changing one thing has no effect on another • As stated by Michael Scott: ▫ Orthogonality means that features can be used in any combination, the combinations all make sense, and the meaning of a given feature is consistent regardless of other features with which it is combined. 261 example: array ...
... – Changing one thing has no effect on another • As stated by Michael Scott: ▫ Orthogonality means that features can be used in any combination, the combinations all make sense, and the meaning of a given feature is consistent regardless of other features with which it is combined. 261 example: array ...
Chapter 8A
... o ________________________: they attempted to make English conform to logic. o ________________________: they attempted to describe how English worked through a system of rules. o ________________________: they associated correct thinking with “proper” English and language use. o ___________________ ...
... o ________________________: they attempted to make English conform to logic. o ________________________: they attempted to describe how English worked through a system of rules. o ________________________: they associated correct thinking with “proper” English and language use. o ___________________ ...
PPT
... An interpreter of L1 in L2 is an L2 program that executes the meaning of a given L1 program Compiler would examine the body of a loop once; an interpreter would examine it every time the loop was executed ...
... An interpreter of L1 in L2 is an L2 program that executes the meaning of a given L1 program Compiler would examine the body of a loop once; an interpreter would examine it every time the loop was executed ...
Aspects of the theory of syntax, by N. Chomsky
... language is recursively enumerable and that the set of their respective relevant structures is recursively enumerable. A grammar is to provide a finite set of rules by which these sets are simultaneously recursively enumerated. The term 'generative grammar', one may suppose, is used in the book and ...
... language is recursively enumerable and that the set of their respective relevant structures is recursively enumerable. A grammar is to provide a finite set of rules by which these sets are simultaneously recursively enumerated. The term 'generative grammar', one may suppose, is used in the book and ...
An Interlingual Approach to Machine Translation
... conditions on the structures passed to it. The phrasestructures that are built by the structurce-building component are underspecified, (i.e., they do not include information about agreement, abstract case, semantic roles, argument structure, etc.); the basis of these structures is a set of template ...
... conditions on the structures passed to it. The phrasestructures that are built by the structurce-building component are underspecified, (i.e., they do not include information about agreement, abstract case, semantic roles, argument structure, etc.); the basis of these structures is a set of template ...