On Classical Electromagnetic Fields (cont
... Derivation of the Paraxial Wave Equation: In point-to-point communication, we may think of the electromagnetic field as propagating in a kind of "searchlight" mode -- i.e. a beam of finite width that propagates in some particular direction. In analyzing this mode of wave propagation, we make use of ...
... Derivation of the Paraxial Wave Equation: In point-to-point communication, we may think of the electromagnetic field as propagating in a kind of "searchlight" mode -- i.e. a beam of finite width that propagates in some particular direction. In analyzing this mode of wave propagation, we make use of ...
Chapter15 - cloudfront.net
... • Describe how light waves interfere with each other to produce bright and dark fringes. ...
... • Describe how light waves interfere with each other to produce bright and dark fringes. ...
Light trapping by photon frequency management
... Fluorescent collectors: trapping light by frequency shift Tom Markvart Solar Energy Lab, Engineering Sciences University of Southampton, UK. Fluorescent collectors have been under consideration for some time, with the aim of reducing the size – and therefore the cost – of solar cells. We shall show ...
... Fluorescent collectors: trapping light by frequency shift Tom Markvart Solar Energy Lab, Engineering Sciences University of Southampton, UK. Fluorescent collectors have been under consideration for some time, with the aim of reducing the size – and therefore the cost – of solar cells. We shall show ...
Electro-Optic Ceramics
... Polarizing filters offer the advantage of reduction the amount of heating of the filter. Polarizing filters typically make use of material such as CaCO3. ...
... Polarizing filters offer the advantage of reduction the amount of heating of the filter. Polarizing filters typically make use of material such as CaCO3. ...
PHYS632_L13_ch_33_El..
... This is the force per unit area felt by an object that absorbs light. (Black piece of paper)) This is the force per unit area felt by an object that reflects light backwards. (Aluminum foil) ...
... This is the force per unit area felt by an object that absorbs light. (Black piece of paper)) This is the force per unit area felt by an object that reflects light backwards. (Aluminum foil) ...
Chip Scale Light Deflector Enables Solid
... broaden in space and time under the combined actions of two universal physical processes: diffraction and dispersion. Researchers have explored strategies to overcome the often undesirable consequences of these two effects since the early days of lasers. In the early 1990s, nonlinear schemes based o ...
... broaden in space and time under the combined actions of two universal physical processes: diffraction and dispersion. Researchers have explored strategies to overcome the often undesirable consequences of these two effects since the early days of lasers. In the early 1990s, nonlinear schemes based o ...
light is a wave
... • If a molecule is hit, the atoms within a molecule vibrate. • Because atoms are thousands of times heavier than electrons they ‘ring’ with a much lower frequencies. • The light given off is in the infra red range of the spectrum. ...
... • If a molecule is hit, the atoms within a molecule vibrate. • Because atoms are thousands of times heavier than electrons they ‘ring’ with a much lower frequencies. • The light given off is in the infra red range of the spectrum. ...
pfb13_week2[1]
... • If a molecule is hit, the atoms within a molecule vibrate. • Because atoms are thousands of times heavier than electrons they ‘ring’ with a much lower frequencies. • The light given off is in the infra red range of the spectrum. ...
... • If a molecule is hit, the atoms within a molecule vibrate. • Because atoms are thousands of times heavier than electrons they ‘ring’ with a much lower frequencies. • The light given off is in the infra red range of the spectrum. ...
Week 13 - Electromagnetic Waves
... they start to oscillate, i.e. they produce a current. For the charges to be able to move significantly they must have some space to move on. Therefore the vertical antennas indicate that the electromagnetic waves are vertically polarized so the electric field in the wave is able to do work on those ...
... they start to oscillate, i.e. they produce a current. For the charges to be able to move significantly they must have some space to move on. Therefore the vertical antennas indicate that the electromagnetic waves are vertically polarized so the electric field in the wave is able to do work on those ...
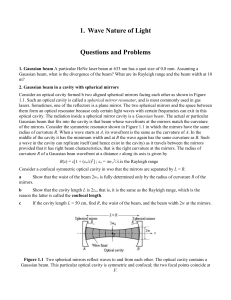
1. Wave Nature of Light
... 1.1. Such an optical cavity is called a spherical mirror resonator, and is most commonly used in gas lasers. Sometimes, one of the reflectors is a plane mirror. The two spherical mirrors and the space between them form an optical resonator because only certain light waves with certain frequencies ca ...
... 1.1. Such an optical cavity is called a spherical mirror resonator, and is most commonly used in gas lasers. Sometimes, one of the reflectors is a plane mirror. The two spherical mirrors and the space between them form an optical resonator because only certain light waves with certain frequencies ca ...
Thomas Young (scientist)
.jpg?width=300)
Thomas Young (13 June 1773 – 10 May 1829) was an English polymath and physician. Young made notable scientific contributions to the fields of vision, light, solid mechanics, energy, physiology, language, musical harmony, and Egyptology. He ""made a number of original and insightful innovations""in the decipherment of Egyptian hieroglyphs (specifically the Rosetta Stone) before Jean-François Champollion eventually expanded on his work. He was mentioned by, among others, William Herschel, Hermann von Helmholtz, James Clerk Maxwell, and Albert Einstein. Young has been described as ""The Last Man Who Knew Everything"".

















![pfb13_week2[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003391392_1-89916bc801a4df63071018672e6152f2-300x300.png)