Solids and Fluids
... Conditions of molecules in a flowing fluid may be unpredictable - difficult to quantify. Therefore it is helpful to identify several conditions of an ideal fluid: Condition 1: Steady flow means that all particles have the same velocity as they pass a given point. Condition 2: Irrotational flow means ...
... Conditions of molecules in a flowing fluid may be unpredictable - difficult to quantify. Therefore it is helpful to identify several conditions of an ideal fluid: Condition 1: Steady flow means that all particles have the same velocity as they pass a given point. Condition 2: Irrotational flow means ...
Flow of liquid through a tube
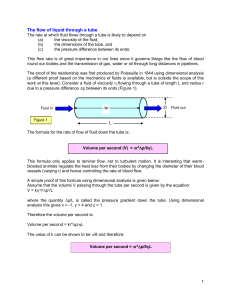
... The rate at which fluid flows through a tube is likely to depend on (a) the viscosity of the fluid, (b) the dimensions of the tube, and (c) the pressure difference between its ends. This flow rate is of great importance in our lives since it governs things like the flow of blood round our bodies and ...
... The rate at which fluid flows through a tube is likely to depend on (a) the viscosity of the fluid, (b) the dimensions of the tube, and (c) the pressure difference between its ends. This flow rate is of great importance in our lives since it governs things like the flow of blood round our bodies and ...
Study Island
... Therefore, the solution to the system of equations is x = 0, y = 2. 9. Notice that there is only one line graphed and when solved for y, both equations have the same slope and the same y-intercept. The two equations graph the same line that will intersect at infinitely ...
... Therefore, the solution to the system of equations is x = 0, y = 2. 9. Notice that there is only one line graphed and when solved for y, both equations have the same slope and the same y-intercept. The two equations graph the same line that will intersect at infinitely ...
Section 7.1
... If the system of equations being solved contains equations that can be easily graphed on a calculator, or are graphs that you can easily sketch (like linear equations), then we can solve the system by finding the point(s) at which all graphs in the system meet. This method gives an estimate to the s ...
... If the system of equations being solved contains equations that can be easily graphed on a calculator, or are graphs that you can easily sketch (like linear equations), then we can solve the system by finding the point(s) at which all graphs in the system meet. This method gives an estimate to the s ...
T - MPS
... The equations of motion do not close, because at any order a new moment of the next higher order appears (closure problem), leading to a chain of equations. In the momentum equation the pressure tensor, Ps, is required, which can be obtained from taking the seond-order moment of Vlasov‘s equation. T ...
... The equations of motion do not close, because at any order a new moment of the next higher order appears (closure problem), leading to a chain of equations. In the momentum equation the pressure tensor, Ps, is required, which can be obtained from taking the seond-order moment of Vlasov‘s equation. T ...
1P1, 2013-14, Thermofluid Mechanics: examples paper 2
... The figure below shows air flowing through a nozzle. The inlet pressure is p1 = 105 kPa and the pressure in the exhausting jet is p2 =101.3 kPa (which is equal to the ambient pressure at the nozzle exit). The nozzle has an inlet diameter of 60 mm, an exit diameter of 10 mm, and the nozzle is connect ...
... The figure below shows air flowing through a nozzle. The inlet pressure is p1 = 105 kPa and the pressure in the exhausting jet is p2 =101.3 kPa (which is equal to the ambient pressure at the nozzle exit). The nozzle has an inlet diameter of 60 mm, an exit diameter of 10 mm, and the nozzle is connect ...