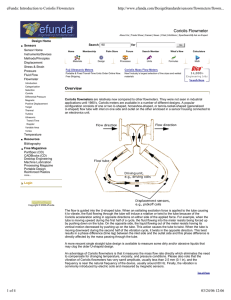
Coriolis Flowmeter
... Suppose that the fluid is flowing into the U-shaped tube at velocity V and the tube is vibrating at angular velocity . Consider a small section of the fluid that is on the inlet side away from the point of flexture at ...
... Suppose that the fluid is flowing into the U-shaped tube at velocity V and the tube is vibrating at angular velocity . Consider a small section of the fluid that is on the inlet side away from the point of flexture at ...
An introduction to the Lorentz
... The potential and field at x are naturally expressed in terms of u, the particle’s proper time when it encounters x’s past light cone, and r, the distance between x and the particle, as measured at that time in the MCLF. This motivates the introduction of a (noninertial) coordinate system for flat s ...
... The potential and field at x are naturally expressed in terms of u, the particle’s proper time when it encounters x’s past light cone, and r, the distance between x and the particle, as measured at that time in the MCLF. This motivates the introduction of a (noninertial) coordinate system for flat s ...
Force as a vector Vectors Pressure Gradient force Pressure gradient
... • 3) This result means that low-pressure systems have a hard time “filling up”, since air cannot “get into them”, but rather circles the low ...
... • 3) This result means that low-pressure systems have a hard time “filling up”, since air cannot “get into them”, but rather circles the low ...
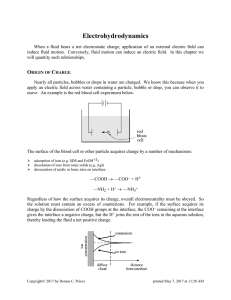
Electrohydrodynamics
... where kT is the thermal energy possessed by every ion or molecule and i is the chemical energy per ion. When the species is charged, we must add an electrical contribution to the chemical energy to obtain the electrochemical potential of each species. electrical potential energy: zie where zi is t ...
... where kT is the thermal energy possessed by every ion or molecule and i is the chemical energy per ion. When the species is charged, we must add an electrical contribution to the chemical energy to obtain the electrochemical potential of each species. electrical potential energy: zie where zi is t ...
Electrostatic turbulence in tokamaks on transport time scales
... Simulating electrostatic turbulence in tokamaks on transport time scales requires retaining and evolving a complete turbulence modified neoclassical transport description, including all the axisymmetric neoclassical and zonal flow radial electric field effects, as well as the turbulent transport nor ...
... Simulating electrostatic turbulence in tokamaks on transport time scales requires retaining and evolving a complete turbulence modified neoclassical transport description, including all the axisymmetric neoclassical and zonal flow radial electric field effects, as well as the turbulent transport nor ...
Review for DSMA 0301 Final Exam
... 39) An object is dropped from the top of a 144-foot building. The height h of the object after t seconds is given by h(t) = -16t2 + 144. How long will it take for the object to hit the ground? ...
... 39) An object is dropped from the top of a 144-foot building. The height h of the object after t seconds is given by h(t) = -16t2 + 144. How long will it take for the object to hit the ground? ...