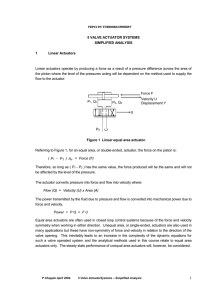
Numerical Solution to the Time-Dependent Maxwell Equations in
... t do not belong to H 1 (Ä)2 (or H1 (Ä)3 ) as is the case in a convex domain, but only to H (curl, Ä) ∩ H (div, Ä). In other words, the “physical” solution of Maxwell’s equations, which only belongs to the functional space H (curl, Ä) ∩ H (div, Ä), goes to infinity when one comes close to a reentrant ...
... t do not belong to H 1 (Ä)2 (or H1 (Ä)3 ) as is the case in a convex domain, but only to H (curl, Ä) ∩ H (div, Ä). In other words, the “physical” solution of Maxwell’s equations, which only belongs to the functional space H (curl, Ä) ∩ H (div, Ä), goes to infinity when one comes close to a reentrant ...
Methods for 3-D vector microcavity problems involving a
... both for free space propagation [1, 2, 3, 4] and in cavity resonators [5]. In particular, recent advances in fabrication technology have given rise to optical cavities which cannot be modeled by effectively two-dimensional, scalar or pseudo-vectorial wave equations [6]. The resulting modes may exhib ...
... both for free space propagation [1, 2, 3, 4] and in cavity resonators [5]. In particular, recent advances in fabrication technology have given rise to optical cavities which cannot be modeled by effectively two-dimensional, scalar or pseudo-vectorial wave equations [6]. The resulting modes may exhib ...
Section 2: Electrostatics
... present at all by simulating the boundary conditions by a small number of (point) charges of appropriate magnitude, suitably placed at positions external to the region of interest. The distribution of these socalled image charges must be of such a nature that their individual electrostatic scalar po ...
... present at all by simulating the boundary conditions by a small number of (point) charges of appropriate magnitude, suitably placed at positions external to the region of interest. The distribution of these socalled image charges must be of such a nature that their individual electrostatic scalar po ...
Controlling the dimensionality of low
... that any perturbation (such as the temporary presence of gallium oxide, or boundary effects along the edges of the forcing area) may completely off balance the overall current distribution should there not be a larger resistance in the circuit. The injection table used in this experiment enabled the ...
... that any perturbation (such as the temporary presence of gallium oxide, or boundary effects along the edges of the forcing area) may completely off balance the overall current distribution should there not be a larger resistance in the circuit. The injection table used in this experiment enabled the ...
F(x, y, z)
... Notice also that the gradient vectors are long where the level curves are close to each other and short where the curves are farther apart. That's because the length of the gradient vector is the value of the directional derivative of f and closely spaced level curves indicate a steep graph. ...
... Notice also that the gradient vectors are long where the level curves are close to each other and short where the curves are farther apart. That's because the length of the gradient vector is the value of the directional derivative of f and closely spaced level curves indicate a steep graph. ...
Buoyancy and electrically driven convection models in thin
... the plane normal to both the quasiplane of the growth and the electrodes, vortex tubes form near the electrodes, as shown in Fig. 1~a!. The interaction of electrical driven vortex rings and gravity driven vortex tubes and their effects on the deposit morphology will be discussed in a forthcoming pap ...
... the plane normal to both the quasiplane of the growth and the electrodes, vortex tubes form near the electrodes, as shown in Fig. 1~a!. The interaction of electrical driven vortex rings and gravity driven vortex tubes and their effects on the deposit morphology will be discussed in a forthcoming pap ...
Ion transport in a partially ionized impure edge plasma
... by introducing impurities into the plasma edge, which gives rise to radiative cooling of the divertor plasma and can lower the temperature to the range of 1 eV or less, where recombination occurs. The neutral atom density then rises in the divertor, and the plasma loses parallel momentum and energy ...
... by introducing impurities into the plasma edge, which gives rise to radiative cooling of the divertor plasma and can lower the temperature to the range of 1 eV or less, where recombination occurs. The neutral atom density then rises in the divertor, and the plasma loses parallel momentum and energy ...
Electrophoretic Motion of Two Spherical Particles with Thick Double
... In the above equations, we have specified constant potential or constant charge boundary conditions but other, intermediate, boundary conditions could be chosen. For the electrophoresis of a uniform sphere, the electrical surface boundary condition does not affect the electrophoretic velocity (11) b ...
... In the above equations, we have specified constant potential or constant charge boundary conditions but other, intermediate, boundary conditions could be chosen. For the electrophoresis of a uniform sphere, the electrical surface boundary condition does not affect the electrophoretic velocity (11) b ...












![[PDF]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008813343_1-c9037c6d214de044e69add9dc387c93c-300x300.png)