Searching for Magnetic Monopoles - LIGO
... NO evidence for Grand Unified Monopoles at level of Astrophysics ...
... NO evidence for Grand Unified Monopoles at level of Astrophysics ...
The Origin of Mass - Massachusetts Institute of Technology
... Linear Collider in the late 1960s, for which Jerome Friedman, Henry Kendall, and Richard Taylor won the Nobel Prize in 1990. Since our analysis of the scaling experiments using QCD was (necessarily) more complicated and indirect, I’ve chosen to focus here on the later, but simpler to understand, exp ...
... Linear Collider in the late 1960s, for which Jerome Friedman, Henry Kendall, and Richard Taylor won the Nobel Prize in 1990. Since our analysis of the scaling experiments using QCD was (necessarily) more complicated and indirect, I’ve chosen to focus here on the later, but simpler to understand, exp ...
1 Press release Brussels, 8 October 2013 Nobel Prize for
... Peter Higgs, authored an article in Physical Review Letters that relates the electromagnetic force, with infinite range, to the "weak" interaction of radioactivity, with a range limited to an atom's nucleus. A mechanism known as "spontaneous symmetry breaking" would indeed unify these two types of i ...
... Peter Higgs, authored an article in Physical Review Letters that relates the electromagnetic force, with infinite range, to the "weak" interaction of radioactivity, with a range limited to an atom's nucleus. A mechanism known as "spontaneous symmetry breaking" would indeed unify these two types of i ...
Atomic Structure
... elucidated by Rutherford. Atomic masses of different atoms could not be explained if it was accepted that atoms consisted only of protons and electrons. Thus, Rutherford (1920) suggested that in an atom, there must be present at least a third type of fundamental particles which should be electricall ...
... elucidated by Rutherford. Atomic masses of different atoms could not be explained if it was accepted that atoms consisted only of protons and electrons. Thus, Rutherford (1920) suggested that in an atom, there must be present at least a third type of fundamental particles which should be electricall ...
Physics 1520, Spring 2013
... objects (nylon against silk, glass against polyester, etc.) and each of the metal balls is charged by touching them with one of these objects. It is found that balls 1 and 2 attract each other and that balls 2 and 3 repel each other. From this we can conclude that (a) ...
... objects (nylon against silk, glass against polyester, etc.) and each of the metal balls is charged by touching them with one of these objects. It is found that balls 1 and 2 attract each other and that balls 2 and 3 repel each other. From this we can conclude that (a) ...
Mirror symmetry and the half-filled Landau level
... equivalence in terms of dual partition functions was provided by Kapustin and Strassler [47]. A proof of the duality was essentially given by Borokhov, Kapustin, and Wu [48] by matching the Hilbert space of the two theories. Additional evidence for the duality was provided recently by a matching of ...
... equivalence in terms of dual partition functions was provided by Kapustin and Strassler [47]. A proof of the duality was essentially given by Borokhov, Kapustin, and Wu [48] by matching the Hilbert space of the two theories. Additional evidence for the duality was provided recently by a matching of ...
Integrable Lattice Models From Gauge Theory
... Actually, there is a subtle but important difference between the R-matrix that solves the YangBaxter equation and the S-matrix that describes particle scattering in an integrable relativistic field theory. The reason for this is that the Yang-Baxter equation is not sensitive to an overall c-number f ...
... Actually, there is a subtle but important difference between the R-matrix that solves the YangBaxter equation and the S-matrix that describes particle scattering in an integrable relativistic field theory. The reason for this is that the Yang-Baxter equation is not sensitive to an overall c-number f ...
Document
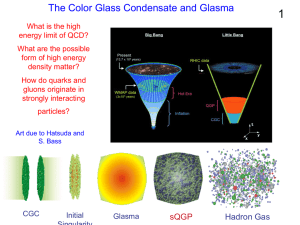
... Time dilation -> Classical field is glassy High phase space density -> Condensate Phase space density: Attractive potential ...
... Time dilation -> Classical field is glassy High phase space density -> Condensate Phase space density: Attractive potential ...