Light consists of electromagnetic waves that have oscillating electric
... systems, such (infinitely spread) plane waves do not exist because of the finite size of the optical elements. Non-planar optical components cause further deviations of the wave from planarity so the wave acquires a ray direction that varies from point to point on the wave front. In a cylindrically ...
... systems, such (infinitely spread) plane waves do not exist because of the finite size of the optical elements. Non-planar optical components cause further deviations of the wave from planarity so the wave acquires a ray direction that varies from point to point on the wave front. In a cylindrically ...
Main presentation title goes here.
... different wavelengths are placed either side of the cavity provide way of measuring coupling ...
... different wavelengths are placed either side of the cavity provide way of measuring coupling ...
TO THE POSSIBILITY OF CALCULATION
... number of detectors in the array. The robustness is limited to that of a single element since the failure of any of them means the loss of the information the damaged one was supposed to receive. Finally, the complexity increases due to the fact that individual detection itself requires a large numb ...
... number of detectors in the array. The robustness is limited to that of a single element since the failure of any of them means the loss of the information the damaged one was supposed to receive. Finally, the complexity increases due to the fact that individual detection itself requires a large numb ...
lecture 3 Introduction to Laser
... current density ( I th) is too high and therefore restricted to operating at very low temperatures. Remedy: Heterostructure semiconductor laser diodes. What must be accomplished? - reduce threshold current to a usable level - improvement of the rate of stimulated emission as well as the efficiency o ...
... current density ( I th) is too high and therefore restricted to operating at very low temperatures. Remedy: Heterostructure semiconductor laser diodes. What must be accomplished? - reduce threshold current to a usable level - improvement of the rate of stimulated emission as well as the efficiency o ...
Electromagnetic forces for an arbitrary optical trapping of a spherical
... missing mechanical measurements in the world of microorganisms and cells that could be correlated to biochemical information. The importance of understanding the optical forces in dielectric beads under different incident beam conditions comes from the fact that they are the natural transducer for f ...
... missing mechanical measurements in the world of microorganisms and cells that could be correlated to biochemical information. The importance of understanding the optical forces in dielectric beads under different incident beam conditions comes from the fact that they are the natural transducer for f ...
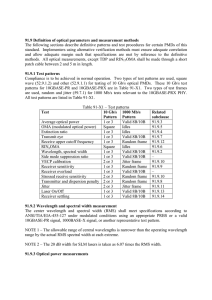
91.9 Definition of optical parameters and measurement methods
... NOTE 1 – This Bessel-Thomson filter is not intended to represent the noise filter within an optical receiver, but is intended to provide uniform measurement conditions on the transmitter. NOTE 2 – The fourth order Bessel-Thomson filter is reactive. In order to suppress reflections, an attenuator may ...
... NOTE 1 – This Bessel-Thomson filter is not intended to represent the noise filter within an optical receiver, but is intended to provide uniform measurement conditions on the transmitter. NOTE 2 – The fourth order Bessel-Thomson filter is reactive. In order to suppress reflections, an attenuator may ...
Experimental implementation of the gyrator transform - E
... We observe that for ␣ = , occurring when the generalized lenses L1 and L2 are reduced to the spherical lenses, the common 4-f system—a cascade of two Fourier transforming systems—is obtained. Therefore the proposed gyrator system can be considered as a generalization of the well-known optical proce ...
... We observe that for ␣ = , occurring when the generalized lenses L1 and L2 are reduced to the spherical lenses, the common 4-f system—a cascade of two Fourier transforming systems—is obtained. Therefore the proposed gyrator system can be considered as a generalization of the well-known optical proce ...
Cost-effective optical coherence tomography spectrometer based on
... The feasibility of a TFBG-spectrometer for SD-OCT was successfully demonstrated. The prototypes maximum sensitivity reaches 108 dB at 100 µs integration time and an overall sensitivity fall-off of -34 dB across 6.4 mm detection length. Cross-sectional 2-D OCT images of a fruit, a human fingertip and ...
... The feasibility of a TFBG-spectrometer for SD-OCT was successfully demonstrated. The prototypes maximum sensitivity reaches 108 dB at 100 µs integration time and an overall sensitivity fall-off of -34 dB across 6.4 mm detection length. Cross-sectional 2-D OCT images of a fruit, a human fingertip and ...
N. Qureshi, H. Schmidt, A. Hawkins, “Near
... In the polar magneto-optic Kerr effect, linearly polarized light impinging normal to the surface of a reflective magnetized material experiences a rotation in the plane of polarization upon reflection6. This results from the fact that the material has different refractive indices for the two circula ...
... In the polar magneto-optic Kerr effect, linearly polarized light impinging normal to the surface of a reflective magnetized material experiences a rotation in the plane of polarization upon reflection6. This results from the fact that the material has different refractive indices for the two circula ...
Optical Monte Carlo modeling of a true port wine stain anatomy
... weight is converted to W [J/cm3] and accumulated in an energy deposition matrix, which has the same dimensions as the material property matrix. The material property matrix can be generated from mathematical constructs or actual data, such as digitized optical coherence tomography, confocal microsco ...
... weight is converted to W [J/cm3] and accumulated in an energy deposition matrix, which has the same dimensions as the material property matrix. The material property matrix can be generated from mathematical constructs or actual data, such as digitized optical coherence tomography, confocal microsco ...
12. confocal microscopy.
... Confocal microscopy can render depth-resolved slices through a 3D object by rejecting much of the out of focus light via a pinhole. In confocal microscopy the image is reconstructed serially, i.e. point by point, using a single photodetector, rather than in parallel (in bright field, phase contrast, ...
... Confocal microscopy can render depth-resolved slices through a 3D object by rejecting much of the out of focus light via a pinhole. In confocal microscopy the image is reconstructed serially, i.e. point by point, using a single photodetector, rather than in parallel (in bright field, phase contrast, ...
Use of Broadband, Continuous-Wave Diode Lasers in Cavity Ring
... Cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS) is a relatively new technique heralded as an extremely sensitive measure of absorption. 1 It has generally been applied to molecules in the gas phase with excellent results. 2 CRDS employs highly re ective mirrors to form an optical cavity. Laser light is allowe ...
... Cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS) is a relatively new technique heralded as an extremely sensitive measure of absorption. 1 It has generally been applied to molecules in the gas phase with excellent results. 2 CRDS employs highly re ective mirrors to form an optical cavity. Laser light is allowe ...
Interferometry
Interferometry is a family of techniques in which waves, usually electromagnetic, are superimposed in order to extract information about the waves. Interferometry is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy (and its applications to chemistry), quantum mechanics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, remote sensing, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, and velocimetry.Interferometers are widely used in science and industry for the measurement of small displacements, refractive index changes and surface irregularities. In analytical science, interferometers are used in continuous wave Fourier transform spectroscopy to analyze light containing features of absorption or emission associated with a substance or mixture. An astronomical interferometer consists of two or more separate telescopes that combine their signals, offering a resolution equivalent to that of a telescope of diameter equal to the largest separation between its individual elements.