Rays and Optical beams
... II. The variational principle and ray propagation in lenslike media Consider the propagation of rays in an optically inhomogeneous medium. In the realm of geometrical optics, a ray travels between two points P1 and P2 along a trajectory such that the time taken is the least. More formally, the traye ...
... II. The variational principle and ray propagation in lenslike media Consider the propagation of rays in an optically inhomogeneous medium. In the realm of geometrical optics, a ray travels between two points P1 and P2 along a trajectory such that the time taken is the least. More formally, the traye ...
45.Z-scan measurement of the nonlinear refractive index of graphene
... shown) on optical transmission measurements. Different graphene samples, with one, two, three, four, and six layers, were used in the experiments reported below. The fabrication process produces loosely stacked graphene layers wherein the optical properties are expected to arise from the cumulative ...
... shown) on optical transmission measurements. Different graphene samples, with one, two, three, four, and six layers, were used in the experiments reported below. The fabrication process produces loosely stacked graphene layers wherein the optical properties are expected to arise from the cumulative ...
Geometric Optics
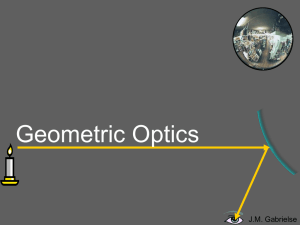
... The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and reflects through the focal point. The second ray comes through the focal point and reflects parallel to the optical axis. The light rays don’t converge, but the sight lines do. A virtual image forms where the sight lines converge. ...
... The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and reflects through the focal point. The second ray comes through the focal point and reflects parallel to the optical axis. The light rays don’t converge, but the sight lines do. A virtual image forms where the sight lines converge. ...
The Dizzying Depths of the Cylindrical Mirror
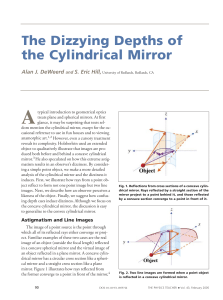
... lines and the eye determines the direction in which the likeness is viewed. This is shown in Fig. 3 for two eyes in different locations. Unlike an image in which a point of an object is mapped to a single point, the likeness cannot be considered to have a fixed location. As an observer moves left or ...
... lines and the eye determines the direction in which the likeness is viewed. This is shown in Fig. 3 for two eyes in different locations. Unlike an image in which a point of an object is mapped to a single point, the likeness cannot be considered to have a fixed location. As an observer moves left or ...
Slide 1
... The light from the input fibre is collimated and applied to the diffraction grating The diffraction grating separates the input light into different angles depending on wavelength The light from the grating is then focused onto an output slit The grating is rotated to select the wavelength that reac ...
... The light from the input fibre is collimated and applied to the diffraction grating The diffraction grating separates the input light into different angles depending on wavelength The light from the grating is then focused onto an output slit The grating is rotated to select the wavelength that reac ...
5. INTERFERENCE. Introduction.
... An important way of achieving the conditions for exhibiting interference effects, ie. obtaining two or more oscillating electric fields and then sending them on different paths before recombining them to observe interference is to split a primary wave into two separate secondary waves by partial ref ...
... An important way of achieving the conditions for exhibiting interference effects, ie. obtaining two or more oscillating electric fields and then sending them on different paths before recombining them to observe interference is to split a primary wave into two separate secondary waves by partial ref ...
Overview
... -So, the index is a function of wavelength -Therefore, the amount of refraction is different -This effect is called chromatic dispersion ...
... -So, the index is a function of wavelength -Therefore, the amount of refraction is different -This effect is called chromatic dispersion ...
Top downloaded Optics Express article for March.
... A review of nanoplasmonics is given. This includes fundamentals, nanolocalization of optical energy and hot spots, ultrafast nanoplasmonics and control of the spatiotemporal nanolocalization of optical fields, and quantum nanoplasmonics (spaser and gain-assisted plasmonics). This article reviews... ...
... A review of nanoplasmonics is given. This includes fundamentals, nanolocalization of optical energy and hot spots, ultrafast nanoplasmonics and control of the spatiotemporal nanolocalization of optical fields, and quantum nanoplasmonics (spaser and gain-assisted plasmonics). This article reviews... ...
Analysis of the detective quantum efficiency of
... A scatteringprocess is characterizedby the modulation transfer function of the stage,T(f), which is equal to the magnitude of the Fourier transform of the scatter line spread function normalized to unity at zero frequency. The signal and noise propagation are given by ...
... A scatteringprocess is characterizedby the modulation transfer function of the stage,T(f), which is equal to the magnitude of the Fourier transform of the scatter line spread function normalized to unity at zero frequency. The signal and noise propagation are given by ...
Scattered Light Predictions for Aluminum Painted Reflectors in
... painted reflectors, micro-roughness causes incident light to be scattered or diffusely reflected off the surface in numerous directions. The geometric nature of the surface determines the distribution of the reflected scattered light. Therefore, measurements of how the material scatters a wellcharac ...
... painted reflectors, micro-roughness causes incident light to be scattered or diffusely reflected off the surface in numerous directions. The geometric nature of the surface determines the distribution of the reflected scattered light. Therefore, measurements of how the material scatters a wellcharac ...
Ray Diagrams Powerpoint
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (the incidence angle, θi) as it reflects off the mirror (the reflection angle, θr). ...
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (the incidence angle, θi) as it reflects off the mirror (the reflection angle, θr). ...
Interferometry
Interferometry is a family of techniques in which waves, usually electromagnetic, are superimposed in order to extract information about the waves. Interferometry is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy (and its applications to chemistry), quantum mechanics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, remote sensing, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, and velocimetry.Interferometers are widely used in science and industry for the measurement of small displacements, refractive index changes and surface irregularities. In analytical science, interferometers are used in continuous wave Fourier transform spectroscopy to analyze light containing features of absorption or emission associated with a substance or mixture. An astronomical interferometer consists of two or more separate telescopes that combine their signals, offering a resolution equivalent to that of a telescope of diameter equal to the largest separation between its individual elements.