Journal of Theoretics MODELS OF THE ATOMIC NUCLEI
... The results of our previous theoretical and experimental investigations are assumed as a basis of formation of the atomic nuclei of the chemical elements [1], [2]. The analysis of the laws of formation of the spectra shows that the electrons in the atoms do not have an orbital movement. The electron ...
... The results of our previous theoretical and experimental investigations are assumed as a basis of formation of the atomic nuclei of the chemical elements [1], [2]. The analysis of the laws of formation of the spectra shows that the electrons in the atoms do not have an orbital movement. The electron ...
CHAPTER 14: Elementary Particles
... act through the strong force. Two classes of hadrons: mesons and baryons. Mesons are particles with integral spin having masses greater than that of the muon (106 MeV/c2). (Mesons are made up of pairs of quarks—a quark and an anti-quark.) They’re unstable and rare. Baryons have masses at least as la ...
... act through the strong force. Two classes of hadrons: mesons and baryons. Mesons are particles with integral spin having masses greater than that of the muon (106 MeV/c2). (Mesons are made up of pairs of quarks—a quark and an anti-quark.) They’re unstable and rare. Baryons have masses at least as la ...
exploring cosmic strings: observable effects and cosmological
... and/or superstring theory. In this regard, I present new mechanisms to produce particles from cosmic (super)strings, and discuss their cosmological and observational effects in this dissertation. The first chapter is devoted to a review of the standard cosmology, cosmic (super)strings and cosmic ray ...
... and/or superstring theory. In this regard, I present new mechanisms to produce particles from cosmic (super)strings, and discuss their cosmological and observational effects in this dissertation. The first chapter is devoted to a review of the standard cosmology, cosmic (super)strings and cosmic ray ...
Inorganic Chemistry - Bharathiar University(Older Version Website)
... anion skeleton is penetrated by channels, giving a honeycomb like structure. These channels are large enough to allow them to exchange certain ions. They can also absorb or lose water, and other small molecules without the structure being broken. Zeolities are often used as ion- ...
... anion skeleton is penetrated by channels, giving a honeycomb like structure. These channels are large enough to allow them to exchange certain ions. They can also absorb or lose water, and other small molecules without the structure being broken. Zeolities are often used as ion- ...
Elliptic Flow Measurement of Heavy-Flavour Decay Electrons in Pb
... of Pb-Pb collisions at sN N = 2.76 TeV with ALICE at LHC. The collective motion of the particles inside the medium which is created in the heavy-ion collisions can be analyzed by a Fourier decomposition of the azimuthal anisotropic particle distribution with respect to the event plane. Elliptic flow ...
... of Pb-Pb collisions at sN N = 2.76 TeV with ALICE at LHC. The collective motion of the particles inside the medium which is created in the heavy-ion collisions can be analyzed by a Fourier decomposition of the azimuthal anisotropic particle distribution with respect to the event plane. Elliptic flow ...
J. J. Thomson From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia This article is
... On 22 December 1884 Thomson was chosen to become Cavendish Professor of Physics at the University of Cambridge.[3] The appointment caused considerable surprise, given that candidates such as Richard Glazebrook were older and more experienced in laboratory work. Thomson was known for his work as a ma ...
... On 22 December 1884 Thomson was chosen to become Cavendish Professor of Physics at the University of Cambridge.[3] The appointment caused considerable surprise, given that candidates such as Richard Glazebrook were older and more experienced in laboratory work. Thomson was known for his work as a ma ...
Describing Dark Matter with Effective Operators
... Dark matter particles from the Galactic halo that pass through the Earth will occasionally scatter off nuclei. The resulting recoil energy of the nucleus can be measured in dedicated low background detectors. Dark matter ...
... Dark matter particles from the Galactic halo that pass through the Earth will occasionally scatter off nuclei. The resulting recoil energy of the nucleus can be measured in dedicated low background detectors. Dark matter ...
here.
... • The physics of particles and fields deals with the fundamental constituents of matter and their interactions. This branch of physics is also called (elementary) particle physics or high energy physics and sometimes sub-atomic or sub-nuclear physics. Sub-atomic/nuclear means of size less than atomi ...
... • The physics of particles and fields deals with the fundamental constituents of matter and their interactions. This branch of physics is also called (elementary) particle physics or high energy physics and sometimes sub-atomic or sub-nuclear physics. Sub-atomic/nuclear means of size less than atomi ...
Notes for course on Physics of Particles and Fields, CMI, Autumn
... • The physics of particles and fields deals with the fundamental constituents of matter and their interactions. This branch of physics is also called (elementary) particle physics or high energy physics and sometimes sub-atomic or sub-nuclear physics. Subatomic/nuclear means of size less than atomic ...
... • The physics of particles and fields deals with the fundamental constituents of matter and their interactions. This branch of physics is also called (elementary) particle physics or high energy physics and sometimes sub-atomic or sub-nuclear physics. Subatomic/nuclear means of size less than atomic ...
ASPECTS OF THE MCMASTER INTENSE POSITRON BEAM
... research reactor located on the campus of McMaster University, and is one of the few research reactors still in operation in North America. ...
... research reactor located on the campus of McMaster University, and is one of the few research reactors still in operation in North America. ...
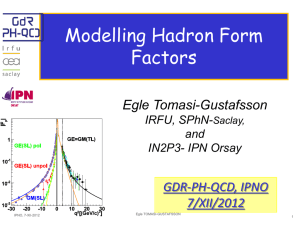
GDR-PH-QCD, IPNO 7/XII/2012
... The point-like hadron pair expands and cools down: the current quarks and antiquarks absorb gluon and transform into constituent quarks ...
... The point-like hadron pair expands and cools down: the current quarks and antiquarks absorb gluon and transform into constituent quarks ...
Chapter 8 CHEM 161
... How to change the energy of the atom? Add energy, as light (E = h) or other form. Electron raised to higher n orbit n = 2, 3, 4, … Higher n orbits = excited states = less stable So electron quickly drops to lower energy orbit and emits photon of energy equal to E between levels ...
... How to change the energy of the atom? Add energy, as light (E = h) or other form. Electron raised to higher n orbit n = 2, 3, 4, … Higher n orbits = excited states = less stable So electron quickly drops to lower energy orbit and emits photon of energy equal to E between levels ...