Strategies for the compensation of specimen
... We now look at the effects of using the iris to reduce the pupil size (effective NA) when focusing to a certain depth in the dermis. The specifications of the lenses we consider are typical of those currently commercially available. For all the following examples we take the wavelength of the illumi ...
... We now look at the effects of using the iris to reduce the pupil size (effective NA) when focusing to a certain depth in the dermis. The specifications of the lenses we consider are typical of those currently commercially available. For all the following examples we take the wavelength of the illumi ...
Chapter 18
... so that each of its two refracting surfaces is a segment of either a sphere or a plane • Lenses are commonly used to form images by refraction in optical instruments • These are examples of converging lenses – they are thickest in the middle and have positive focal lengths ...
... so that each of its two refracting surfaces is a segment of either a sphere or a plane • Lenses are commonly used to form images by refraction in optical instruments • These are examples of converging lenses – they are thickest in the middle and have positive focal lengths ...
Super-resolution Microscopy
... technological advances have enabled elucidation of biological phenomenon at cellular, subcellular and even at molecular levels. However, the latest incarnation of the modern fluorescence microscope has led to a paradigm shift. This wave is about breaking the diffraction limit first proposed in 1873 ...
... technological advances have enabled elucidation of biological phenomenon at cellular, subcellular and even at molecular levels. However, the latest incarnation of the modern fluorescence microscope has led to a paradigm shift. This wave is about breaking the diffraction limit first proposed in 1873 ...
VII-3
... Huygens’ Principle III • If light is traveling through homogeneous isotropic media without obstacles Huygens’ principle gives us the same results as ray (geometrical) optics including effects as reflection and refraction. • However, when there is e.g. an obstacle then wave fronts will be not only d ...
... Huygens’ Principle III • If light is traveling through homogeneous isotropic media without obstacles Huygens’ principle gives us the same results as ray (geometrical) optics including effects as reflection and refraction. • However, when there is e.g. an obstacle then wave fronts will be not only d ...
LAB #10 - GEOCITIES.ws
... bench at the 100 cm mark. Move the lens back and forth along the bench until you obtain a sharp image of the light on the screen. NOTE: For one of the lenses you may be unable to obtain a clear image. Identify this lens in your notes and continue with the next. Record both the image and the object d ...
... bench at the 100 cm mark. Move the lens back and forth along the bench until you obtain a sharp image of the light on the screen. NOTE: For one of the lenses you may be unable to obtain a clear image. Identify this lens in your notes and continue with the next. Record both the image and the object d ...
Atchison Eye Models For Correction
... The refractive index of the eye lens is not constant The refractive index increases from the edge towards the centre i.e. there is a gradient index This gradient index means that light does not travel in straight lines inside the lens The gradient index produce its own power independent of lens surf ...
... The refractive index of the eye lens is not constant The refractive index increases from the edge towards the centre i.e. there is a gradient index This gradient index means that light does not travel in straight lines inside the lens The gradient index produce its own power independent of lens surf ...
Subwavelength dynamic focusing in plasmonic nanostructures using time reversal * Guy Bartal,
... spatial frequencies, propagating back with a propagation constant of the same magnitude 共and opposite sign兲. The time-reversed beam intensity at the MDML output is plotted in 关Fig. 3共d兲兴. The intensity full width at half maximum 共FWHM兲 is limited by the width of the dielectric waveguide, to 30 nm. N ...
... spatial frequencies, propagating back with a propagation constant of the same magnitude 共and opposite sign兲. The time-reversed beam intensity at the MDML output is plotted in 关Fig. 3共d兲兴. The intensity full width at half maximum 共FWHM兲 is limited by the width of the dielectric waveguide, to 30 nm. N ...
RAY OPTICS I
... initially parallel to the axis of the lens. According to the definition of the focal point of the lens, that ray will be bent so that it goes through the focal point on the other side of the lens. 3. The third principal ray is that particular ray that moves away from the point in a direction initial ...
... initially parallel to the axis of the lens. According to the definition of the focal point of the lens, that ray will be bent so that it goes through the focal point on the other side of the lens. 3. The third principal ray is that particular ray that moves away from the point in a direction initial ...
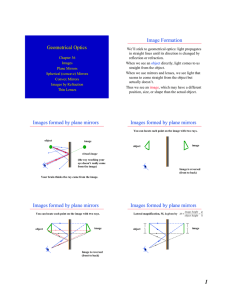
Geometrical Optics Image Formation Images formed by plane
... • A lens is an optical device in which the optical path length is varied so that images can be formed. Snell’s Law applied at each surface will show where the light comes to a focus. ...
... • A lens is an optical device in which the optical path length is varied so that images can be formed. Snell’s Law applied at each surface will show where the light comes to a focus. ...
LxxA, Overview of Microscopy methods, part a
... • Chemical composition of materials can be obtained using electron microprobes to produce characteristic X-ray emissions and electron energy losses. • Imaging (surface) can be characterized using secondary electrons, backscattered electrons, photo-electron, Auger electrons and ion scattering. • Crys ...
... • Chemical composition of materials can be obtained using electron microprobes to produce characteristic X-ray emissions and electron energy losses. • Imaging (surface) can be characterized using secondary electrons, backscattered electrons, photo-electron, Auger electrons and ion scattering. • Crys ...
waves-summary-notes-gairloch1
... can be passed through a lens and picked up by another bundle of fibres and carried back outside the body where it can be viewed by the doctor. Other devices use optical fibres to carry light inside the patient but the reflected light is picked up by a tiny camera. This picture can then be displayed ...
... can be passed through a lens and picked up by another bundle of fibres and carried back outside the body where it can be viewed by the doctor. Other devices use optical fibres to carry light inside the patient but the reflected light is picked up by a tiny camera. This picture can then be displayed ...
Porous Biomimetic Microlens Arrays as Multifunctional Optical
... corneal lens that can create a field-of-view (FOV) on its own and vary in an angle, which then overlap to provide a composite image of the world to the insect brain. A dragonfly eye contains about 28, 000 ommatidia, which covers a 70o horizontal and 90o vertical range of view. Some vertebrate animal ...
... corneal lens that can create a field-of-view (FOV) on its own and vary in an angle, which then overlap to provide a composite image of the world to the insect brain. A dragonfly eye contains about 28, 000 ommatidia, which covers a 70o horizontal and 90o vertical range of view. Some vertebrate animal ...
Ch7 Microscopes Notes Powerpoint
... the visible absorption spectrum or IR spectrum of the material being observed. • This instrument is especially useful in the examination of trace evidence, paint, fiber, and ink evidence. FORENSIC SCIENCE An Introduction By Richard Saferstein ...
... the visible absorption spectrum or IR spectrum of the material being observed. • This instrument is especially useful in the examination of trace evidence, paint, fiber, and ink evidence. FORENSIC SCIENCE An Introduction By Richard Saferstein ...
... In recent years important progress has been made in the generation of ultrashort laser pulses. The maximum intensity is fundamental in many applications, therefore the measurement of these pulses is also fundamental. It is important that these measurements be performed with optical elements that do ...
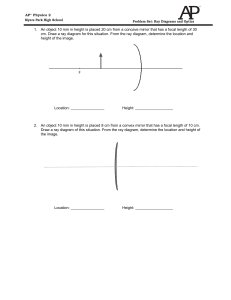
AP® Physics 2 Myers Park High School Problem Set: Ray Diagrams
... b. vacuum c. air d. glass 2. Refraction, as light goes from air to glass, results from differences in light's _____. a. frequency in air and glass b. incident angle c. speed in air and glass d. all of the above. 3. Light refracts when traveling from air into glass because light _____. a. intensity i ...
... b. vacuum c. air d. glass 2. Refraction, as light goes from air to glass, results from differences in light's _____. a. frequency in air and glass b. incident angle c. speed in air and glass d. all of the above. 3. Light refracts when traveling from air into glass because light _____. a. intensity i ...
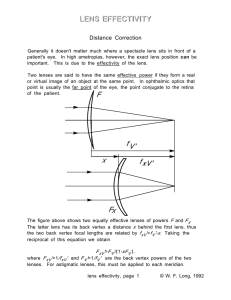
Lens Effectivity (WP)
... vergence of light reaching the first principal plane of the eye is B P =-11D/[1-(0.017m)(-11D)]=-9.267D. The ocular refraction (principal point refraction) of the eye is K =-8D/[1-(0.017m)(-8D)]=-7.042D. The required principal point accommodation is A = K-B P = -7.042D-(-9.267D)=+2.22D. For the eigh ...
... vergence of light reaching the first principal plane of the eye is B P =-11D/[1-(0.017m)(-11D)]=-9.267D. The ocular refraction (principal point refraction) of the eye is K =-8D/[1-(0.017m)(-8D)]=-7.042D. The required principal point accommodation is A = K-B P = -7.042D-(-9.267D)=+2.22D. For the eigh ...
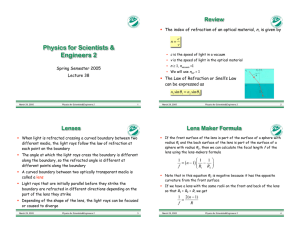
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2
... ! Assume that a light ray parallel to the optical axis is incident on a concave glass lens ! At the surface of the lens, the light rays are refracted toward the normal ! When the rays leave the lens, they are refracted away from the normal as shown ! The extrapolated line shown as a red and black da ...
... ! Assume that a light ray parallel to the optical axis is incident on a concave glass lens ! At the surface of the lens, the light rays are refracted toward the normal ! When the rays leave the lens, they are refracted away from the normal as shown ! The extrapolated line shown as a red and black da ...
Chapter 23
... so that each of its two refracting surfaces is a segment of either a sphere or a plane • Lenses are commonly used to form images by refraction in optical instruments • These are examples of converging lenses – they are thickest in the middle and have positive focal lengths ...
... so that each of its two refracting surfaces is a segment of either a sphere or a plane • Lenses are commonly used to form images by refraction in optical instruments • These are examples of converging lenses – they are thickest in the middle and have positive focal lengths ...
New imaging modes for lenslet-array tandem scanning microscopes
... the illumination and detection pinhole arrays are placed diametrically opposite on a spinning Nipkow disc. A subsequent development permitted the same pinhole array to be used for both illumination and detection (Xiao et al., 1988). A recent development to this ‘single-sided’ TSM has been the introd ...
... the illumination and detection pinhole arrays are placed diametrically opposite on a spinning Nipkow disc. A subsequent development permitted the same pinhole array to be used for both illumination and detection (Xiao et al., 1988). A recent development to this ‘single-sided’ TSM has been the introd ...
PHYS 202 Notes, Week 10
... This week we learn about optical instruments, interference, and thin films. ...
... This week we learn about optical instruments, interference, and thin films. ...
Palladium Ultra Thin Layer Profiles Evaluation by Evanescent Light
... field optical microscopy measurement technique developed to achieve a high resolution for nanometer profiles investigations albeit only into the depth, i.e., z-direction of the samples surface [1-4]. The technique is based on the phenomenon of Total Internal Reflection (TIR) [5,6] at interfaces wher ...
... field optical microscopy measurement technique developed to achieve a high resolution for nanometer profiles investigations albeit only into the depth, i.e., z-direction of the samples surface [1-4]. The technique is based on the phenomenon of Total Internal Reflection (TIR) [5,6] at interfaces wher ...
TO THE POSSIBILITY OF CALCULATION
... are evident: first, a single Airy Disk covers several photodetectors therefore it should create a blurry image, according to the diffraction limit for CCDs; second, the minimum detectable detail size, given by the minimum angle of resolution through this criterion, is about 50 seconds of arc. ...
... are evident: first, a single Airy Disk covers several photodetectors therefore it should create a blurry image, according to the diffraction limit for CCDs; second, the minimum detectable detail size, given by the minimum angle of resolution through this criterion, is about 50 seconds of arc. ...
Full text
... this study, we have focused our attention on simple shapes including annuli and single spots, although the TAG lens is capable of more complex patterns [17]. We denote these instantaneous patterns as our “basis.” In general, the frequency affects the diameter of the ring, while the amplitude affects ...
... this study, we have focused our attention on simple shapes including annuli and single spots, although the TAG lens is capable of more complex patterns [17]. We denote these instantaneous patterns as our “basis.” In general, the frequency affects the diameter of the ring, while the amplitude affects ...
Dynamic pulsed-beam shaping using a TAG lens in the
... this study, we have focused our attention on simple shapes including annuli and single spots, although the TAG lens is capable of more complex patterns [17]. We denote these instantaneous patterns as our “basis.” In general, the frequency affects the diameter of the ring, while the amplitude affects ...
... this study, we have focused our attention on simple shapes including annuli and single spots, although the TAG lens is capable of more complex patterns [17]. We denote these instantaneous patterns as our “basis.” In general, the frequency affects the diameter of the ring, while the amplitude affects ...
Fourier domain optical coherence tomography with an
... into Polymethyl-methacrylate (PMMA) on an E-beam machine, and then used in a stepper as a phase mask to create an analog axicon profile on a silica wafer. It was then developed and etched into the silica wafer. The fabricated axicon picture is shown in Fig. 3 (a). We also analyzed the etched axicon ...
... into Polymethyl-methacrylate (PMMA) on an E-beam machine, and then used in a stepper as a phase mask to create an analog axicon profile on a silica wafer. It was then developed and etched into the silica wafer. The fabricated axicon picture is shown in Fig. 3 (a). We also analyzed the etched axicon ...
Superlens

A practical superlens, or super lens, is a lens which uses metamaterials to go beyond the diffraction limit. The diffraction limit is a feature of conventional lenses and microscopes that limits the fineness of their resolution. Many lens designs have been proposed that go beyond the diffraction limit in some way, but there are constraints and obstacles involved in realizing each of them.