Binomial random variables
... 3. The probability is 0.04 that a person reached on a “cold call” by a telemarketer will make a purchase. If the telemarketer calls 40 people, what is the probability that at least one sale with ...
... 3. The probability is 0.04 that a person reached on a “cold call” by a telemarketer will make a purchase. If the telemarketer calls 40 people, what is the probability that at least one sale with ...
Sec. 6.3 Part 2 Blank Notes
... The probability of ____________________________ is then found by __________________________of all branches that are part of ________________ ...
... The probability of ____________________________ is then found by __________________________of all branches that are part of ________________ ...
Notes on Random Variables, Expectations, Probability Densities
... This definition is often not very helpful if we are trying to calculate conditional expectations, but it makes it easy to understand the main applications of conditional expectations in finance. Just as we can take the expectation of an indicator function to get the probability of a set of numbers ( ...
... This definition is often not very helpful if we are trying to calculate conditional expectations, but it makes it easy to understand the main applications of conditional expectations in finance. Just as we can take the expectation of an indicator function to get the probability of a set of numbers ( ...
Lecture 8. Random Variables (continued), Expected Value, Variance
... in x, however, is not part of the model itself, but is a choice we make in posing a question that we put to the model. On the other hand, the function X expresses the variation that occurs within the model. Within the model itself, X truly has many values, each being determined by evaluating X at a ...
... in x, however, is not part of the model itself, but is a choice we make in posing a question that we put to the model. On the other hand, the function X expresses the variation that occurs within the model. Within the model itself, X truly has many values, each being determined by evaluating X at a ...
Distinctions Between Probability Situations
... The main formula P(A B) P A P B P A B is still good. The value of P A B has to be obtained by some experience. It is neither zero, like mutually exclusive events, nor is it P(A)P(B), like independent events. Conditional probability is the probability that an event will occur ...
... The main formula P(A B) P A P B P A B is still good. The value of P A B has to be obtained by some experience. It is neither zero, like mutually exclusive events, nor is it P(A)P(B), like independent events. Conditional probability is the probability that an event will occur ...
Discrete Distributions
... Discrete Distributions place probability on specific numbers. For example, the Binomial distribution places probability only on the values 0,1,2, …, n. This is why the probability distributions for discrete random variables are often referred to as probability mass functions. Some random variables, ...
... Discrete Distributions place probability on specific numbers. For example, the Binomial distribution places probability only on the values 0,1,2, …, n. This is why the probability distributions for discrete random variables are often referred to as probability mass functions. Some random variables, ...
1 Math 1313 Expected Value Mean of a Data Set From the last
... From the last lesson, you should be familiar with random variables, and you should be able to construct a probability distribution for a random variable. In this lesson, you will learn how to compute the expected value of a probability distribution of a random variable. We begin with a familiar defi ...
... From the last lesson, you should be familiar with random variables, and you should be able to construct a probability distribution for a random variable. In this lesson, you will learn how to compute the expected value of a probability distribution of a random variable. We begin with a familiar defi ...
Lecture 1
... Definition 3.1 [Filtration] Let (Ω, F, P) be a probability space. A filtration (Fn )n∈N is an increasing sequence of sub σ-algebras of F, i.e., F1 ⊂ F2 ⊂ · · · ⊂ Fn ⊂ · · · ⊂ F. We can think of Fn as information available up to time n. Definition 3.2 [Martingale, super-martingale and sub-martingale] ...
... Definition 3.1 [Filtration] Let (Ω, F, P) be a probability space. A filtration (Fn )n∈N is an increasing sequence of sub σ-algebras of F, i.e., F1 ⊂ F2 ⊂ · · · ⊂ Fn ⊂ · · · ⊂ F. We can think of Fn as information available up to time n. Definition 3.2 [Martingale, super-martingale and sub-martingale] ...
Ch. 4-6 PowerPoint Review
... P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A and B) P(A and B) = P(A) P(B|A) A and B are independent if and only if P(B) = P(B|A) ...
... P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A and B) P(A and B) = P(A) P(B|A) A and B are independent if and only if P(B) = P(B|A) ...
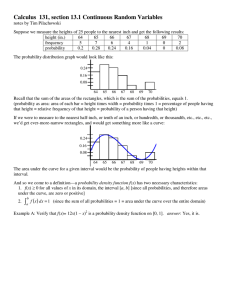
Calculus 131, section 13.1 Continuous Random Variables
... 12 x 1 − x 2 dx = 0 . This isn’t to say that P(x) could never equal zero, ...
... 12 x 1 − x 2 dx = 0 . This isn’t to say that P(x) could never equal zero, ...
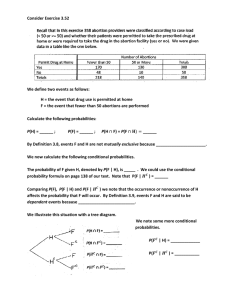
Consider Exercise 3.52 We define two events as follows: H = the
... By Definition 3.8, events F and H are not mutually exclusive because ______________________. We now calculate the following conditional probabilities. The probability of F given H, denoted by P(F | H), is _____ . We could use the conditional probability formula on page 138 of our text. Note that P(F ...
... By Definition 3.8, events F and H are not mutually exclusive because ______________________. We now calculate the following conditional probabilities. The probability of F given H, denoted by P(F | H), is _____ . We could use the conditional probability formula on page 138 of our text. Note that P(F ...