Ocean and Coastal Processes Ocean Basins Ocean Basins Tides
... • The tidal bulge forms on the side facing the moon and the side away from the moon. • If there were no land the tide would pass around the Earth with a 12 h period. • The presence of land masses can cancel or multiply the amplitude. ...
... • The tidal bulge forms on the side facing the moon and the side away from the moon. • If there were no land the tide would pass around the Earth with a 12 h period. • The presence of land masses can cancel or multiply the amplitude. ...
Ch. 11 Coastal Ocean - Seattle Central College
... seismic wave? Which has the longest wavelength? As waves approach shore, when do they break? What 3 factors determine the size of open ocean wind waves? Explain constructive, destructive and mixed interference of waves. Why do waves bend (refract) when they approach shore? How is this different from ...
... seismic wave? Which has the longest wavelength? As waves approach shore, when do they break? What 3 factors determine the size of open ocean wind waves? Explain constructive, destructive and mixed interference of waves. Why do waves bend (refract) when they approach shore? How is this different from ...
Read the article
... mainly northerly wind over western and northern Europe. Then the subtropical high over the Azores is weak as is the Icelandic low. The different phases may last from some years to 20 or more years. At present (2006) we are in a long-lasting positive phase (2). Although these kinds of variability may ...
... mainly northerly wind over western and northern Europe. Then the subtropical high over the Azores is weak as is the Icelandic low. The different phases may last from some years to 20 or more years. At present (2006) we are in a long-lasting positive phase (2). Although these kinds of variability may ...
Intertidal Zone
... are not long-lasting features. The salinity of tidepools varies from the salinity of the sea to much less salty, when rainwater or runoff dilutes it. When salt water left in tide pools evaporates, all that is left is salt deposits. the are Animals that must adapt their systems to these variations. S ...
... are not long-lasting features. The salinity of tidepools varies from the salinity of the sea to much less salty, when rainwater or runoff dilutes it. When salt water left in tide pools evaporates, all that is left is salt deposits. the are Animals that must adapt their systems to these variations. S ...
Global Variations of Chemical Composition of Oceans
... The surface layer salinity ranges from 30-32 to 36.5-37.5‰ in open oceanic waters, far from river-mouths while in the river-mouths it drops down to 1-2‰. In inland seas such as the Red Sea and Arabian Gulf salinity increases up to 40-41‰. The mean surface salinity of the World Ocean is 34.73‰. In th ...
... The surface layer salinity ranges from 30-32 to 36.5-37.5‰ in open oceanic waters, far from river-mouths while in the river-mouths it drops down to 1-2‰. In inland seas such as the Red Sea and Arabian Gulf salinity increases up to 40-41‰. The mean surface salinity of the World Ocean is 34.73‰. In th ...
Tides and topographic waves in the vicinity of the Svalbard islands
... Strong tidal currents occur east of Spitsbergen in the Freeman Sound between the Barents Island and Edge Island, in Heleysundet between the Barents Island and Nordaustlandet, and also in the Hinlopen Strait between Spitsbergen and Nordaustlandet. This is a result of the almost 180 degree phase diffe ...
... Strong tidal currents occur east of Spitsbergen in the Freeman Sound between the Barents Island and Edge Island, in Heleysundet between the Barents Island and Nordaustlandet, and also in the Hinlopen Strait between Spitsbergen and Nordaustlandet. This is a result of the almost 180 degree phase diffe ...
STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 3 TEST 2009
... 15) An oil spill from a tanker is an example of what type of pollution? Point-source pollution 16) Estuaries are important because they? provide breeding grounds for migratory birds, filter out pollution from runoff before it reaches the ocean, is a nutrient rich habitat for many species of aquatic ...
... 15) An oil spill from a tanker is an example of what type of pollution? Point-source pollution 16) Estuaries are important because they? provide breeding grounds for migratory birds, filter out pollution from runoff before it reaches the ocean, is a nutrient rich habitat for many species of aquatic ...
General Circulation and Climate Zones
... sea where the sea ice is usually about 2 to 3 meters thick with a lesser amount of seasonality, and a water column which is very stratified. There is some evidence that global warming is reducing the area of year round sea ice in Arctic, but not (yet?) within the Southern Ocean. ...
... sea where the sea ice is usually about 2 to 3 meters thick with a lesser amount of seasonality, and a water column which is very stratified. There is some evidence that global warming is reducing the area of year round sea ice in Arctic, but not (yet?) within the Southern Ocean. ...
Deep seabed mining - Pacific Ecologist
... country also looking to seabed mining in its waters, or what it claims as its own waters.12 Some mainstream media acknowledge environmental risks, e.g. changing the geography of the ocean floor, and the “dramatic impact” on sea life from water columns or “plumes.”13 It is even acknowledged that the ...
... country also looking to seabed mining in its waters, or what it claims as its own waters.12 Some mainstream media acknowledge environmental risks, e.g. changing the geography of the ocean floor, and the “dramatic impact” on sea life from water columns or “plumes.”13 It is even acknowledged that the ...
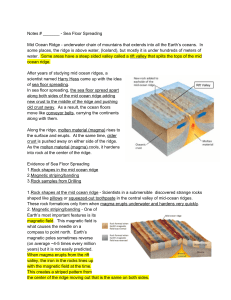
Notes # ______ Sea Floor Spreading Mid Ocean Ridge underwater
... in the central valley of midocean ridges. These rock formations only form when magma erupts underwater and hardens very quickly ...
... in the central valley of midocean ridges. These rock formations only form when magma erupts underwater and hardens very quickly ...
Chapter 8 Review
... • When water stands (lakes), it is called a lentic body of water and when the water flows (rivers) it is called a lotic body of water. These freshwater systems cover less than 2.2% of the earths surface but they still provide many goods and services. • Lakes are formed by precipitation or runoff fil ...
... • When water stands (lakes), it is called a lentic body of water and when the water flows (rivers) it is called a lotic body of water. These freshwater systems cover less than 2.2% of the earths surface but they still provide many goods and services. • Lakes are formed by precipitation or runoff fil ...
Write about this….
... How about this….. • Warm less dense air rises at the equator • Cold dense air falls at the poles ...
... How about this….. • Warm less dense air rises at the equator • Cold dense air falls at the poles ...
Chapter One
... alternating magnetization parallel to the midoceanic ridges. This is evidence for continuous formation of new rock at these ridges. As new rock forms, older rock is pushed farther away from the ridge, producing these patterns in the rock. ...
... alternating magnetization parallel to the midoceanic ridges. This is evidence for continuous formation of new rock at these ridges. As new rock forms, older rock is pushed farther away from the ridge, producing these patterns in the rock. ...
Oceans of Fun
... I'll ride on a wave. In water, I'm brave! My friends will be leading my trail! My friends are the dolphins; my friends are the whales. My friends are the creatures of seafaring tales. They sing in the ocean, they sing in the sea. I know when they're singing, they're singing with me! My friends swim ...
... I'll ride on a wave. In water, I'm brave! My friends will be leading my trail! My friends are the dolphins; my friends are the whales. My friends are the creatures of seafaring tales. They sing in the ocean, they sing in the sea. I know when they're singing, they're singing with me! My friends swim ...
pdf
... 14C – formed from 14N from cosmic radia=on (now bomb 14C is present), absorbed by living organisms, decays to 12C with =me aeer death. Possible up to 40,000 BP. Uranium Series – Corals incorp ...
... 14C – formed from 14N from cosmic radia=on (now bomb 14C is present), absorbed by living organisms, decays to 12C with =me aeer death. Possible up to 40,000 BP. Uranium Series – Corals incorp ...
Exhibits_2015 - Maui Ocean Center
... The Aquarium operates on a semi-open seawater system, pumping ocean water through each exhibit. This exhibit gives visitors a sneak-peek ‘through the walls’ at Maui Ocean Center with a diagram of the Aquarium’s open seawater system, using water pumped from the ocean instead of manufacturing artifici ...
... The Aquarium operates on a semi-open seawater system, pumping ocean water through each exhibit. This exhibit gives visitors a sneak-peek ‘through the walls’ at Maui Ocean Center with a diagram of the Aquarium’s open seawater system, using water pumped from the ocean instead of manufacturing artifici ...
MARINE RESOURCES In PAKISTAN
... The following recommendations are made to expedite resource development of the Pakistan coastal area • Promote education and research in marine science and technology. • Development, management and sustainable utilization of all coasta marine resources. education, research and technology development ...
... The following recommendations are made to expedite resource development of the Pakistan coastal area • Promote education and research in marine science and technology. • Development, management and sustainable utilization of all coasta marine resources. education, research and technology development ...
MBT lec 4
... systems rely on underwater turbines, either horizontal or vertical, which rotate due to either change in the ocean current or changing tide (either one way or bi-directionally), almost like an underwater windmill. ...
... systems rely on underwater turbines, either horizontal or vertical, which rotate due to either change in the ocean current or changing tide (either one way or bi-directionally), almost like an underwater windmill. ...
Short-Hand Notes
... (iv) the chance of a truly monstrous wave is about 1 in a billon but it does happen b) What creates Rouge Waves? ...
... (iv) the chance of a truly monstrous wave is about 1 in a billon but it does happen b) What creates Rouge Waves? ...
Earth Systems:
... what temperature is the salt most effective? ____________________________ Physical Properties of Seawater- Absorption of Light • Light only penetrates the upper 100 m of seawater. Below that depth, everything is ____. • In the darkness of the deep ocean, some organisms including some fish, shrimp, a ...
... what temperature is the salt most effective? ____________________________ Physical Properties of Seawater- Absorption of Light • Light only penetrates the upper 100 m of seawater. Below that depth, everything is ____. • In the darkness of the deep ocean, some organisms including some fish, shrimp, a ...
High Seas Gems - Marine Conservation Biology Institute
... which formed many years ago from a “hotspot” of rising magma. These volcanoes were produced as tectonic plates moved over the hotspot. Some of these eventually pierced the surface, cooled and were colonized by plants, spiders and other land life. Then rain, wind and waves eroded some of the islands ...
... which formed many years ago from a “hotspot” of rising magma. These volcanoes were produced as tectonic plates moved over the hotspot. Some of these eventually pierced the surface, cooled and were colonized by plants, spiders and other land life. Then rain, wind and waves eroded some of the islands ...
How can we minimise negative impacts on ocean health?
... as agreed in Paris), some further effects on the marine environment are inevitable (Figure 2). Nevertheless, some species may naturally adapt, if the rate of change is slow enough. This could involve: • genetic selection for strains that tolerate low pH conditions; • changes in distribution, such ...
... as agreed in Paris), some further effects on the marine environment are inevitable (Figure 2). Nevertheless, some species may naturally adapt, if the rate of change is slow enough. This could involve: • genetic selection for strains that tolerate low pH conditions; • changes in distribution, such ...
Seafloor Spreading
... 2. The magma erupts as lava and forms new seafloor. Magnetic polarity is set when rock cools. 3. The newly-formed rock is pushed away from the ridge axis as more lava erupts. 4. If the oceanic crust reaches a deep sea trench, it sinks into the trench and is lost into the mantle. ...
... 2. The magma erupts as lava and forms new seafloor. Magnetic polarity is set when rock cools. 3. The newly-formed rock is pushed away from the ridge axis as more lava erupts. 4. If the oceanic crust reaches a deep sea trench, it sinks into the trench and is lost into the mantle. ...
Sea

A sea is a large body of salt water that is surrounded in whole or in part by land. More broadly, the sea (with the definite article) is the interconnected system of Earth's salty, oceanic waters—considered as one global ocean or as several principal oceanic divisions. The sea moderates Earth's climate and has important roles in the water cycle, carbon cycle, and nitrogen cycle. Although the sea has been travelled and explored since prehistory, the modern scientific study of the sea—oceanography—dates broadly to the British Challenger expedition of the 1870s. The sea is conventionally divided into up to five large oceanic sections—including the IHO's four named oceans (the Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, and Arctic) and the Southern Ocean; smaller, second-order sections, such as the Mediterranean, are known as seas.Owing to the present state of continental drift, the Northern Hemisphere is now fairly equally divided between land and sea (a ratio of about 2:3) but the South is overwhelmingly oceanic (1:4.7). Salinity in the open ocean is generally in a narrow band around 3.5% by mass, although this can vary in more landlocked waters, near the mouths of large rivers, or at great depths. About 85% of the solids in the open sea are sodium chloride. Deep-sea currents are produced by differences in salinity and temperature. Surface currents are formed by the friction of waves produced by the wind and by tides, the changes in local sea level produced by the gravity of the Moon and Sun. The direction of all of these is governed by surface and submarine land masses and by the rotation of the Earth (the Coriolis effect).Former changes in the sea levels have left continental shelves, shallow areas in the sea close to land. These nutrient-rich waters teem with life, which provide humans with substantial supplies of food—mainly fish, but also shellfish, mammals, and seaweed—which are both harvested in the wild and farmed. The most diverse areas surround great tropical coral reefs. Whaling in the deep sea was once common but whales' dwindling numbers prompted international conservation efforts and finally a moratorium on most commercial hunting. Oceanography has established that not all life is restricted to the sunlit surface waters: even under enormous depths and pressures, nutrients streaming from hydrothermal vents support their own unique ecosystem. Life may have started there and aquatic microbial mats are generally credited with the oxygenation of Earth's atmosphere; both plants and animals first evolved in the sea.The sea is an essential aspect of human trade, travel, mineral extraction, and power generation. This has also made it essential to warfare and left major cities exposed to earthquakes and volcanoes from nearby faults; powerful tsunami waves; and hurricanes, typhoons, and cyclones produced in the tropics. This importance and duality has affected human culture, from early sea gods to the epic poetry of Homer to the changes induced by the Columbian Exchange, from Viking funerals to Basho's haikus to hyperrealist marine art, and inspiring music ranging from the shanties in The Complaynt of Scotland to Rimsky-Korsakov's ""The Sea and Sinbad's Ship"" to A-mei's ""Listen to the Sea"". It is the scene of leisure activities including swimming, diving, surfing, and sailing. However, population growth, industrialization, and intensive farming have all contributed to present-day marine pollution. Atmospheric carbon dioxide is being absorbed in increasing amounts, lowering its pH in a process known as ocean acidification. The shared nature of the sea has made overfishing an increasing problem.