weathering and soil notes
... Mechanical weathering breaks apart rocks without changing their chemical composition. They remain the same, the size is different. This can be done by the force of running water, forcing rocks to hit each other and break apart. Plants can cause mechanical weathering when tree roots or plants get in ...
... Mechanical weathering breaks apart rocks without changing their chemical composition. They remain the same, the size is different. This can be done by the force of running water, forcing rocks to hit each other and break apart. Plants can cause mechanical weathering when tree roots or plants get in ...
Weathering and Erosion Study Guide
... ____________________ When chemical reactions dissolve or alter the minerals in rocks or change them into different minerals ____________________ When rocks are broken apart by physical processes ____________________ Process in which surface materials are worn away and transported from one plac ...
... ____________________ When chemical reactions dissolve or alter the minerals in rocks or change them into different minerals ____________________ When rocks are broken apart by physical processes ____________________ Process in which surface materials are worn away and transported from one plac ...
Earth Science Chapter 7: Weathering, Erosion, and Soil Chapter
... The climate of an area is a major influence on the rate of physical and chemical weathering of Earth’s materials. Variables of climate include precipitation, temperature, and evaporation, and the interaction between temperature and precipitation has the greatest effect on a region’s rate of weatheri ...
... The climate of an area is a major influence on the rate of physical and chemical weathering of Earth’s materials. Variables of climate include precipitation, temperature, and evaporation, and the interaction between temperature and precipitation has the greatest effect on a region’s rate of weatheri ...
Soil Erosion
... Farmers in the United State are now losing about 5 tons of soil for every ton of grain they produce. In India the soil erosion rate is estimated to be more than twice as high. The world’s most productive soils are being depleted at the rate of 7% each decade. Increased farming in the region above a ...
... Farmers in the United State are now losing about 5 tons of soil for every ton of grain they produce. In India the soil erosion rate is estimated to be more than twice as high. The world’s most productive soils are being depleted at the rate of 7% each decade. Increased farming in the region above a ...
Weathering
... Usually in the presence of heat weathering rates will also increase. Different climates and temperatures produce more favorable forms of weathering. ...
... Usually in the presence of heat weathering rates will also increase. Different climates and temperatures produce more favorable forms of weathering. ...
Physical and Chemical Weathering
... Usually in the presence of heat weathering rates will also increase. Different climates and temperatures produce more favorable forms of weathering. ...
... Usually in the presence of heat weathering rates will also increase. Different climates and temperatures produce more favorable forms of weathering. ...
Weathering Notes
... Tiny root hairs seek out small cracks and pits in rock. Once the root hairs find a place they grow and expand. The expansion causes great pressure and cracks the rock. 3) ___________ the peeling of rock due to release of pressure experienced when rock was formed -Rocks formed deep in the Earth are m ...
... Tiny root hairs seek out small cracks and pits in rock. Once the root hairs find a place they grow and expand. The expansion causes great pressure and cracks the rock. 3) ___________ the peeling of rock due to release of pressure experienced when rock was formed -Rocks formed deep in the Earth are m ...
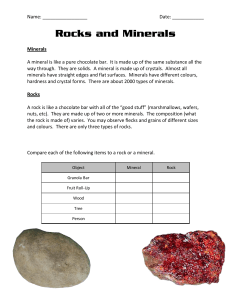
Rocks and Minerals
... A mineral is like a pure chocolate bar. It is made up of the same substance all the way through. They are solids. A mineral is made up of crystals. Almost all minerals have straight edges and flat surfaces. Minerals have different colours, hardness and crystal forms. There are about 2000 types of mi ...
... A mineral is like a pure chocolate bar. It is made up of the same substance all the way through. They are solids. A mineral is made up of crystals. Almost all minerals have straight edges and flat surfaces. Minerals have different colours, hardness and crystal forms. There are about 2000 types of mi ...
Earth*s External Processes
... is in the form of clay minerals • Quartz – the other component of granite is very resistant to chemical weathering • Quartz (SiO2) is basically unaltered, but is carried away as silica ...
... is in the form of clay minerals • Quartz – the other component of granite is very resistant to chemical weathering • Quartz (SiO2) is basically unaltered, but is carried away as silica ...
Mineral Resources Notes 11-12
... Ore distribution is not equal across the world Some nations are rich in mineral resources ...
... Ore distribution is not equal across the world Some nations are rich in mineral resources ...
Chemical Weathering
... How do mechanical and chemical weathering work together to speed up the weathering process? Answer: Mechanical weathering breaks rocks down into smaller pieces. This gives the rock a larger surface area for chemical reactions to take place. Chemical weathering weakens rock, making it easier for it t ...
... How do mechanical and chemical weathering work together to speed up the weathering process? Answer: Mechanical weathering breaks rocks down into smaller pieces. This gives the rock a larger surface area for chemical reactions to take place. Chemical weathering weakens rock, making it easier for it t ...
Ch3S3
... i. Some minerals are the source of metals such as aluminum, iron, copper, or silver. ii. Metals are usually softer than gemstones iii.Useful because they can be stretched into wire, flattened into sheets, and hammered or molded without breaking iv.Found in metal tools and machinery, the metal filame ...
... i. Some minerals are the source of metals such as aluminum, iron, copper, or silver. ii. Metals are usually softer than gemstones iii.Useful because they can be stretched into wire, flattened into sheets, and hammered or molded without breaking iv.Found in metal tools and machinery, the metal filame ...
Plutonic Rocks
... When water freezes into ice it expands This small expansion slowly makes the crack larger, so more water can fill in Over time and successive melting and freezing cycles the cracks open up enough to split the rock into pieces ...
... When water freezes into ice it expands This small expansion slowly makes the crack larger, so more water can fill in Over time and successive melting and freezing cycles the cracks open up enough to split the rock into pieces ...
How Granite Weathers Chemical weathering
... Only size changes occur in this process No chemical composition change occurs in mechanical weathering Same chemical composition as the parent rock Results in increased surface area ...
... Only size changes occur in this process No chemical composition change occurs in mechanical weathering Same chemical composition as the parent rock Results in increased surface area ...
File - Boreal Agrominerals
... chiefly comprised of olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, biotite and iron minerals. High levels of base cations and low silica content characterize them. In the weathering process this group of rocks weather to very important secondary clay minerals (vermiculite, illite, montromillinite) and in the proces ...
... chiefly comprised of olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, biotite and iron minerals. High levels of base cations and low silica content characterize them. In the weathering process this group of rocks weather to very important secondary clay minerals (vermiculite, illite, montromillinite) and in the proces ...
Weathering & Erosion
... 1.Water seeps into small cracks in rocks. 2.When the water freezes it expands creating great pressure. 3.The crack widens and allows water to seep deeper into the rock. 4.Alternating Freezing and Thawing ...
... 1.Water seeps into small cracks in rocks. 2.When the water freezes it expands creating great pressure. 3.The crack widens and allows water to seep deeper into the rock. 4.Alternating Freezing and Thawing ...
Rocks, Minerals, and Soil
... Science--6 M. Skidmore Rocks, Minerals, Soil Strand: All matter is made of small particles called atoms. The properties of matter are based on the order and organization of atoms and molecules. Cells, minerals, rocks, and soil are all examples of matter. Topic: This topic focuses on the study of roc ...
... Science--6 M. Skidmore Rocks, Minerals, Soil Strand: All matter is made of small particles called atoms. The properties of matter are based on the order and organization of atoms and molecules. Cells, minerals, rocks, and soil are all examples of matter. Topic: This topic focuses on the study of roc ...
Name: Date: Period: _____ Chapter 14 Study Guide Honors
... 13. What are lava flows? Long streams of molten rock from volcanoes 14. In what type of climate does chemical weathering occur the fastest? Hot and wet climates 15. What components make up soil? Weathered rock, mineral material, organic matter, water, and air 16. What happens to sediment eroded by w ...
... 13. What are lava flows? Long streams of molten rock from volcanoes 14. In what type of climate does chemical weathering occur the fastest? Hot and wet climates 15. What components make up soil? Weathered rock, mineral material, organic matter, water, and air 16. What happens to sediment eroded by w ...
Teacher Background on Erosion, Weathering, Soil
... Have you ever visited or seen Providence Canyon in Georgia? The Canyon apparently began forming in the early 1800’s. It is thought that the forests in this area were clear cut for farming. The natural vegetation was removed exposing the easily eroded Providence Sand. The erosion continued at a high ...
... Have you ever visited or seen Providence Canyon in Georgia? The Canyon apparently began forming in the early 1800’s. It is thought that the forests in this area were clear cut for farming. The natural vegetation was removed exposing the easily eroded Providence Sand. The erosion continued at a high ...
Mechanical weathering - occurs when physical forces break rock
... Residual soil - parent material for that soil is the bedrock directly below it. Transported soil - parent material for that soil has been carried from elsewhere and deposited Soil horizons are zones or layers of soil. Soil profile is a vertical section through all the soil horizons. Pedalfer - commo ...
... Residual soil - parent material for that soil is the bedrock directly below it. Transported soil - parent material for that soil has been carried from elsewhere and deposited Soil horizons are zones or layers of soil. Soil profile is a vertical section through all the soil horizons. Pedalfer - commo ...
READ MORE - Multotec
... Tonnage is computed from dimensions revealed in outcrops, trenches, drill holes, underground workings and grade from the results of adequate sampling. The sites for inspection, sampling and measurement are so well spaced and the geological character so well defined that size, shape and mineral conte ...
... Tonnage is computed from dimensions revealed in outcrops, trenches, drill holes, underground workings and grade from the results of adequate sampling. The sites for inspection, sampling and measurement are so well spaced and the geological character so well defined that size, shape and mineral conte ...
Laterite

Laterite is a soil and rock type rich in iron and aluminium, and is commonly considered to have formed in hot and wet tropical areas. Nearly all laterites are of rusty-red coloration, because of high iron oxide content. They develop by intensive and long-lasting weathering of the underlying parent rock. Tropical weathering (laterization) is a prolonged process of chemical weathering which produces a wide variety in the thickness, grade, chemistry and ore mineralogy of the resulting soils. The majority of the land area containing laterites is between the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn.Laterite has commonly been referred to as a soil type as well as being a rock type. This and further variation in the modes of conceptualizing about laterite (e.g. also as a complete weathering profile or theory about weathering) has led to calls for the term to be abandoned altogether. At least a few researchers specializing in regolith development have considered that hopeless confusion has evolved around the name. There is no likelihood, however, that the name will ever be abandoned; for material that looks highly similar to the Indian laterite occurs abundantly worldwide, and it is reasonable to call such material laterite.Historically, laterite was cut into brick-like shapes and used in monument-building. After 1000 CE, construction at Angkor Wat and other southeast Asian sites changed to rectangular temple enclosures made of laterite, brick and stone. Since the mid-1970s, some trial sections of bituminous-surfaced, low-volume roads have used laterite in place of stone as a base course. Thick laterite layers are porous and slightly permeable, so the layers can function as aquifers in rural areas. Locally available laterites have been used in an acid solution, followed by precipitation to remove phosphorus and heavy metals at sewage-treatment facilities.Laterites are a source of aluminium ore; the ore exists largely in clay minerals and the hydroxides, gibbsite, boehmite, and diaspore, which resembles the composition of bauxite. In Northern Ireland they once provided a major source of iron and aluminium ores. Laterite ores also were the early major source of nickel.