Rock stars of soil science head for Vic
... For full terms and conditions, please visit: http://kondininarchive.farmingahead.com.au/web_files/Earlybird_Giveaway_TCs_January.pdf ...
... For full terms and conditions, please visit: http://kondininarchive.farmingahead.com.au/web_files/Earlybird_Giveaway_TCs_January.pdf ...
Soil Nutrients
... A hobby gardener buys a bag of "Scott's Turfbuilder" for $31.95. The bag weighs 62 pounds and has an analysis of 22-3-10. ...
... A hobby gardener buys a bag of "Scott's Turfbuilder" for $31.95. The bag weighs 62 pounds and has an analysis of 22-3-10. ...
30.1 Organization of the Human Body
... stomach, and small intestine. ▶ Mechanical digestion begins as teeth tear and grind food. Saliva contains amylase, an enzyme that breaks down starches into sugars. This begins the process of chemical digestion. Once food is chewed, it is pushed into the pharynx. ▶ The tube leading from the pharynx t ...
... stomach, and small intestine. ▶ Mechanical digestion begins as teeth tear and grind food. Saliva contains amylase, an enzyme that breaks down starches into sugars. This begins the process of chemical digestion. Once food is chewed, it is pushed into the pharynx. ▶ The tube leading from the pharynx t ...
BIOL 4120: Principles of Ecology Lecture 5: Terrestrial Environment
... Soil is medium for plant growth; the basis of all terrestrial life. Without soil, there would be no plants, no soil microorganism and no land animals Plants obtain many of their water and nutrients from soil and it provides an place to attach to. ...
... Soil is medium for plant growth; the basis of all terrestrial life. Without soil, there would be no plants, no soil microorganism and no land animals Plants obtain many of their water and nutrients from soil and it provides an place to attach to. ...
PRE-LAB Questions
... (thoracic) cavity. Use dissecting scissors to carefully cut through the ribs and sternum. Using dissecting pins, pin open the thoracic cavity of the pig. 2. Remove the thymus gland so that the chambers of the heart will be accessible. 3. Using figure 4, identify the following structures of the circu ...
... (thoracic) cavity. Use dissecting scissors to carefully cut through the ribs and sternum. Using dissecting pins, pin open the thoracic cavity of the pig. 2. Remove the thymus gland so that the chambers of the heart will be accessible. 3. Using figure 4, identify the following structures of the circu ...
Section 2: Energy Flow in Ecosystems
... The ability to move increases the chance of survival by allowing a person to gather food, seek shelter, and escape ...
... The ability to move increases the chance of survival by allowing a person to gather food, seek shelter, and escape ...
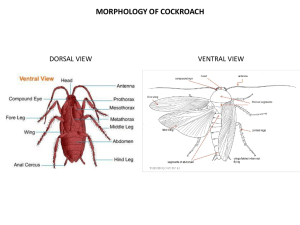
anatomy-of-cockroach
... Ventrally, an opening called mouth is present on the head that remains surrounded by the mouth parts consisting of a pair of mandibles, first maxillae, labium or fused second maxillae, hypopharynx and labrum. The mouth parts of the cockroach help in 'biting and chewing' its food. Functions of the mo ...
... Ventrally, an opening called mouth is present on the head that remains surrounded by the mouth parts consisting of a pair of mandibles, first maxillae, labium or fused second maxillae, hypopharynx and labrum. The mouth parts of the cockroach help in 'biting and chewing' its food. Functions of the mo ...
Optimal soil structure for plant growth
... drainage or different cropping. Such degraded soil is shown as pans, clods, smeared surfaces and smelly layers. In temperate countries it is usually associated with compaction damage. Restoration of continuous macroporosity is then a priority. Some guidelines for improvement are given in Table 2. Ti ...
... drainage or different cropping. Such degraded soil is shown as pans, clods, smeared surfaces and smelly layers. In temperate countries it is usually associated with compaction damage. Restoration of continuous macroporosity is then a priority. Some guidelines for improvement are given in Table 2. Ti ...
Materials and Practices Guidelines for Lake Whatcom
... amendments tested and labeled as containing more than trace amounts of phosphorus in the Lake Whatcom Watershed. All labeled products should list a “0” for the content of phosphorus by weight. For mulches, bulk soil amendments, and fertilizers, a range of locally-available materials have been ident ...
... amendments tested and labeled as containing more than trace amounts of phosphorus in the Lake Whatcom Watershed. All labeled products should list a “0” for the content of phosphorus by weight. For mulches, bulk soil amendments, and fertilizers, a range of locally-available materials have been ident ...
Introduction to Soils - Ms Kim`s Biology Class
... has major significance on the development of soil. • Microorganisms help develop soils by decomposing organic matter and forming weak acids that dissolve minerals faster than would pure water. ...
... has major significance on the development of soil. • Microorganisms help develop soils by decomposing organic matter and forming weak acids that dissolve minerals faster than would pure water. ...
Phinizy Down Under - Phinizy Center for Water Sciences
... • Soil texture is used by soil scientists to determine the percentage of silt, sand, and clay in mineral soils. This determines the type of soil. The texture of a soil is important in indicating the availability of moisture and nutrients for plant growth. • By feeling damp soil between fingers or in ...
... • Soil texture is used by soil scientists to determine the percentage of silt, sand, and clay in mineral soils. This determines the type of soil. The texture of a soil is important in indicating the availability of moisture and nutrients for plant growth. • By feeling damp soil between fingers or in ...
Soil Conservation
... Biological nitrogen fixation can be represented by the following equation, in which two moles of ammonia are produced from one mole of nitrogen gas, at the expense of 16 moles of ATP and a supply of electrons and protons (hydrogen ions): ...
... Biological nitrogen fixation can be represented by the following equation, in which two moles of ammonia are produced from one mole of nitrogen gas, at the expense of 16 moles of ATP and a supply of electrons and protons (hydrogen ions): ...
Life in the Soil: A Biological Approach to Gardening
... of the roots that allow the plant to reach farther in the soil for more effective and increased water and nutrient uptake –More ...
... of the roots that allow the plant to reach farther in the soil for more effective and increased water and nutrient uptake –More ...
Soil pH Experiment - Stonehill College
... phosphorus, and potassium – are required for healthy plant growth. Because plants need them in large quantities, they are called macronutrients. They are the main ingredients of most fertilizers that farmers and gardeners add to their soil. Other nutrients such as iron and manganese are also needed ...
... phosphorus, and potassium – are required for healthy plant growth. Because plants need them in large quantities, they are called macronutrients. They are the main ingredients of most fertilizers that farmers and gardeners add to their soil. Other nutrients such as iron and manganese are also needed ...
Synopsis - Department of Plant Biology
... Normally Offered: Fall every other year (odd numbered years only). By Dr. S. Murphy. Pre-requisites and other registration restrictions: 11:375:360, “Soils & Water” or equivalent; 01:119:101-102 or 01:119:115-116 General Biology ...
... Normally Offered: Fall every other year (odd numbered years only). By Dr. S. Murphy. Pre-requisites and other registration restrictions: 11:375:360, “Soils & Water” or equivalent; 01:119:101-102 or 01:119:115-116 General Biology ...
Assessment of grass root effects on soil piping in sandy soils using
... mixture of grasses with fibrous roots. All soil samples were placed on a sandbox with a 100 mm head for 24 hours to ensure a similar water content for all samples. In total, 67 pinhole tests (lasting 5 minutes each) were conducted, i.e. 43 root-permeated soil samples with RD ranging from 0.01 to 0.9 ...
... mixture of grasses with fibrous roots. All soil samples were placed on a sandbox with a 100 mm head for 24 hours to ensure a similar water content for all samples. In total, 67 pinhole tests (lasting 5 minutes each) were conducted, i.e. 43 root-permeated soil samples with RD ranging from 0.01 to 0.9 ...
Rule file
... (1) “Background concentrations” means concentrations of contaminants that are naturally occurring in the ground water, surface water, soil or sediment in the vicinity of the site. (2) “Cleaned soil” means soil which has been treated at a soil treatment facility, which has received a completed post-t ...
... (1) “Background concentrations” means concentrations of contaminants that are naturally occurring in the ground water, surface water, soil or sediment in the vicinity of the site. (2) “Cleaned soil” means soil which has been treated at a soil treatment facility, which has received a completed post-t ...
Supplemental material
... # We also estimated the N input from NPP (P). Here, we use a tundra NPP value from Shaver (2013), a published dataset from 1982 at Toolik Lake, AK that estimates NPP (above and belowground) at 430 g biomass /m2. We assume that the same amount of biomass is returned to the soil annually as is created ...
... # We also estimated the N input from NPP (P). Here, we use a tundra NPP value from Shaver (2013), a published dataset from 1982 at Toolik Lake, AK that estimates NPP (above and belowground) at 430 g biomass /m2. We assume that the same amount of biomass is returned to the soil annually as is created ...
Document
... •the body wall consists of two cell layers •the pores of the body wall are connected to an internal canal system •collar cells - have flagellum that create (1 way) current to draw water and food in to gut •no tissues, organs, nervous system, or brain •no circulatory system (no heart, blood or veins) ...
... •the body wall consists of two cell layers •the pores of the body wall are connected to an internal canal system •collar cells - have flagellum that create (1 way) current to draw water and food in to gut •no tissues, organs, nervous system, or brain •no circulatory system (no heart, blood or veins) ...
Lecture 3, January 25, 2017 - EPSc 413 Introduction to Soil Science
... TAXONOMIC CLASS: Fine-silty, mixed, superactive, mesic Typic Hapludalfs ...
... TAXONOMIC CLASS: Fine-silty, mixed, superactive, mesic Typic Hapludalfs ...
soil type and areas of peat(uk) - British Council Schools Online
... •Loam soil feels soft and crumbly and is easy to work over a wide range of moisture conditions. ...
... •Loam soil feels soft and crumbly and is easy to work over a wide range of moisture conditions. ...
Platyhelminthes
... body and shorter nerves run across. Eyespot; detects light change. Flatworms have specialized cells that detect stimuli. The nervous system locates food. ...
... body and shorter nerves run across. Eyespot; detects light change. Flatworms have specialized cells that detect stimuli. The nervous system locates food. ...
Soil pH and Plant Nutrients
... strongly pH dependent. The difference between NH3 and NH4+ is a H+. For example, if NH4+ were applied to a soil at pH 7, the equilibrium condition would be 99% NH4+ and 1% NH3. At pH 8, approximately 10% would exist as NH3. This means that a fertilizer like urea (46-0-0) is generally subject to high ...
... strongly pH dependent. The difference between NH3 and NH4+ is a H+. For example, if NH4+ were applied to a soil at pH 7, the equilibrium condition would be 99% NH4+ and 1% NH3. At pH 8, approximately 10% would exist as NH3. This means that a fertilizer like urea (46-0-0) is generally subject to high ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... • Formation or retention of stable materials • Physical changes such as the rounding of corners or edges ...
... • Formation or retention of stable materials • Physical changes such as the rounding of corners or edges ...
Lecture 2 - jan.ucc.nau.edu
... 4. The pore space within a soil volume is air and water. The water is called the soil solution. This solution contains soluble salts, organic solutes, and some suspended colloids (solids that suspend in a fluid). The behavior of soil water is controlled to a great extend by pore size. Small pores ha ...
... 4. The pore space within a soil volume is air and water. The water is called the soil solution. This solution contains soluble salts, organic solutes, and some suspended colloids (solids that suspend in a fluid). The behavior of soil water is controlled to a great extend by pore size. Small pores ha ...
Earthworm

An earthworm is a tube-shaped, segmented worm found in the phylum Annelida. They are commonly found living in soil, feeding on live and dead organic matter. Its digestive system runs through the length of its body. It conducts respiration through its skin. An earthworm has a double transport system composed of coelomic fluid that moves within the fluid-filled coelom and a simple, closed blood circulatory system. It has a central and a peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system consists of two ganglia above the mouth, one on either side, connected to a nerve cord running back along its length to motor neurons and sensory cells in each segment. Large numbers of chemoreceptors are concentrated near its mouth. Circumferential and longitudinal muscles on the periphery of each segment enable the worm to move. Similar sets of muscles line the gut, and their actions move the digesting food toward the worm's anus.Earthworms are hermaphrodites—each individual carries both male and female sex organs. They lack either an internal skeleton or exoskeleton, but maintain their structure with fluid-filled coelom chambers that function as a hydrostatic skeleton.""Earthworm"" is the common name for the largest members of Oligochaeta (which is either a class or a subclass depending on the author). In classical systems, they were placed in the order Opisthopora, on the basis of the male pores opening posterior to the female pores, though the internal male segments are anterior to the female. Theoretical cladistic studies have placed them, instead, in the suborder Lumbricina of the order Haplotaxida, but this may again soon change. Folk names for the earthworm include ""dew-worm"", ""rainworm"", ""night crawler"", and ""angleworm"" (due to its use as fishing bait).Larger terrestrial earthworms are also called megadriles (or big worms), as opposed to the microdriles (or small worms) in the semiaquatic families Tubificidae, Lumbriculidae, and Enchytraeidae, among others. The megadriles are characterized by having a distinct clitellum (which is more extensive than that of microdriles) and a vascular system with true capillaries.Earthworms are far less abundant in disturbed environments and are typically active only if water is present.