Name: Date
... Important vocabulary: nose, pharynx, larynx, epiglottis, trachea, bronchus (bronchi, plural), bronchiole, alveoli, diaphragm, and lungs Summary: Respiration is a process by which a body gets and uses oxygen and releases carbon dioxide and water. Respiration is divided into two parts. The first part ...
... Important vocabulary: nose, pharynx, larynx, epiglottis, trachea, bronchus (bronchi, plural), bronchiole, alveoli, diaphragm, and lungs Summary: Respiration is a process by which a body gets and uses oxygen and releases carbon dioxide and water. Respiration is divided into two parts. The first part ...
Review of the new Soil component in APSIM
... Review of the new Soil component in APSIM Greg McLean & Neal Dalgliesh This component is an improvement on the current release and has a number of advantages. The ability to include SWIM is perhaps one that will be most appreciated by those in the soils world. The reviewers would like to make the fo ...
... Review of the new Soil component in APSIM Greg McLean & Neal Dalgliesh This component is an improvement on the current release and has a number of advantages. The ability to include SWIM is perhaps one that will be most appreciated by those in the soils world. The reviewers would like to make the fo ...
SIR EDWARD JOHlN RUSSELL
... microfauna. Some idea of the intensity of the attack on this problem is gained from the fact that, for a whole year, daily counts were made of the bacteria, amoebae, ciliates, and flagellates in the soil of certain of the field plots. In due time, however, the several microbiologists who had been as ...
... microfauna. Some idea of the intensity of the attack on this problem is gained from the fact that, for a whole year, daily counts were made of the bacteria, amoebae, ciliates, and flagellates in the soil of certain of the field plots. In due time, however, the several microbiologists who had been as ...
Doc 7
... from millions of species Total weight of living organisms in the top six inches of an acre of soil can range from 5,000 pounds to as much as 20,000 pounds. Soil from one spot may house a very different community from soil just a meter away, because of variations in the availability of water or n ...
... from millions of species Total weight of living organisms in the top six inches of an acre of soil can range from 5,000 pounds to as much as 20,000 pounds. Soil from one spot may house a very different community from soil just a meter away, because of variations in the availability of water or n ...
sketch layout of system - the Oklahoma Department of
... bottom shall be no shallower than _____ inches and no deeper than ______ inches. Septic tank with a liquid capacity of __________ gallons and a lagoon with bottom dimensions of ___________ feet by ___________ feet. Septic tank with a liquid capacity of ___________ gallons and __________ feet of evap ...
... bottom shall be no shallower than _____ inches and no deeper than ______ inches. Septic tank with a liquid capacity of __________ gallons and a lagoon with bottom dimensions of ___________ feet by ___________ feet. Septic tank with a liquid capacity of ___________ gallons and __________ feet of evap ...
37plantnutrition
... ion to form ammonium (NH4+), which plants can absorb. • However, nitrifying bacteria in the soil quickly oxidize ammonium to nitrate (NO3-) which is the form of nitrogen that plants absorb the most. – After nitrate is absorbed by roots, plant enzymes reduce nitrate back to ammonium, which other enzy ...
... ion to form ammonium (NH4+), which plants can absorb. • However, nitrifying bacteria in the soil quickly oxidize ammonium to nitrate (NO3-) which is the form of nitrogen that plants absorb the most. – After nitrate is absorbed by roots, plant enzymes reduce nitrate back to ammonium, which other enzy ...
SOILS Soils are Crucial for Life on Earth
... roots and supplying nutrient elements that are essential to the entire plant. • Soil properties are the principal factor controlling the fate of water in the hydrologic system. Water loss, utilization, contamination and purification are all affected by the soil. • Soils function as nature’s recyclin ...
... roots and supplying nutrient elements that are essential to the entire plant. • Soil properties are the principal factor controlling the fate of water in the hydrologic system. Water loss, utilization, contamination and purification are all affected by the soil. • Soils function as nature’s recyclin ...
Organic Matter
... "tied up" (used as food) this is very important when considering re-cropping and not allowing the soil to have a year in fallow to allow for mineralization in order to reduce the nitrogen tie-up. ...
... "tied up" (used as food) this is very important when considering re-cropping and not allowing the soil to have a year in fallow to allow for mineralization in order to reduce the nitrogen tie-up. ...
Assessment of grass root effects on soil piping in sandy soils using
... Soil piping is a complex land degradation process, which involves the hydraulic removal of soil particles by subsurface flow. This process is frequently underestimated and omitted in most soil erosion studies. However, during the last decades several studies reported the importance of soil piping in ...
... Soil piping is a complex land degradation process, which involves the hydraulic removal of soil particles by subsurface flow. This process is frequently underestimated and omitted in most soil erosion studies. However, during the last decades several studies reported the importance of soil piping in ...
soil intro - Ms Kim`s Biology Class
... • The activity of living plants and animals (macro and microorganisms) has major significance on the development of soil. • Microorganisms help develop soils by decomposing organic matter and forming weak acids that dissolve minerals faster than would pure water. • Fibrous root systems of grasses ha ...
... • The activity of living plants and animals (macro and microorganisms) has major significance on the development of soil. • Microorganisms help develop soils by decomposing organic matter and forming weak acids that dissolve minerals faster than would pure water. • Fibrous root systems of grasses ha ...
Chapter 14 concept review
... rocks wear away at a faster rather than harder, more weather resistant rocks do ...
... rocks wear away at a faster rather than harder, more weather resistant rocks do ...
4 per 1000 Carbon sequestration in soils for food security and the
... Thanks to plants and living organisms, soils contain two to three times more carbon than the atmosphere. Carbon-rich soil organic matter is essential: it retains the water, nitrogen and phosphorus that are indispensable to agriculture. But alternating phases of drought and intense rainfall accentuat ...
... Thanks to plants and living organisms, soils contain two to three times more carbon than the atmosphere. Carbon-rich soil organic matter is essential: it retains the water, nitrogen and phosphorus that are indispensable to agriculture. But alternating phases of drought and intense rainfall accentuat ...
LandSlides - European Soil Portal
... • Detailed scale maps (> 1:5,000 to 1: 1:500): Prepared as part of a landslide hazard assessment of a specific site and should be accurate enough to guide layout of individual structures or specific operations or to plan ...
... • Detailed scale maps (> 1:5,000 to 1: 1:500): Prepared as part of a landslide hazard assessment of a specific site and should be accurate enough to guide layout of individual structures or specific operations or to plan ...
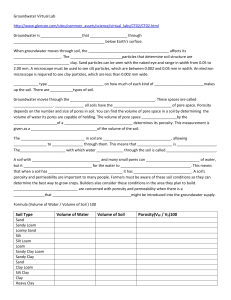
2015-2016 Groundwater Virtual Lab
... 5. Explain why surface runoff, or rain not absorbed by the soil, occurs much more often in areas with soils with high clay content. ...
... 5. Explain why surface runoff, or rain not absorbed by the soil, occurs much more often in areas with soils with high clay content. ...
Moravian Geographical Reports volume 11 number 1/2003
... The Desná River is a left-bank tributary of the Morava R. springing in the highest and most dissected parts of the Hrubý Jeseník in the Eastern Sudetes. In July 1997, this territory was affected by a flood which resulted from abundant rains lasting four days and which showed in an extraordinary geom ...
... The Desná River is a left-bank tributary of the Morava R. springing in the highest and most dissected parts of the Hrubý Jeseník in the Eastern Sudetes. In July 1997, this territory was affected by a flood which resulted from abundant rains lasting four days and which showed in an extraordinary geom ...
Worm Castings Information and Instruction Sheet
... Earthworms as they cultivate and feed, swallow great quantities of soil, digest it, extract its food value and expel the residue as worm castings – these worm castings are 5 times richer in the nutrients necessary for maximum plant growth and production, than the top 6 inches of top soil. Just as im ...
... Earthworms as they cultivate and feed, swallow great quantities of soil, digest it, extract its food value and expel the residue as worm castings – these worm castings are 5 times richer in the nutrients necessary for maximum plant growth and production, than the top 6 inches of top soil. Just as im ...
The Soil Profile
... elsewhere, usually by wind or water, at different speeds • Climate: the amount, intensity, timing, and kind of precipitation that breaks down parts of ecosystem (i.e. rocks, trees) into soil • Topography: Slope and Aspect affect the angle of the land and position toward/away from the sun that soil w ...
... elsewhere, usually by wind or water, at different speeds • Climate: the amount, intensity, timing, and kind of precipitation that breaks down parts of ecosystem (i.e. rocks, trees) into soil • Topography: Slope and Aspect affect the angle of the land and position toward/away from the sun that soil w ...
6. Slovakia - Soil patterns
... The lowland soil types Topography (foothill zoning) predetermined the following soil types: Black earth – the driest and warmest climate ...
... The lowland soil types Topography (foothill zoning) predetermined the following soil types: Black earth – the driest and warmest climate ...
Mutualism- A symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit
... o Heavy rainfall washes nutrients from soil which limits primary production o Trees have shallow root systems and one long tap root as adaptation to thin soil. o Canopy protects soil from heavy rainfall o after logging soil quickly erodes making it difficult for plants to grow ...
... o Heavy rainfall washes nutrients from soil which limits primary production o Trees have shallow root systems and one long tap root as adaptation to thin soil. o Canopy protects soil from heavy rainfall o after logging soil quickly erodes making it difficult for plants to grow ...
Soil Organic Matter
... tissue under favorable conditions: • 1) immediately starts rapid multiplication of bacteria, fungi, and actinomycetes, • 2) which are soon actively decomposing the fresh tissue. ...
... tissue under favorable conditions: • 1) immediately starts rapid multiplication of bacteria, fungi, and actinomycetes, • 2) which are soon actively decomposing the fresh tissue. ...
Parent materials
... What is topography and how does it affect the development of soil? Topography refers to the slope characteristics of a soil. It includes the degree or steepness, length, shape, and direction of a slope. These factors influence the amount of rainwater runoff, or the amount that enters the soil or ...
... What is topography and how does it affect the development of soil? Topography refers to the slope characteristics of a soil. It includes the degree or steepness, length, shape, and direction of a slope. These factors influence the amount of rainwater runoff, or the amount that enters the soil or ...
Gas Exchange
... to absorb helpful gases necessary for the chemical processes of metabolism. When Is Respiration Not Breathing? The word respiration is used in two different but related ways in biology. In one sense, respiration means the act of bringing air into the lungs and expelling waste gases. We call this for ...
... to absorb helpful gases necessary for the chemical processes of metabolism. When Is Respiration Not Breathing? The word respiration is used in two different but related ways in biology. In one sense, respiration means the act of bringing air into the lungs and expelling waste gases. We call this for ...
How is Soil Formed
... Ask the class after they are done the flipbook if any of them think that the jar is soil? Did anyone’s prediction change? What factors or factor makes it not soil? Emphasize with the students that soil formation is a long process, which takes many years. Soil development takes a very long time. It m ...
... Ask the class after they are done the flipbook if any of them think that the jar is soil? Did anyone’s prediction change? What factors or factor makes it not soil? Emphasize with the students that soil formation is a long process, which takes many years. Soil development takes a very long time. It m ...
Disaster Management Plan of Industry Department
... using chemicals could be supplemented through various organic means, i.e., application of FYM, compost, vermi-compost, green manuring with an objective to regenerate the wasted potential in eco-friendly manner. • It is essential to revitalize the soil system through organic residues and materials. • ...
... using chemicals could be supplemented through various organic means, i.e., application of FYM, compost, vermi-compost, green manuring with an objective to regenerate the wasted potential in eco-friendly manner. • It is essential to revitalize the soil system through organic residues and materials. • ...
Soil respiration

Soil respiration refers to the production of carbon dioxide when soil organisms respire. This includes respiration of plant roots, the rhizosphere, microbes and fauna.Soil respiration is a key ecosystem process that releases carbon from the soil in the form of CO2. CO2 is acquired from the atmosphere and converted into organic compounds in the process of photosynthesis. Plants use these organic compounds to build structural components or respire them to release energy. When plant respiration occurs below-ground in the roots, it adds to soil respiration. Over time, plant structural components are consumed by heterotrophs. This heterotrophic consumption releases CO2 and when this CO2 is released by below-ground organisms, it is considered soil respiration.The amount of soil respiration that occurs in an ecosystem is controlled by several factors. The temperature, moisture, nutrient content and level of oxygen in the soil can produce extremely disparate rates of respiration. These rates of respiration can be measured in a variety of methods. Other methods can be used to separate the source components, in this case the type of photosynthetic pathway (C3/C4), of the respired plant structures.Soil respiration rates can be largely affected by human activity. This is because humans have the ability to and have been changing the various controlling factors of soil respiration for numerous years. Global climate change is composed of numerous changing factors including rising atmospheric CO2, increasing temperature and shifting precipitation patterns. All of these factors can affect the rate of global soil respiration. Increased nitrogen fertilization by humans also has the potential to effect rates over the entire Earth.Soil respiration and its rate across ecosystems is extremely important to understand. This is because soil respiration plays a large role in global carbon cycling as well as other nutrient cycles. The respiration of plant structures releases not only CO2 but also other nutrients in those structures, such as nitrogen. Soil respiration is also associated with positive feedbacks with global climate change. Positive feedbacks are when a change in a system produces response in the same direction of the change. Therefore, soil respiration rates can be effected by climate change and then respond by enhancing climate change.