When are soils most likely to erode?
... A student put sedimentary rocks in pile 1, igneous in pile 2, and metamorphic in pile 3. Which of the following would belong in pile 2? a. marble, gneiss, and schist b. Basalt, obsidian, and pumice c. Sandstone, conglomerate, and shale d. Granite, slate, and mudstone ...
... A student put sedimentary rocks in pile 1, igneous in pile 2, and metamorphic in pile 3. Which of the following would belong in pile 2? a. marble, gneiss, and schist b. Basalt, obsidian, and pumice c. Sandstone, conglomerate, and shale d. Granite, slate, and mudstone ...
When are soils most likely to erode?
... A student put sedimentary rocks in pile 1, igneous in pile 2, and metamorphic in pile 3. Which of the following would belong in pile 2? a. marble, gneiss, and schist b. Basalt, obsidian, and pumice c. Sandstone, conglomerate, and shale d. Granite, slate, and mudstone ...
... A student put sedimentary rocks in pile 1, igneous in pile 2, and metamorphic in pile 3. Which of the following would belong in pile 2? a. marble, gneiss, and schist b. Basalt, obsidian, and pumice c. Sandstone, conglomerate, and shale d. Granite, slate, and mudstone ...
Rocks, Minerals, and Soil
... A student put sedimentary rocks in pile 1, igneous in pile 2, and metamorphic in pile 3. Which of the following would belong in pile 2? a. marble, gneiss, and schist b. Basalt, obsidian, and pumice c. Sandstone, conglomerate, and shale d. Granite, slate, and mudstone ...
... A student put sedimentary rocks in pile 1, igneous in pile 2, and metamorphic in pile 3. Which of the following would belong in pile 2? a. marble, gneiss, and schist b. Basalt, obsidian, and pumice c. Sandstone, conglomerate, and shale d. Granite, slate, and mudstone ...
Study Guide 2
... 1. flattens and lines up 2. change with substances in surrounding mineral 3. separate into layers of different densities In each case the result (final product) is DIFFERENT from the original. How are Metamorphic Rocks used? ...
... 1. flattens and lines up 2. change with substances in surrounding mineral 3. separate into layers of different densities In each case the result (final product) is DIFFERENT from the original. How are Metamorphic Rocks used? ...
Earth`s Rocks and Soil C40-53
... 1. flattens and lines up 2. change with substances in surrounding mineral 3. separate into layers of different densities In each case the result (final product) is DIFFERENT from the original. How are Metamorphic Rocks used? ...
... 1. flattens and lines up 2. change with substances in surrounding mineral 3. separate into layers of different densities In each case the result (final product) is DIFFERENT from the original. How are Metamorphic Rocks used? ...
Fertile soils: friend or foe of a clean environment? -the
... no gains in terms of total N loss to water or wilderness conservation, if the same volume of grain is to be produced ...
... no gains in terms of total N loss to water or wilderness conservation, if the same volume of grain is to be produced ...
This dataset consists of 3 GIS maps that indicate the soil biomass
... This dataset consists of 3 GIS maps that indicate the soil biomass productivity of grasslands and pasture, of croplands and of forest areas in the European Union (EU27). The degree to which the soil carries out its biomass production service was evaluated on the basis of soil properties under prevai ...
... This dataset consists of 3 GIS maps that indicate the soil biomass productivity of grasslands and pasture, of croplands and of forest areas in the European Union (EU27). The degree to which the soil carries out its biomass production service was evaluated on the basis of soil properties under prevai ...
File
... crumb structure is the best for soil aeration, water content and fertility. Overgrazing can change the structure to a platy structure or destroy the structure completely. As a result it can be easily erodes by wind and rain and pasture growth is also reduced. Too many animals on the land will eat al ...
... crumb structure is the best for soil aeration, water content and fertility. Overgrazing can change the structure to a platy structure or destroy the structure completely. As a result it can be easily erodes by wind and rain and pasture growth is also reduced. Too many animals on the land will eat al ...
Example format for answering text review questions and key word
... A soil which is located in a arid or semi-arid environment. They are dominant in the shrub lands or 'badlands' which accounts for about Y:J of earth's surface land ...
... A soil which is located in a arid or semi-arid environment. They are dominant in the shrub lands or 'badlands' which accounts for about Y:J of earth's surface land ...
Appendix C: Typical Soil Types
... relative proportions of sand, silt and clay found in a particular soil sample determine soil texture. Overall, there are 12 recognized soil textural classifications based on the particle size. The percentages of particle sizes that can pass through various sieve sizes will determine soil texture. A ...
... relative proportions of sand, silt and clay found in a particular soil sample determine soil texture. Overall, there are 12 recognized soil textural classifications based on the particle size. The percentages of particle sizes that can pass through various sieve sizes will determine soil texture. A ...
Name: Date: Period: _____
... What is the transportation of the earth’s surface materials by wind or water? deposition, erosion, or weathering What gas mixes with condensing water vapor to produce acid rain? – helium, oxygen, or sulfur dioxide What is the slow, imperceptible downhill movement of weathered material? – creep, eart ...
... What is the transportation of the earth’s surface materials by wind or water? deposition, erosion, or weathering What gas mixes with condensing water vapor to produce acid rain? – helium, oxygen, or sulfur dioxide What is the slow, imperceptible downhill movement of weathered material? – creep, eart ...
Activity 7
... 5. Look at the link below and use colored pencils to fill in the rest of the map on Student Sheet 7.1. http://www.sepuplhs.org/pdfs/IAES-P008.pdf 6. Locate the following three places on the map. Mark each with an “X” and label the map with their names. Chris’s school (Label it “Phoenix.”) Orland ...
... 5. Look at the link below and use colored pencils to fill in the rest of the map on Student Sheet 7.1. http://www.sepuplhs.org/pdfs/IAES-P008.pdf 6. Locate the following three places on the map. Mark each with an “X” and label the map with their names. Chris’s school (Label it “Phoenix.”) Orland ...
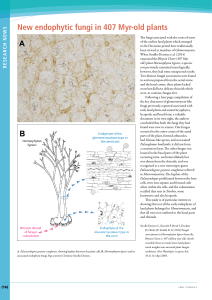
Research News
... biomass and their roles in biomineralization and particularly the decomposition of plant and animal remains. The importance of mycorrhizal fungi has been studied by Averill et al. (2014), who examined the carbon contents of soils dominated by ectomycorrhizal and ericoid plants (EEM) and those with a ...
... biomass and their roles in biomineralization and particularly the decomposition of plant and animal remains. The importance of mycorrhizal fungi has been studied by Averill et al. (2014), who examined the carbon contents of soils dominated by ectomycorrhizal and ericoid plants (EEM) and those with a ...
FERTILITY CAPABILITY CLASSIFICATION Problem soils have been
... Problem soils have been defined as soils with inherent physical or chemical constraints to agricultural production. In these soils degradation hazards are more severe and adequate soil management measures are more difficult or costly to apply. Such soils, if improperly used or inadequately managed w ...
... Problem soils have been defined as soils with inherent physical or chemical constraints to agricultural production. In these soils degradation hazards are more severe and adequate soil management measures are more difficult or costly to apply. Such soils, if improperly used or inadequately managed w ...
Read Article - Equinox Landscape
... our soil. Your food waste and garden clippings are the very things needed to regenerate the soil. Composting combines organic materials (such as food and garden waste) with animal fertilizers containing beneficial bacteria and soil containing microbes. As the soil food web breaks down the organic ma ...
... our soil. Your food waste and garden clippings are the very things needed to regenerate the soil. Composting combines organic materials (such as food and garden waste) with animal fertilizers containing beneficial bacteria and soil containing microbes. As the soil food web breaks down the organic ma ...
Soil Wetting Agent - Organic Crop Protectants
... organic matter favour dry sandy soils; 4. Sandy soil dry out easily and once the sand particles are coated with organic acids and dry-out, the sand particles become non-wetting. There are some cultural practices that can be used to reduce the on-set of non-wetting conditions. However in turf situati ...
... organic matter favour dry sandy soils; 4. Sandy soil dry out easily and once the sand particles are coated with organic acids and dry-out, the sand particles become non-wetting. There are some cultural practices that can be used to reduce the on-set of non-wetting conditions. However in turf situati ...
12.1 Soil - Union High School
... 1. Mineral matter and organic matter together make up about 50 percent of soil. What two substances make up the other 50 percent? ...
... 1. Mineral matter and organic matter together make up about 50 percent of soil. What two substances make up the other 50 percent? ...
Soil and Nutrients
... • Chemical fertilizers - adds artificial nutrients to aid plant growth – Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium ...
... • Chemical fertilizers - adds artificial nutrients to aid plant growth – Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium ...
Soil Chemistry (continued)
... • heterotrophs (bacteria, fungi) & autotrophs (algae, cyanobacteria) ...
... • heterotrophs (bacteria, fungi) & autotrophs (algae, cyanobacteria) ...
Soil Vocabulary
... Components: the parts of an object or a system. Humus: the broken down remains of plants and animals found in soil. Humus can hold large amounts of water and nutrients. Particle: a very small portion of matter; a small piece of something. Sand: the largest grain size, or sediment piece, that makes u ...
... Components: the parts of an object or a system. Humus: the broken down remains of plants and animals found in soil. Humus can hold large amounts of water and nutrients. Particle: a very small portion of matter; a small piece of something. Sand: the largest grain size, or sediment piece, that makes u ...
Soil Matrix Cleanup The Soil Matrix cleanup level is the allowable
... n Most sites in the Portland area have a cleanup level of 500 ppm and removing impacted to less than 500 ppm is considered a “Soil Matrix Cleanup.” n The DEQ requires the removal of any free-‐p ...
... n Most sites in the Portland area have a cleanup level of 500 ppm and removing impacted to less than 500 ppm is considered a “Soil Matrix Cleanup.” n The DEQ requires the removal of any free-‐p ...
Soil erosion and biodiversity control on small
... regarding soil, slope, vegetation cover, land use, etc. (all these maps obtained by professional GPS measurements and GIS techniques), along with the long-term expertise in soil erosion control and land degradation monitoring, both in the country and the research center, will help us to provide the ...
... regarding soil, slope, vegetation cover, land use, etc. (all these maps obtained by professional GPS measurements and GIS techniques), along with the long-term expertise in soil erosion control and land degradation monitoring, both in the country and the research center, will help us to provide the ...
4/FS/O/C - India Environment Portal
... lead to more rainfall variability and increased frequency of extreme events, resulting in more and longer dry spells due to global warming. Soil is the key Innovative strategies are required to help the dryland farmer overcome these difficulties. As the world’s top research centre for dryland agricu ...
... lead to more rainfall variability and increased frequency of extreme events, resulting in more and longer dry spells due to global warming. Soil is the key Innovative strategies are required to help the dryland farmer overcome these difficulties. As the world’s top research centre for dryland agricu ...