
VLF Designs specializing in Analog Telemetry Earthquake
... The receiver manufacturers schematics and troubleshooting for the VHF version of the receiver are provided as part of this manual. The UHF version is similar. Because this receiver can be used for many different applications, not all of the manufacturers information will be applicable to the telemet ...
... The receiver manufacturers schematics and troubleshooting for the VHF version of the receiver are provided as part of this manual. The UHF version is similar. Because this receiver can be used for many different applications, not all of the manufacturers information will be applicable to the telemet ...
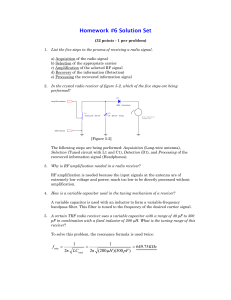
Homework #6 Solution Set
... L1 performs two functions in this circuit. It acts as the receiving antenna as well as part of the selector band-pass filter circuit. 12. Explain the operation of a loopstick antenna. What portion of the radio wave is such an antenna sensitive to? A loopstick antenna is a coil of fine wire wound on ...
... L1 performs two functions in this circuit. It acts as the receiving antenna as well as part of the selector band-pass filter circuit. 12. Explain the operation of a loopstick antenna. What portion of the radio wave is such an antenna sensitive to? A loopstick antenna is a coil of fine wire wound on ...
RFI Unit Objectives - MIT Haystack Observatory
... Investigate radio waves from the Sun using the Yagi antenna, Discone antenna and long wire antenna connected to the Winradio Communications Receiver. o Determine which antennas are directional and which are non-directional by pointing them to the Sun and then away. o Identify the frequency where eac ...
... Investigate radio waves from the Sun using the Yagi antenna, Discone antenna and long wire antenna connected to the Winradio Communications Receiver. o Determine which antennas are directional and which are non-directional by pointing them to the Sun and then away. o Identify the frequency where eac ...
lecture notes
... The reasons for doing this include: (i) signal losses (e.g. in cables) typically go as frequency2; (ii) it is much easier to mainpulate the signal (e.g. amplify, filter, delay, sample/process/digitise it) at lower frequencies. We use so-called “heterodyne” systems to mix the RF signal with a pure, m ...
... The reasons for doing this include: (i) signal losses (e.g. in cables) typically go as frequency2; (ii) it is much easier to mainpulate the signal (e.g. amplify, filter, delay, sample/process/digitise it) at lower frequencies. We use so-called “heterodyne” systems to mix the RF signal with a pure, m ...
Instructor Guide - Columbia Institute for Tele
... 0.000000001 = 10 - 9 nano (n) 0.000000000001 = 10 - 1 2 pico (p) ...
... 0.000000001 = 10 - 9 nano (n) 0.000000000001 = 10 - 1 2 pico (p) ...
Digital Cinema Amplifiers
... amplifiers to give you four channels of power in a compact package that doesn’t eat up precious rack space. And, compared to the cost of two stereo amplifiers, you’ll find they leave more room in your budget as well. In addition to their superior performance we’ve packed these amps with useful featu ...
... amplifiers to give you four channels of power in a compact package that doesn’t eat up precious rack space. And, compared to the cost of two stereo amplifiers, you’ll find they leave more room in your budget as well. In addition to their superior performance we’ve packed these amps with useful featu ...
CCLRC Template - Science and Technology Facilities Council
... So maximum speed of electron or hole in Si is ~3×10^8 cm/s = 0.01 c In big transistor say characteristic size = 1 cm So electron or hole would take ~3 ns to travel across/through transistor RF period must be >> 3 ns, say 10 ns, thereby limiting RF frequency to 100 MHz If make transistor bigger to di ...
... So maximum speed of electron or hole in Si is ~3×10^8 cm/s = 0.01 c In big transistor say characteristic size = 1 cm So electron or hole would take ~3 ns to travel across/through transistor RF period must be >> 3 ns, say 10 ns, thereby limiting RF frequency to 100 MHz If make transistor bigger to di ...
Lab 11 - Physics Department, Princeton University
... the modulation circuit results in a change of frequencies, it cannot be built using only linear circuit elements, but we do not pursue this further here. ...
... the modulation circuit results in a change of frequencies, it cannot be built using only linear circuit elements, but we do not pursue this further here. ...
ph104exp11_AM_Radio_04 - Physics Department, Princeton
... the modulation circuit results in a change of frequencies, it cannot be built using only linear circuit elements, but we do not pursue this further here. ...
... the modulation circuit results in a change of frequencies, it cannot be built using only linear circuit elements, but we do not pursue this further here. ...
Radio astronomy receiver overview
... In principle, we could measure the power from a radio source by measuring how much it raises the temperature of an energy absorber tied to the antenna. However, radio sources are much too weak to do this directly. We need to amplify the radio source signal enough to drive a power detector. This adds ...
... In principle, we could measure the power from a radio source by measuring how much it raises the temperature of an energy absorber tied to the antenna. However, radio sources are much too weak to do this directly. We need to amplify the radio source signal enough to drive a power detector. This adds ...
1 - Telecommunications Industry Association
... to measure broadband energy in the frequency range 270 kHz to 30 MHz (see comment 4 and 5). (11) Condition the EUT to the on-hook state. (12) Set the digital oscilloscope to provide: (a) ...
... to measure broadband energy in the frequency range 270 kHz to 30 MHz (see comment 4 and 5). (11) Condition the EUT to the on-hook state. (12) Set the digital oscilloscope to provide: (a) ...
BPL - uidaho.edu
... Attenuation at higher frequencies is very frequency dependent and may exceed 30 dB/km ...
... Attenuation at higher frequencies is very frequency dependent and may exceed 30 dB/km ...
1 - Telecommunications Industry Association
... to measure broadband energy in the frequency range 270 kHz to 30 MHz (see comment 4 and 5). (11) Condition the EUT to the on-hook state. (12) Set the digital oscilloscope to provide: (a) ...
... to measure broadband energy in the frequency range 270 kHz to 30 MHz (see comment 4 and 5). (11) Condition the EUT to the on-hook state. (12) Set the digital oscilloscope to provide: (a) ...
Which of the following is a method to investigate the stability of
... What is the range of frequencies for the radiotelegraph transmitter? 10 kHz to 200 MHz Binary pattern of 1’s and 0’s arrange in random. Pseudorandom Code ...
... What is the range of frequencies for the radiotelegraph transmitter? 10 kHz to 200 MHz Binary pattern of 1’s and 0’s arrange in random. Pseudorandom Code ...
Sept. 17
... The unity gain frequency of this op-amp is 5 MHz. What is the 3 db frequency of this circuit? 50 kHz 500 kHz 5 MHz 50 MHz Can not be determined ...
... The unity gain frequency of this op-amp is 5 MHz. What is the 3 db frequency of this circuit? 50 kHz 500 kHz 5 MHz 50 MHz Can not be determined ...
T4B [15]-[25]
... Where should an in-line SWR meter be connected to monitor the standing wave ratio of the station antenna system? A. In series with the feed line, between the transmitter and antenna B. In series with the station’s ground C. In parallel with the push-to-talk line and the antenna D. In series with the ...
... Where should an in-line SWR meter be connected to monitor the standing wave ratio of the station antenna system? A. In series with the feed line, between the transmitter and antenna B. In series with the station’s ground C. In parallel with the push-to-talk line and the antenna D. In series with the ...
Compare and contrast Tuned Radio Frequency
... selectivity and each circuit are ganged so that they resonate at the same frequency. But in a superhet receiver, this principle is not followed, instead, the RF amplifier, mixer and local oscillator are ganged to produce an intermediate frequency. ...
... selectivity and each circuit are ganged so that they resonate at the same frequency. But in a superhet receiver, this principle is not followed, instead, the RF amplifier, mixer and local oscillator are ganged to produce an intermediate frequency. ...
CM-300/350 (V2) - General Dynamics Mission Systems
... the General Dynamics family of Air Traffic Control (ATC) radios. Based on the FAA NEXCOM Segment 2 radio requirements, these rack mounted transmitter and receiver systems are specifically designed to meet the dynamic mission requirements of air traffic control centers, commercial airports, military ...
... the General Dynamics family of Air Traffic Control (ATC) radios. Based on the FAA NEXCOM Segment 2 radio requirements, these rack mounted transmitter and receiver systems are specifically designed to meet the dynamic mission requirements of air traffic control centers, commercial airports, military ...
Plx cut sheets
... circuitry by charging the supply rails 230,000 times a second through an ultra-low impedance circuit, so that unlike high-powered amps with conventional supplies, the audio signal is never starved prematurely, but remains crisp and clean. It’s a way of cutting wasted heat and boosting reliability. I ...
... circuitry by charging the supply rails 230,000 times a second through an ultra-low impedance circuit, so that unlike high-powered amps with conventional supplies, the audio signal is never starved prematurely, but remains crisp and clean. It’s a way of cutting wasted heat and boosting reliability. I ...
PLX2402
... circuitry by charging the supply rails 230,000 times a second through an ultra-low impedance circuit, so that unlike high-powered amps with conventional supplies, the audio signal is never starved prematurely, but remains crisp and clean. It’s a way of cutting wasted heat and boosting reliability. I ...
... circuitry by charging the supply rails 230,000 times a second through an ultra-low impedance circuit, so that unlike high-powered amps with conventional supplies, the audio signal is never starved prematurely, but remains crisp and clean. It’s a way of cutting wasted heat and boosting reliability. I ...
PLX1602
... circuitry by charging the supply rails 230,000 times a second through an ultra-low impedance circuit, so that unlike high-powered amps with conventional supplies, the audio signal is never starved prematurely, but remains crisp and clean. It’s a way of cutting wasted heat and boosting reliability. I ...
... circuitry by charging the supply rails 230,000 times a second through an ultra-low impedance circuit, so that unlike high-powered amps with conventional supplies, the audio signal is never starved prematurely, but remains crisp and clean. It’s a way of cutting wasted heat and boosting reliability. I ...
4099P, 4099P Stereo Microphone System for Piano and
... 4099P, 4099P Stereo Microphone System for Piano and more ...
... 4099P, 4099P Stereo Microphone System for Piano and more ...
RLH Vocabulary List1
... but finds a shortcut instead. Often the current goes directly from the negative powersupply terminal to the positive one, bypassing the rest of the circuit. Simplex Operation – Receiving and transmitting on the same frequency. Skip Zone – An area of poor radio communication, too distant for ground w ...
... but finds a shortcut instead. Often the current goes directly from the negative powersupply terminal to the positive one, bypassing the rest of the circuit. Simplex Operation – Receiving and transmitting on the same frequency. Skip Zone – An area of poor radio communication, too distant for ground w ...
PLX1202
... circuitry by charging the supply rails 230,000 times a second through an ultra-low impedance circuit, so that unlike high-powered amps with conventional supplies, the audio signal is never starved prematurely, but remains crisp and clean. It’s a way of cutting wasted heat and boosting reliability. I ...
... circuitry by charging the supply rails 230,000 times a second through an ultra-low impedance circuit, so that unlike high-powered amps with conventional supplies, the audio signal is never starved prematurely, but remains crisp and clean. It’s a way of cutting wasted heat and boosting reliability. I ...
FM broadcasting

FM broadcasting is a VHF broadcasting technology, pioneered by Edwin Howard Armstrong, which uses frequency modulation (FM) to provide high-fidelity sound over broadcast radio. The term ""FM band"" describes the frequency band in a given country which is dedicated to FM broadcasting. This term is slightly misleading, as it equates a modulation method with a range of frequencies.













![T4B [15]-[25]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005928511_1-974b25e2a6d2fb87d6e11948369e8362-300x300.png)








