Arm and Cubital Fossa
... dissecting 600 criminals…..live criminals •1300 AD Europe Pope Boniface VIII edict to stop dissection to reduce the flow of bodies “parted out and boiled” from the crusades. Unclear if this is broad ban or very narrow. ...
... dissecting 600 criminals…..live criminals •1300 AD Europe Pope Boniface VIII edict to stop dissection to reduce the flow of bodies “parted out and boiled” from the crusades. Unclear if this is broad ban or very narrow. ...
*Abdominal: The belly part of the body that contains all of the
... *Anterior (ventral): The front opposed to the posterior of any structure. The ventral surfaces of the body include the chest, abdomen, shins, palms, and soles. ...
... *Anterior (ventral): The front opposed to the posterior of any structure. The ventral surfaces of the body include the chest, abdomen, shins, palms, and soles. ...
Spinal cord
... The human spinal cord is divided into 31 different segments. At every segment, right and left pairs of spinal nerves (mixed; sensory and motor) form. Six to eight motor nerve rootlets branch out of right and left ventro lateral sulci in a very orderly manner. Nerve rootlets combine to form nerve roo ...
... The human spinal cord is divided into 31 different segments. At every segment, right and left pairs of spinal nerves (mixed; sensory and motor) form. Six to eight motor nerve rootlets branch out of right and left ventro lateral sulci in a very orderly manner. Nerve rootlets combine to form nerve roo ...
Ligaments You Need to Know
... Glenoid cavity of scapula and humorus Glenoid cavity of scapula and humorus Glenoid cavity of scapula and humorus ...
... Glenoid cavity of scapula and humorus Glenoid cavity of scapula and humorus Glenoid cavity of scapula and humorus ...
In Class Review 11/19/03 - Logan Class of December 2011
... buttock line and the ischial tuberosity. Hand contact: lateral 1/3 of the thumb, hand should be pronated, palm away from the adjustor, elbow down. The thumb should arc headward, laterally and slightly posterior. The line of force/drive is always 90° between the vertical line of the spine and a horiz ...
... buttock line and the ischial tuberosity. Hand contact: lateral 1/3 of the thumb, hand should be pronated, palm away from the adjustor, elbow down. The thumb should arc headward, laterally and slightly posterior. The line of force/drive is always 90° between the vertical line of the spine and a horiz ...
Transcripts/1_29_09_8
... a. [S3] The anterior triangle (green area), is bounded by the midline of the neck, inferior border of the mandible (superior boundary), and SCM (posterior boundary). b. [S4] There are number of osteological landmarks that you be useful to you for identifying certain things. i. The Hyoid bone is U-sh ...
... a. [S3] The anterior triangle (green area), is bounded by the midline of the neck, inferior border of the mandible (superior boundary), and SCM (posterior boundary). b. [S4] There are number of osteological landmarks that you be useful to you for identifying certain things. i. The Hyoid bone is U-sh ...
Anatomy of the Female Reproductive System
... uteri), which is round or oval before parturition but takes the form of a transverse slit in women who have borne children. ...
... uteri), which is round or oval before parturition but takes the form of a transverse slit in women who have borne children. ...
The shoulder joint
... • The convex humeral head moves within the concave glenoid fossa • The convex joint surface (humeral head) moves in a direction opposite to the movement of the body segment (humeral shaft) • Flexion – humeral head glides _____________________ • Abduction – humeral head glides _____________________ • ...
... • The convex humeral head moves within the concave glenoid fossa • The convex joint surface (humeral head) moves in a direction opposite to the movement of the body segment (humeral shaft) • Flexion – humeral head glides _____________________ • Abduction – humeral head glides _____________________ • ...
REPRODUCTIVE ANATOMY ANATOMY OF THE MATERNAL
... These are hair-covered fibro fatty folds that extend from the mons pubis above the perineum below. They have both sweat and sebaceous glands, and a few specialized apocrine glands and are homologous with the scrotum in the male. In the deepest part of each is a core of fatty tissue continuous with t ...
... These are hair-covered fibro fatty folds that extend from the mons pubis above the perineum below. They have both sweat and sebaceous glands, and a few specialized apocrine glands and are homologous with the scrotum in the male. In the deepest part of each is a core of fatty tissue continuous with t ...
Head and Neck ROM Assessments
... the head and neck. They are likely to limit flexion by invoking their referral to the back of the head and neck along with a band of pain around the head. A pull may be felt into the upper back. Suboccipitals are likely to limit flexion of the head at the neck. Their pain tends to spread laterally a ...
... the head and neck. They are likely to limit flexion by invoking their referral to the back of the head and neck along with a band of pain around the head. A pull may be felt into the upper back. Suboccipitals are likely to limit flexion of the head at the neck. Their pain tends to spread laterally a ...
Thyroid, Parathyroid and Suprarenal Glands
... which projects from the upper border of the isthmus usually to left of middle line. Pyramidal lobe is connected to hyoid bone by a fibrous or ...
... which projects from the upper border of the isthmus usually to left of middle line. Pyramidal lobe is connected to hyoid bone by a fibrous or ...
Thyroid, Parathyroid and Suprarenal Glands
... which projects from the upper border of the isthmus usually to left of middle line. Pyramidal lobe is connected to hyoid bone by a fibrous or ...
... which projects from the upper border of the isthmus usually to left of middle line. Pyramidal lobe is connected to hyoid bone by a fibrous or ...
AURICULAR: Ear Acupuncture Handbook, © 2002.
... Withered, dry, black: extreme exhaustion of kidney qi Anatomy: The ear structure functions as a funnel and screen for sound waves. It can also be thought of as a castle that protects the gateway to the emperor‟s chambers (the brain). Orientation: (see fig.2) (Oleson) Anterior: front side of ear ...
... Withered, dry, black: extreme exhaustion of kidney qi Anatomy: The ear structure functions as a funnel and screen for sound waves. It can also be thought of as a castle that protects the gateway to the emperor‟s chambers (the brain). Orientation: (see fig.2) (Oleson) Anterior: front side of ear ...
MC - WordPress.com
... 36. All of the following arteries provide blood to the breast with the EXCEPTION of: a. internal thoracic artery b. anterior intercostal artery c. lateral thoracic artery d. thoracoacromial trunk (artery) e. subcostal artery 37. Which of the following statements concerning the azygos vein is TRUE? a ...
... 36. All of the following arteries provide blood to the breast with the EXCEPTION of: a. internal thoracic artery b. anterior intercostal artery c. lateral thoracic artery d. thoracoacromial trunk (artery) e. subcostal artery 37. Which of the following statements concerning the azygos vein is TRUE? a ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 12 Martini Lecture Outline
... A Regional Approach to Surface Anatomy Upper Limbs: Arm and forearm Other areas (continued) Tendon of flexor carpi radialis Tendon of palmaris longus Tendon of flexor digitorum superficialis ...
... A Regional Approach to Surface Anatomy Upper Limbs: Arm and forearm Other areas (continued) Tendon of flexor carpi radialis Tendon of palmaris longus Tendon of flexor digitorum superficialis ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 12 Martini Lecture Outline
... A Regional Approach to Surface Anatomy Upper Limbs: Arm and forearm Other areas (continued) Tendon of flexor carpi radialis Tendon of palmaris longus Tendon of flexor digitorum superficialis ...
... A Regional Approach to Surface Anatomy Upper Limbs: Arm and forearm Other areas (continued) Tendon of flexor carpi radialis Tendon of palmaris longus Tendon of flexor digitorum superficialis ...
Guidelines for Foundational Knowledge in Massage Therapy
... are required to ensure that their graduates possess this foundational knowledge, by including it in their curriculum. ...
... are required to ensure that their graduates possess this foundational knowledge, by including it in their curriculum. ...
File - Dentalelle Tutoring
... Anterior to the external meatus the Zygomatic Process has its origin. This process projects forward toward the face and its articulation with the temporal process of the zygomatic. Just anterior of the external meatus and inferior of the origin of the zygomatic process is the Glenoid or Mandibular F ...
... Anterior to the external meatus the Zygomatic Process has its origin. This process projects forward toward the face and its articulation with the temporal process of the zygomatic. Just anterior of the external meatus and inferior of the origin of the zygomatic process is the Glenoid or Mandibular F ...
Approaches to the knee
... on posterior border of biceps femoris Popliteal artery: at risk posterior to posterior horn of lateral meniscus ...
... on posterior border of biceps femoris Popliteal artery: at risk posterior to posterior horn of lateral meniscus ...
Deep Cervical Nodes
... and digestive systems forms a ring. The lateral part of the ring is fanned by the palatine tonsils and tubal tonsils (lymphoid tissue around the opening of the auditory tube in the lateral wall of the ...
... and digestive systems forms a ring. The lateral part of the ring is fanned by the palatine tonsils and tubal tonsils (lymphoid tissue around the opening of the auditory tube in the lateral wall of the ...
1. During an intramural baseball game a player is hit in the side of
... sphenoid and squamous part of the temporal bones laterally and the petrous part of the temporal bones posteriorly. See Netter Plate 6 and 7 for a better picture of this. Several cranial nerves enter foramina in the middle cranial fossa; all of these nerves might have been damaged in the fall. The tr ...
... sphenoid and squamous part of the temporal bones laterally and the petrous part of the temporal bones posteriorly. See Netter Plate 6 and 7 for a better picture of this. Several cranial nerves enter foramina in the middle cranial fossa; all of these nerves might have been damaged in the fall. The tr ...
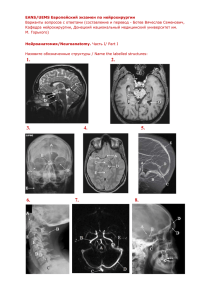
Нейроанатомия
... The foramen rotundum is projected below the inferior rim of the orbit on facial radiographs and connects the middle cranial fossa with the pterygopalatine fossa. The crista galli is a ridge of bone that extends superiorly from the cribriform plate. It forms the anterior attachment for the falx cereb ...
... The foramen rotundum is projected below the inferior rim of the orbit on facial radiographs and connects the middle cranial fossa with the pterygopalatine fossa. The crista galli is a ridge of bone that extends superiorly from the cribriform plate. It forms the anterior attachment for the falx cereb ...
Leg, Hands and Feet
... Fibular notch of tibia Articular surface for talus Medial malleolus ...
... Fibular notch of tibia Articular surface for talus Medial malleolus ...
Gross 8/27/99 - GEOCITIES.ws
... B. Secondary curvature—lumbar and cervical (when baby can stand then the secondary curvature will have full development. Development may be somewhat when he/she can sit) C. Kyphosis—hunchback Lordodsis—sway back Scoliosis D. Foramen Vertebral foramen—spinal cord Intervertebral foramen—spinal nerves— ...
... B. Secondary curvature—lumbar and cervical (when baby can stand then the secondary curvature will have full development. Development may be somewhat when he/she can sit) C. Kyphosis—hunchback Lordodsis—sway back Scoliosis D. Foramen Vertebral foramen—spinal cord Intervertebral foramen—spinal nerves— ...
Vertebra

In the vertebrate spinal column, each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, the proportions of which vary according to the segment of the backbone and the species of vertebrate animal.The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the large part is the body, and the central part is the centrum. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles, two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava. There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conducts for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebra and the vertebral arch form the vertebral foramen, the larger, central opening that accommodates the spinal canal, which encloses and protects the spinal cord.Vertebrae articulate with each other to give strength and flexibility to the spinal column, and the shape at their back and front aspects determines the range of movement. Structurally, vertebrae are essentially alike across the vertebrate species, with the greatest difference seen between an aquatic animal and other vertebrate animals. As such, vertebrates take their name from the vertebrae that compose the vertebral column.