Fighting Back
... soaps and nearly 30% of bar soaps…contained some type of antibacterial agent. Nearly half of all commercial soaps studied contained Triclosan” (qtd. in Glaser 13). Because this chemical is present in so many consumer goods and household items, mutated bacteria become immune to its effects, and resea ...
... soaps and nearly 30% of bar soaps…contained some type of antibacterial agent. Nearly half of all commercial soaps studied contained Triclosan” (qtd. in Glaser 13). Because this chemical is present in so many consumer goods and household items, mutated bacteria become immune to its effects, and resea ...
Lab 8
... infections include gastroenteritis, toxic shock syndrome (TSS), pneumonia, meningitis, osteomylelitis, bacteremia, urinary tract infections (UTI). S. saprophyticus is one of the leading causes of UTI’s in sexually active women. S. epidermidis is associated with infections of catheters, IV lines, and ...
... infections include gastroenteritis, toxic shock syndrome (TSS), pneumonia, meningitis, osteomylelitis, bacteremia, urinary tract infections (UTI). S. saprophyticus is one of the leading causes of UTI’s in sexually active women. S. epidermidis is associated with infections of catheters, IV lines, and ...
Sorbact for fungal infection in skin folds 2008-16
... the microbial load in open wounds without enhancing nosocomial spread, and can reduce the use of antibiotics. Hydrophobic microorganisms bind to the dressing, preferably in a humid environment, and are removed with it. They multiply to quite low extent when absorbed in the dressing, and may not prod ...
... the microbial load in open wounds without enhancing nosocomial spread, and can reduce the use of antibiotics. Hydrophobic microorganisms bind to the dressing, preferably in a humid environment, and are removed with it. They multiply to quite low extent when absorbed in the dressing, and may not prod ...
Antimicrobial Drugs - LSU School of Medicine
... Choosing the right antibiotic – is it really needed? • Nature of the illness – is it a bacterial infection or something else? • Presumptive diagnosis (based on history and clinical symptoms) says yes! • Empiric therapy – broad spectrum drug • Specific therapy – narrow spectrum ...
... Choosing the right antibiotic – is it really needed? • Nature of the illness – is it a bacterial infection or something else? • Presumptive diagnosis (based on history and clinical symptoms) says yes! • Empiric therapy – broad spectrum drug • Specific therapy – narrow spectrum ...
Bacterial resistance: How to detect three types T
... wo important — and opposing — trends are occurring simultaneously, and they both have a significant influence on the treatment of infectious diseases. One trend is the relentless increase in bacterial resistance to currently used antibiotics. The opposing trend is that fewer new antibiotics are bein ...
... wo important — and opposing — trends are occurring simultaneously, and they both have a significant influence on the treatment of infectious diseases. One trend is the relentless increase in bacterial resistance to currently used antibiotics. The opposing trend is that fewer new antibiotics are bein ...
22 Staphylococci
... activated in the complex, resulting in the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. This is the basis of the tube coagulase test, in which a clot is formed in plasma after incubation with the S aureus broth-culture supernatant. Coagulase is a traditional marker for identifying S aureus in the clinical mi ...
... activated in the complex, resulting in the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. This is the basis of the tube coagulase test, in which a clot is formed in plasma after incubation with the S aureus broth-culture supernatant. Coagulase is a traditional marker for identifying S aureus in the clinical mi ...
Causes of Otitis media
... -Aerobic fastidious oxidase positive bacteria. 4-Other normal flora of upper respiratory tracts(rare). ...
... -Aerobic fastidious oxidase positive bacteria. 4-Other normal flora of upper respiratory tracts(rare). ...
FAQs: Boils
... What causes boils? A boil is an infection of the skin, usually caused by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. Boils present as one or more tender red spots, lumps or pustules. Careful inspection reveals that the boil is centred on a hair follicle. A boil is a deep form of bacterial folliculitis; superfic ...
... What causes boils? A boil is an infection of the skin, usually caused by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. Boils present as one or more tender red spots, lumps or pustules. Careful inspection reveals that the boil is centred on a hair follicle. A boil is a deep form of bacterial folliculitis; superfic ...
MRSA: Information for Coaches and Athletes (PDF: 23KB/1 page)
... If you suspect that an athlete might have a staph skin infection, have them consult their healthcare provider as soon as possible. Early treatment can help prevent the infection from getting worse. The athlete should be sure to follow all the directions the healthcare provider gives, including takin ...
... If you suspect that an athlete might have a staph skin infection, have them consult their healthcare provider as soon as possible. Early treatment can help prevent the infection from getting worse. The athlete should be sure to follow all the directions the healthcare provider gives, including takin ...
methicillin-resistant staphyloccus aureus infections
... Learning Break: You may notice that methicillin is not included in the list. Methicillin is an old antibiotic that was developed inn the ‘50s to treat penicillin-resistant infections. It is no longer manufactured because other antibiotics are more stable and more effective, but the term methicillin ...
... Learning Break: You may notice that methicillin is not included in the list. Methicillin is an old antibiotic that was developed inn the ‘50s to treat penicillin-resistant infections. It is no longer manufactured because other antibiotics are more stable and more effective, but the term methicillin ...
METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCCUS AUREUS INFECTIONS
... Learning Break: You may notice that methicillin is not included in the list. Methicillin is an old antibiotic that was developed inn the ‘50s to treat penicillin-resistant infections. It is no longer manufactured because other antibiotics are more stable and more effective, but the term methicillin ...
... Learning Break: You may notice that methicillin is not included in the list. Methicillin is an old antibiotic that was developed inn the ‘50s to treat penicillin-resistant infections. It is no longer manufactured because other antibiotics are more stable and more effective, but the term methicillin ...
Thyroid Pathology
... catalase positive, coagulase positive part of normal flora of skin, nose Streptococcus pneumoniae gram positive diplococci catalase negative alpha-hemolytic encapsulated Propionibacterium acnes gram-positive rod causes acne ...
... catalase positive, coagulase positive part of normal flora of skin, nose Streptococcus pneumoniae gram positive diplococci catalase negative alpha-hemolytic encapsulated Propionibacterium acnes gram-positive rod causes acne ...
3. What is your Initial Impression and give your Differential Diagnosis.
... Characterized by soft tissue swelling and tenderness in joints of the hands, wrist, and knees ...
... Characterized by soft tissue swelling and tenderness in joints of the hands, wrist, and knees ...
Characterization of TLR2, NOD2, and related cytokines in mammary
... Findings Staphylococcus aureus causes infections in humans and animals [1, 2]. The pathogen often leads to subclinical bovine mastitis and tends to develop into persistent and chronic infections [3, 4]. Long-term infection causes reduced milk production, resulting in economic loss for dairy produce ...
... Findings Staphylococcus aureus causes infections in humans and animals [1, 2]. The pathogen often leads to subclinical bovine mastitis and tends to develop into persistent and chronic infections [3, 4]. Long-term infection causes reduced milk production, resulting in economic loss for dairy produce ...
The War Against MRSA
... • Colonization often precedes invasive infection • In 2003, up to 60% of hospitalized patients with MRSA colonization developed an infection, and 5–15% of colonized residents in a LTCF developed an MRSA infection (McNeil, 2003). ...
... • Colonization often precedes invasive infection • In 2003, up to 60% of hospitalized patients with MRSA colonization developed an infection, and 5–15% of colonized residents in a LTCF developed an MRSA infection (McNeil, 2003). ...
Acute purulent surgical infections
... If escape of pus does not occur spontaneously or with application of iodine, removal of the affected hair allows ready escape of pus. Antibiotic is usually not required. After escape of pus this placet should be cleaned twice with a suitable disinfectant e.g. hexachlorophene. If boils are recurrent, ...
... If escape of pus does not occur spontaneously or with application of iodine, removal of the affected hair allows ready escape of pus. Antibiotic is usually not required. After escape of pus this placet should be cleaned twice with a suitable disinfectant e.g. hexachlorophene. If boils are recurrent, ...
Lectures 5. Purulent infections
... If escape of pus does not occur spontaneously or with application of iodine, removal of the affected hair allows ready escape of pus. Antibiotic is usually not required. After escape of pus this placet should be cleaned twice with a suitable disinfectant e.g. hexachlorophene. If boils are recurrent, ...
... If escape of pus does not occur spontaneously or with application of iodine, removal of the affected hair allows ready escape of pus. Antibiotic is usually not required. After escape of pus this placet should be cleaned twice with a suitable disinfectant e.g. hexachlorophene. If boils are recurrent, ...
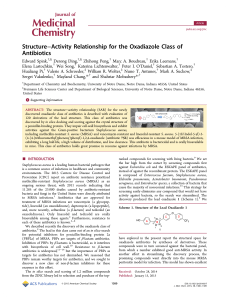
Structure−Activity Relationship for the Oxadiazole Class of Antibiotics
... This animal model of infection is widely used, it is easy to carry out, and the end points (death or survival) are rapidly assessed, making it less resource-intensive compared to other infection models. In addition, excellent correlation between MIC and ED50 has been shown for 14 β-lactam antibiotic ...
... This animal model of infection is widely used, it is easy to carry out, and the end points (death or survival) are rapidly assessed, making it less resource-intensive compared to other infection models. In addition, excellent correlation between MIC and ED50 has been shown for 14 β-lactam antibiotic ...
(PATH) Act
... The undersigned organizations write to urge you to pass S. 185, the bipartisan Promise for Antibiotics and Therapeutics for Health (PATH) Act, this year in order to establish a new limited population antibacterial drug (LPAD) approval pathway for antibiotics to treat serious or life-threatening infe ...
... The undersigned organizations write to urge you to pass S. 185, the bipartisan Promise for Antibiotics and Therapeutics for Health (PATH) Act, this year in order to establish a new limited population antibacterial drug (LPAD) approval pathway for antibiotics to treat serious or life-threatening infe ...
Antibiotic Resistance by Dr Sarma
... Pharmaceuticals, Inc) for the treatment of complicated skin and skin structure infections caused by certain gram-positive infections and for bloodstream infections, including right-sided infective endocarditis, caused by S. aureus. ...
... Pharmaceuticals, Inc) for the treatment of complicated skin and skin structure infections caused by certain gram-positive infections and for bloodstream infections, including right-sided infective endocarditis, caused by S. aureus. ...
Important human pathogens of Gram
... After 2-7 days of incubation, patients presented with high fever, painful lymphadenopathy, enlarged, tender nodes (“buboes”: hence bubonic plague) in groin and axillae. Sometimes with vomiting and diarrhoea. Later disseminated intravascular coagulation leads to hypotension, altered mental status, re ...
... After 2-7 days of incubation, patients presented with high fever, painful lymphadenopathy, enlarged, tender nodes (“buboes”: hence bubonic plague) in groin and axillae. Sometimes with vomiting and diarrhoea. Later disseminated intravascular coagulation leads to hypotension, altered mental status, re ...
Staphylococcus aureus

Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive coccal bacterium that is a member of the Firmicutes, and is frequently found in the respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction. Although S. aureus is not always pathogenic, it is a common cause of skin infections such as abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing potent protein toxins, and expressing cell-surface proteins that bind and inactivate antibodies. The emergence of antibiotic-resistant forms of S. aureus such as MRSA is a worldwide problem in clinical medicine.Staphylococcus was first identified in 1880 in Aberdeen, Scotland, by the surgeon Sir Alexander Ogston in pus from a surgical abscess in a knee joint. This name was later appended to Staphylococcus aureus by Friedrich Julius Rosenbach, who was credited by the official system of nomenclature at the time. An estimated 20% of the human population are long-term carriers of S. aureus which can be found as part of the normal skin flora and in the nostrils. S. aureus is the most common species of Staphylococcus to cause Staph infections and is a successful pathogen due to a combination of nasal carriage and bacterial immunoevasive strategies.S. aureus can cause a range of illnesses, from minor skin infections, such as pimples, impetigo, boils, cellulitis, folliculitis, carbuncles, scalded skin syndrome, and abscesses, to life-threatening diseases such as pneumonia, meningitis, osteomyelitis, endocarditis, toxic shock syndrome, bacteremia, and sepsis. Its incidence ranges from skin, soft tissue, respiratory, bone, joint, endovascular to wound infections. It is still one of the five most common causes of hospital-acquired infections and is often the cause of postsurgical wound infections. Each year, around 500,000 patients in United States' hospitals contract a staphylococcal infection.